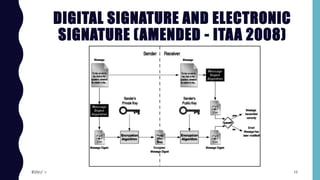
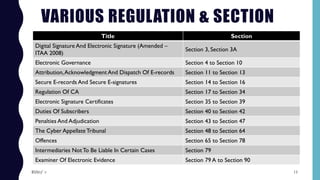
This document provides an overview of cyber security and the amendments made to the Indian IT Act. It discusses the reasons for amending the act, which included adding new cyber crimes and increasing data protection. The objectives of the amendments were to facilitate electronic transactions, storage, and filing. Key definitions related to digital signatures, electronic signatures, and cyber security are also outlined. The various sections of the amended act that regulate certifying authorities, electronic signature certificates, subscriber duties, and penalties are also listed.