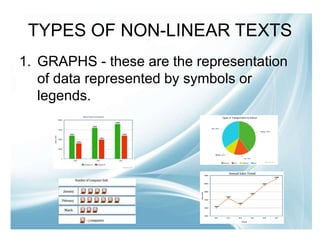
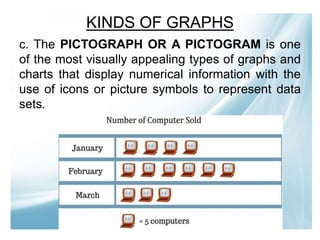
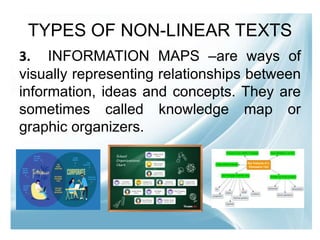
This document provides an introduction to a lesson on interpreting non-linear texts. It defines linear and non-linear texts, and describes various types of non-linear texts like graphs, tables, and information maps. Examples are given for different kinds of graphs and information maps. Students are instructed to complete an activity where they will transcode information from a linear paragraph into a non-linear format. They will then be assigned to compare Korean and Filipino culture using an appropriate non-linear text.