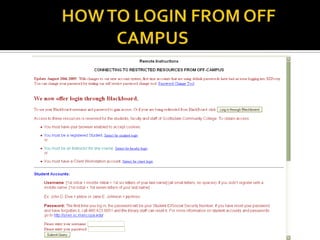
This document provides instructions for locating sources such as magazine, newspaper, and scholarly journal articles. It discusses using specialized search engines and library databases, which contain full-text articles. The document recommends several library databases for article searching, including Academic Search Premier, Academic One File, CQ Researcher, and Opposing Viewpoints. It also provides tips for searching the web and login information for accessing databases off campus.