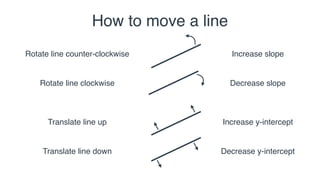
This document provides an overview of linear regression. It begins by showing an example of housing prices based on number of rooms. It then explains how to move a linear regression line closer to data points by changing the slope and y-intercept. An algorithm for linear regression is presented using gradient descent to iteratively minimize the distance between the line and points. Finally, it discusses using an absolute value approach instead of squares to handle different types of errors.