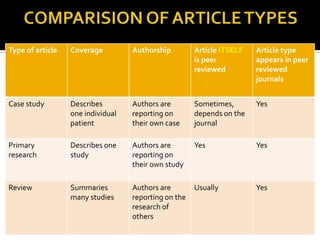
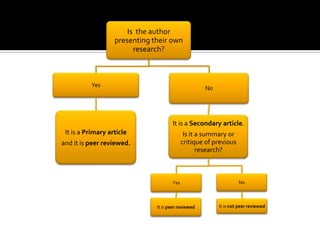
The document discusses different types of research articles, including primary research articles, review articles, and case studies. Primary research articles present original research findings and undergo peer review, while review articles summarize and critically evaluate previous research on a topic and may also be peer reviewed. Case studies provide an in-depth look at a single patient or case and aim to identify new areas for further research.