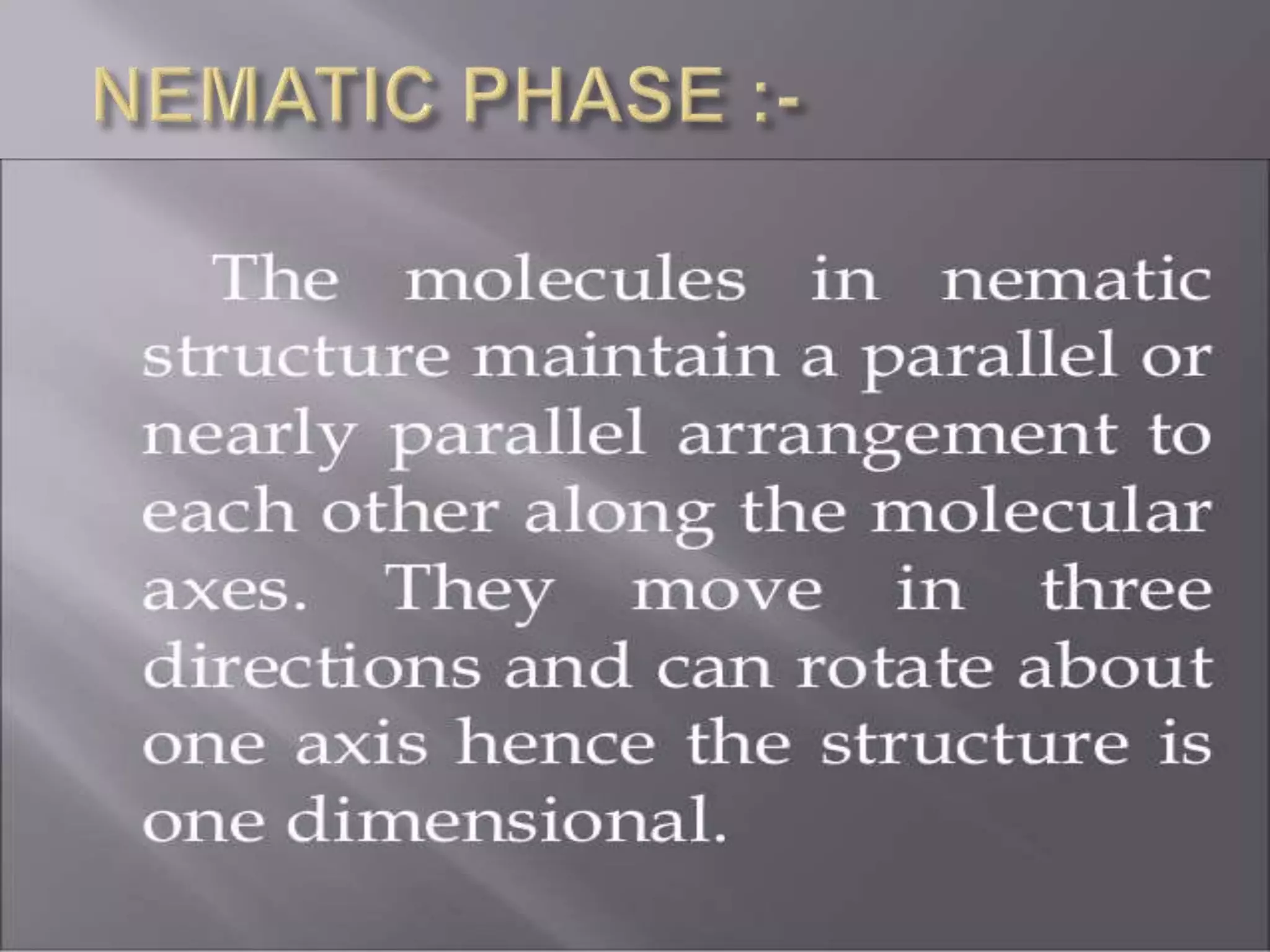
Liquid crystals are a state of matter that has properties between those of a conventional liquid and solid crystal. They may flow like a liquid but their molecules can be oriented in a crystal-like way. Friedrich Reinitzer discovered important features of cholesteric liquid crystals in 1888, including thermotropic, lyotropic, and metallotropic phases. Common liquid crystal phases are nematic, smectic, and cholesteric/chiral. Blue phases have a regular three-dimensional cubic structure of defects with a lattice period of several hundred nanometers. Liquid crystals can flow like liquids due to loss of positional order, and transition between solid and liquid crystal states caused by temperature change gives rise to thermotropic liquid crystals