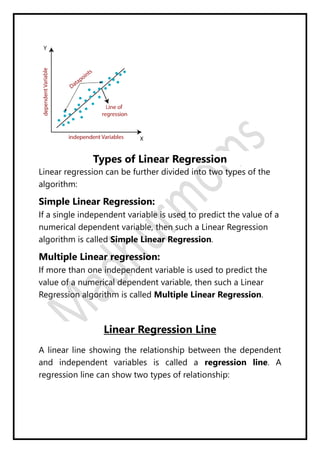
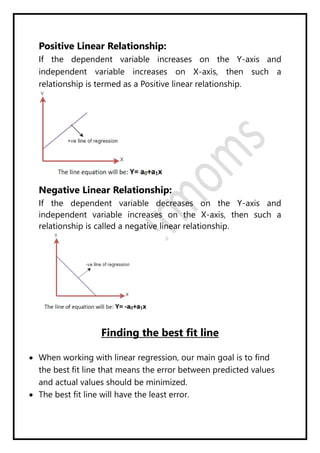
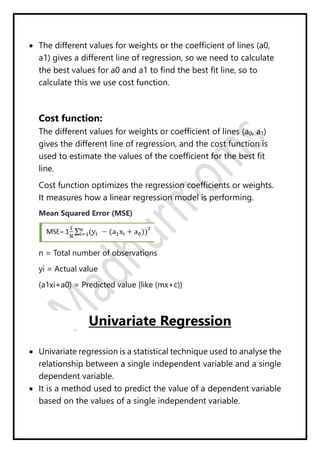
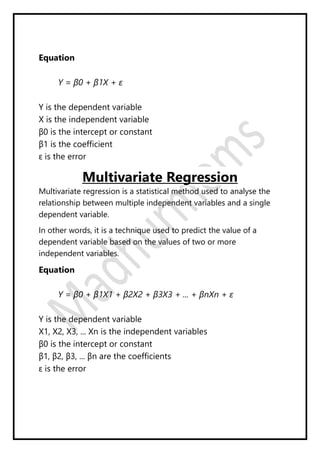
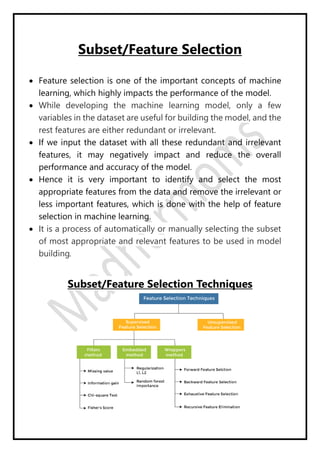
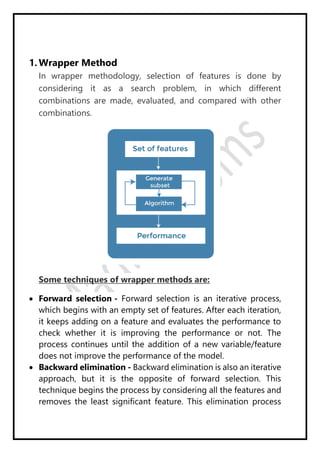
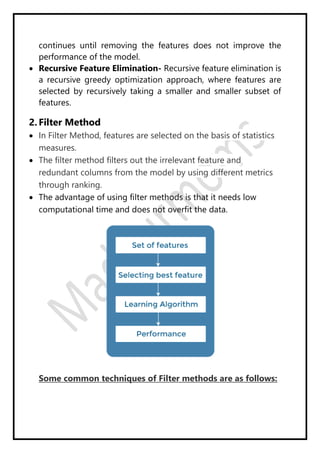
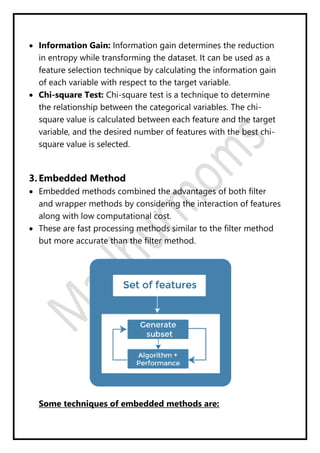
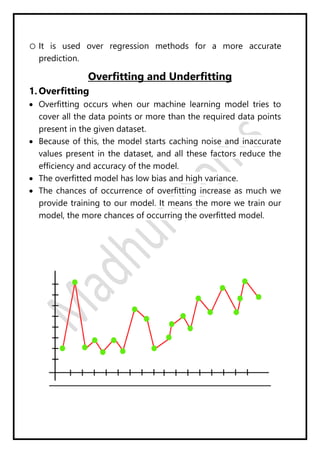
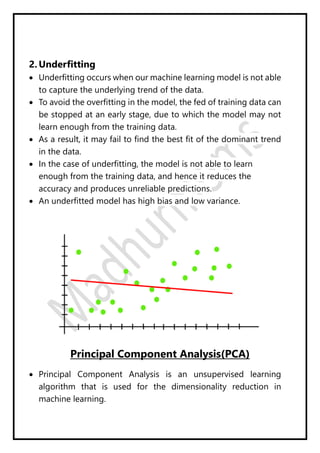
Regression analysis models the relationship between a dependent (target) variable and one or more independent (predictor) variables. Linear regression predicts continuous variables using a linear equation. Simple linear regression uses one independent variable, while multiple linear regression uses more than one. The goal is to find the "best fit" line that minimizes error between predicted and actual values. Feature selection identifies important predictors by removing irrelevant or redundant features. Techniques include wrapper, filter, and embedded methods. Overfitting and underfitting occur when models are too complex or simple, respectively. Dimensionality reduction through techniques like principal component analysis (PCA) transform correlated variables into linearly uncorrelated components.