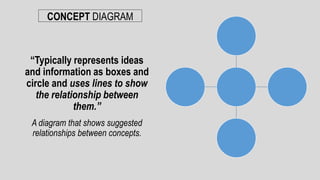
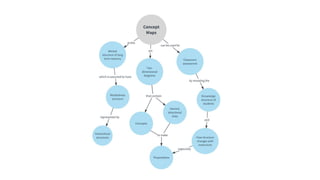
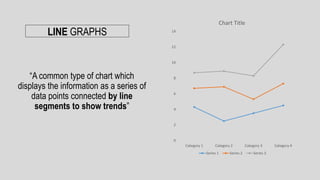
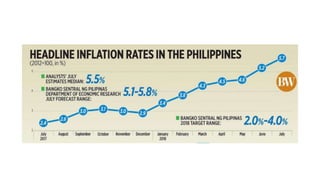
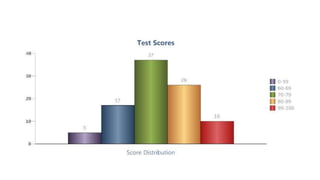
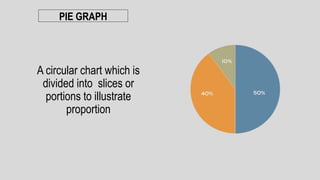
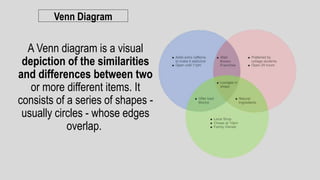
The document discusses linear and non-linear texts. Linear texts must be read sequentially from beginning to end, like novels and poems. Non-linear texts can be understood without a strict sequence, using visuals, graphs, charts or diagrams. Examples of non-linear texts include concept maps, line graphs, bar graphs, histograms, pie charts and Venn diagrams. These use visual representations like boxes, circles and relationships to convey information and concepts.