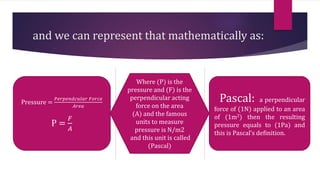
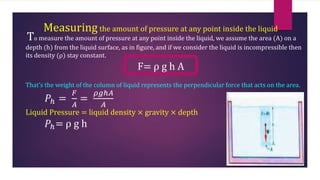
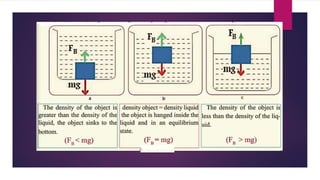
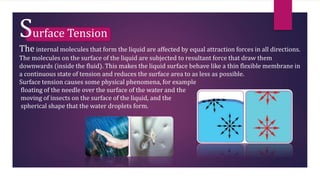
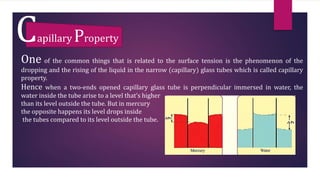
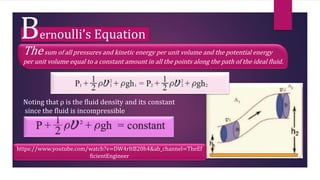
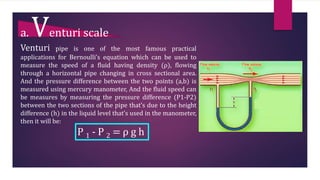
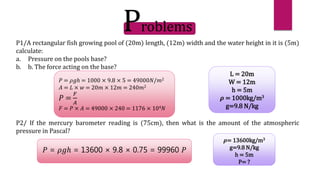
This document provides information about static fluids and their properties. It defines fluids as materials that cannot maintain a definite shape and take the shape of their container. Liquids and gases are given as examples of fluids. It also discusses measuring pressure in fluids, Pascal's principle which states that pressure is transmitted equally in all directions in an enclosed fluid, buoyancy, surface tension, and capillary action. Key equations for pressure, buoyant force, and relationships between pressure and force/area are also presented.