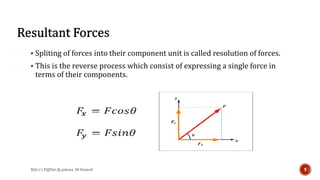
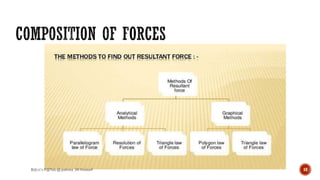
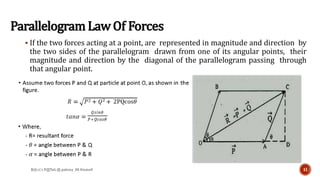
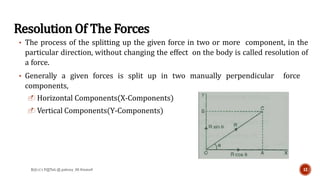
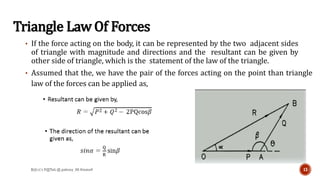
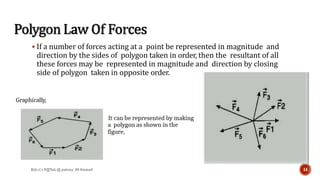
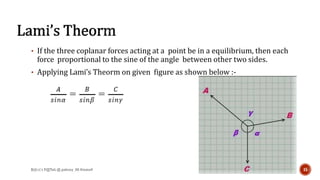
This document is a presentation on mechanics of solids that was prepared by four students and guided by Heena Mam of the civil department. It covers fundamental principles of mechanics including the principle of physical independence of forces, principle of transmissibility, principle of superposition, and resultant forces. Methods for composition of forces such as the parallelogram law, resolution of forces, triangle law, and polygon law are discussed. Lami's theorem is also introduced.