This document discusses the equations of motion for rigid bodies subjected to various accelerations in fluids. It begins by deriving the general equation of motion for a rigid fluid body subjected to any acceleration. It then applies this equation to several examples:
1) A fluid at rest, where pressure is constant horizontally and varies with depth.
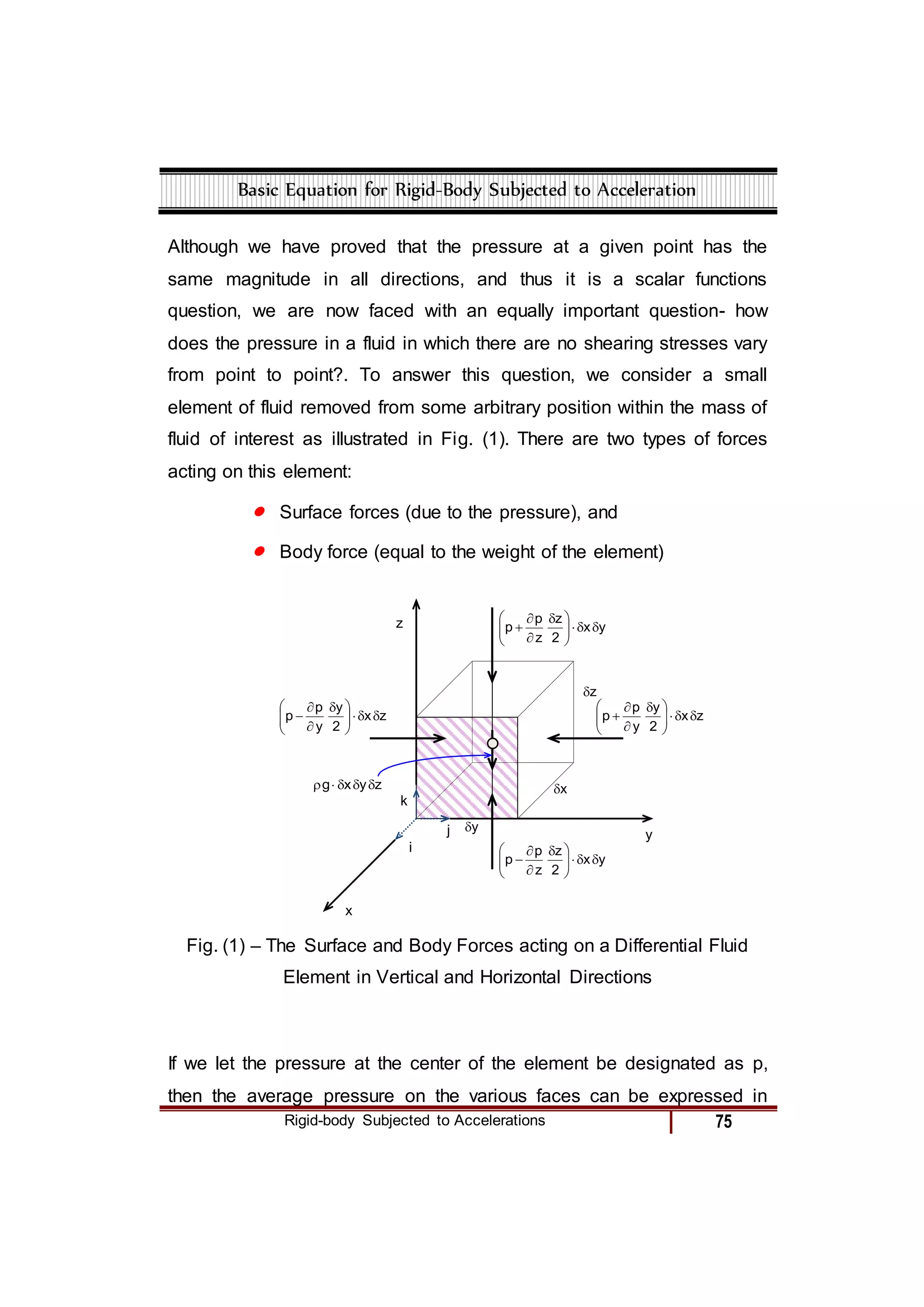
2) A freely falling fluid body, where pressure is constant.
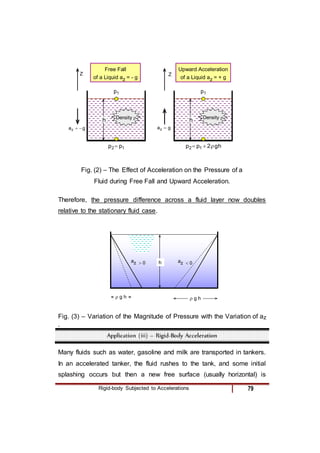
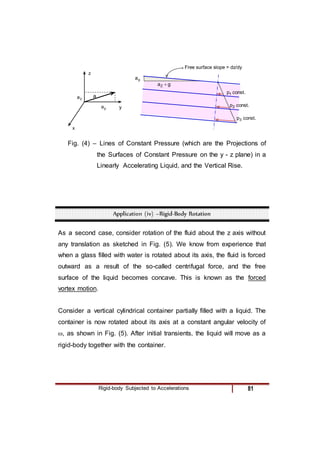
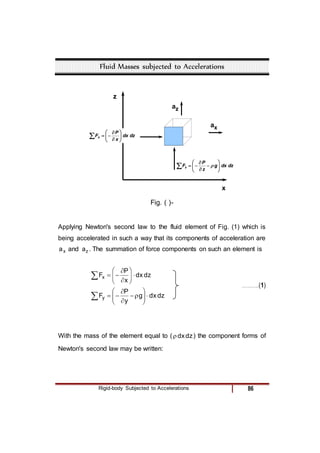
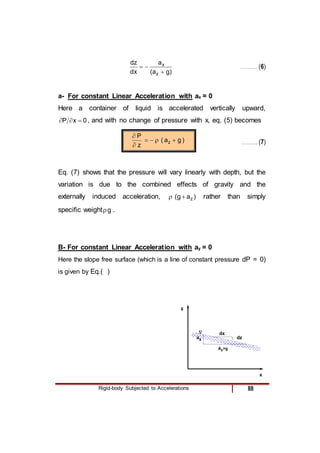
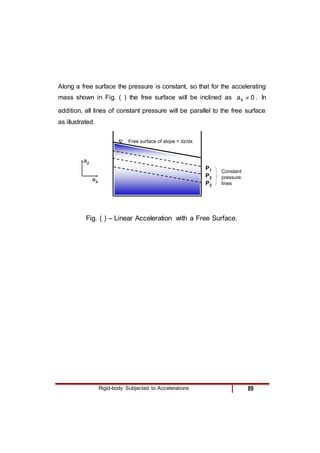
3) A linearly accelerating fluid body, where lines of constant pressure slope according to the acceleration components.
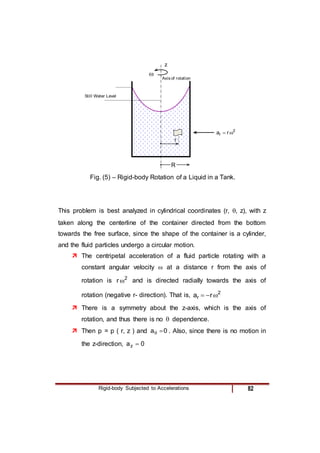
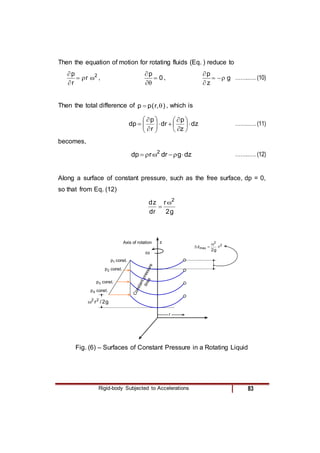
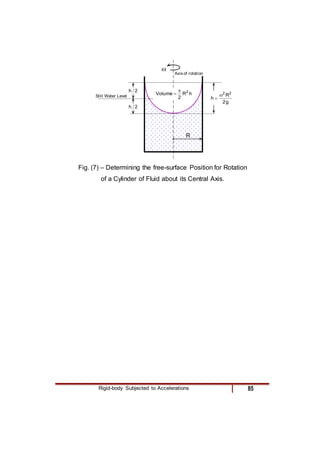
4) A fluid body rotating rigidly in a cylinder, where pressure increases radially outward due to centripetal acceleration.