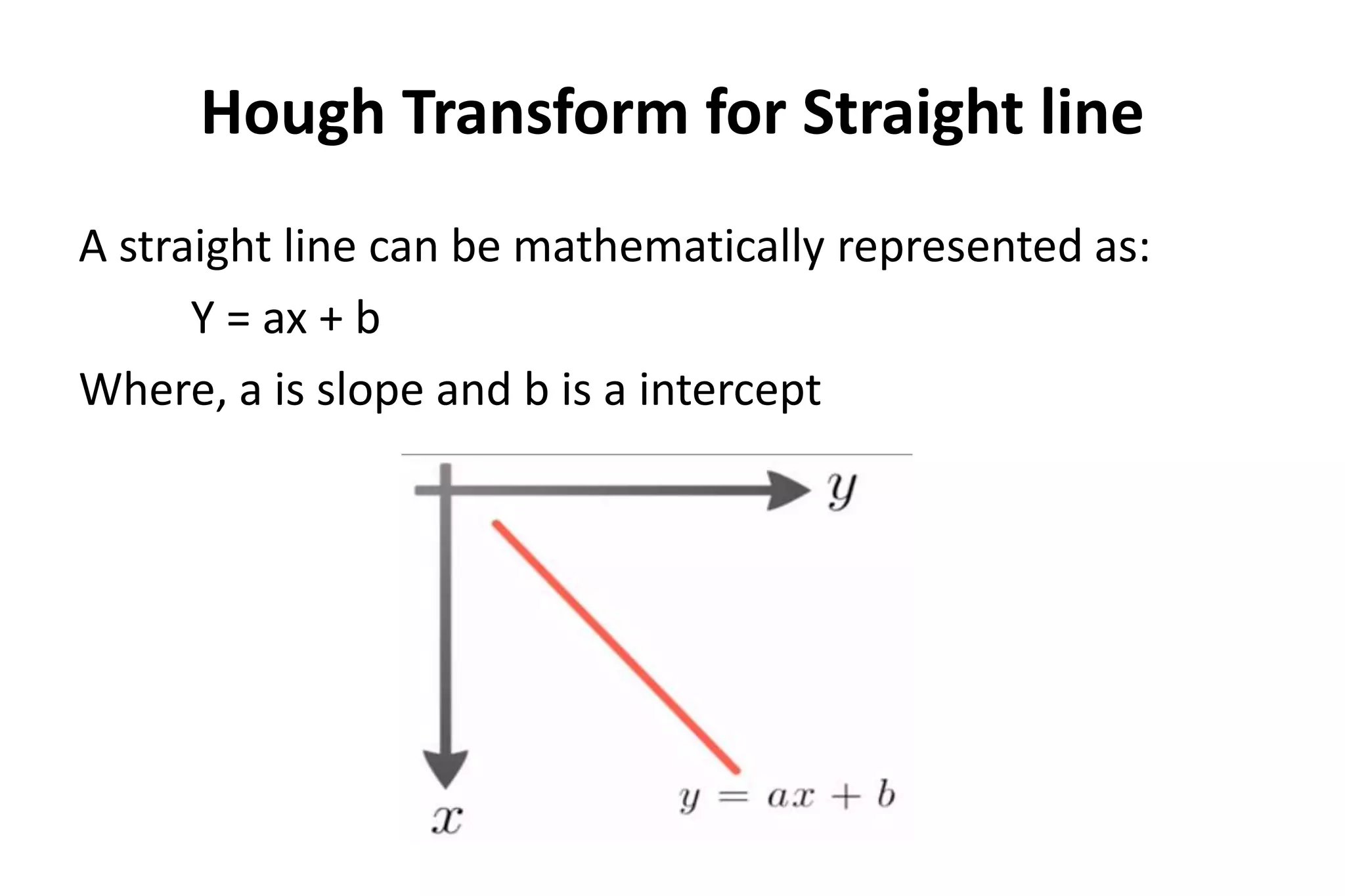
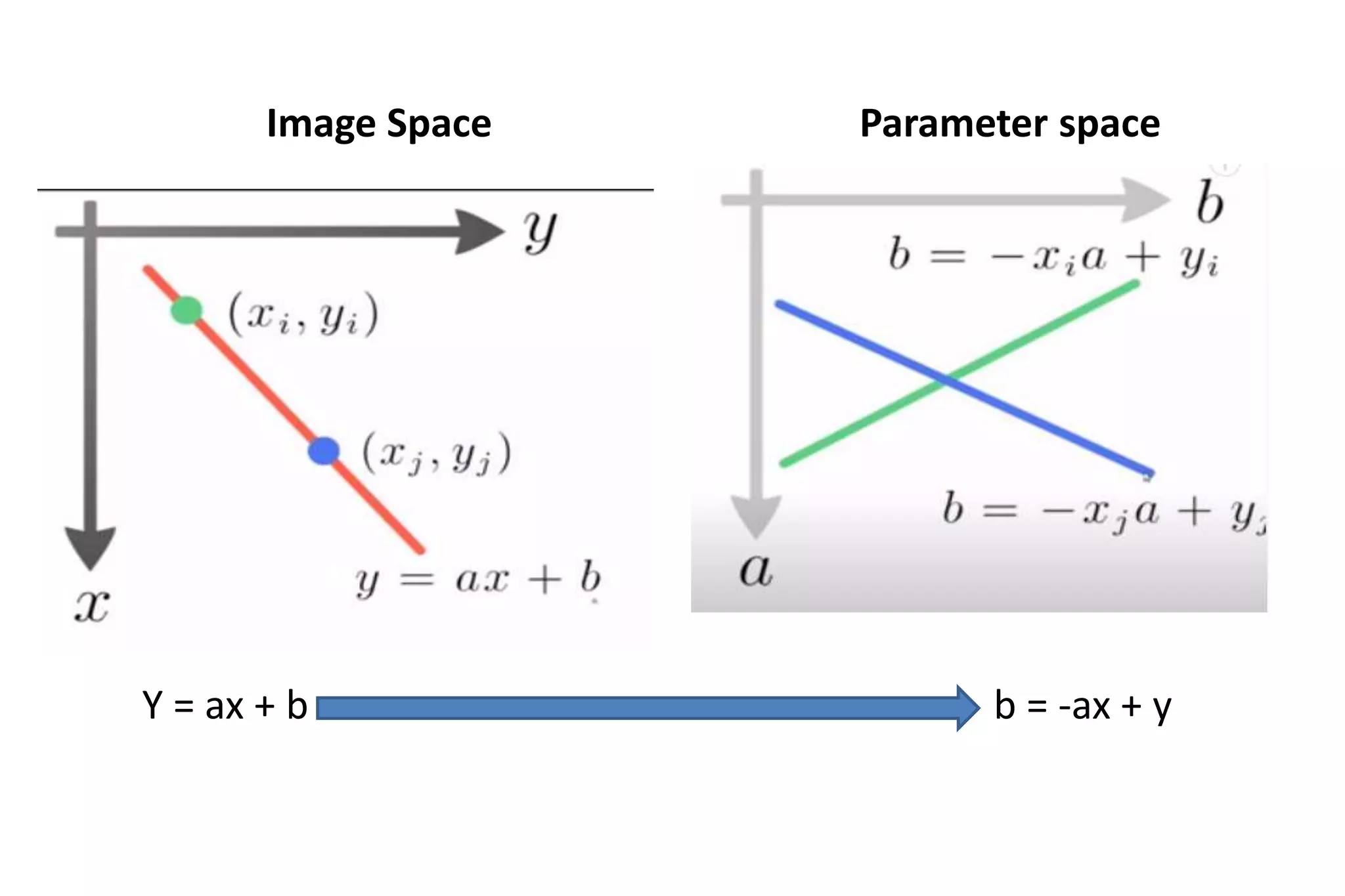
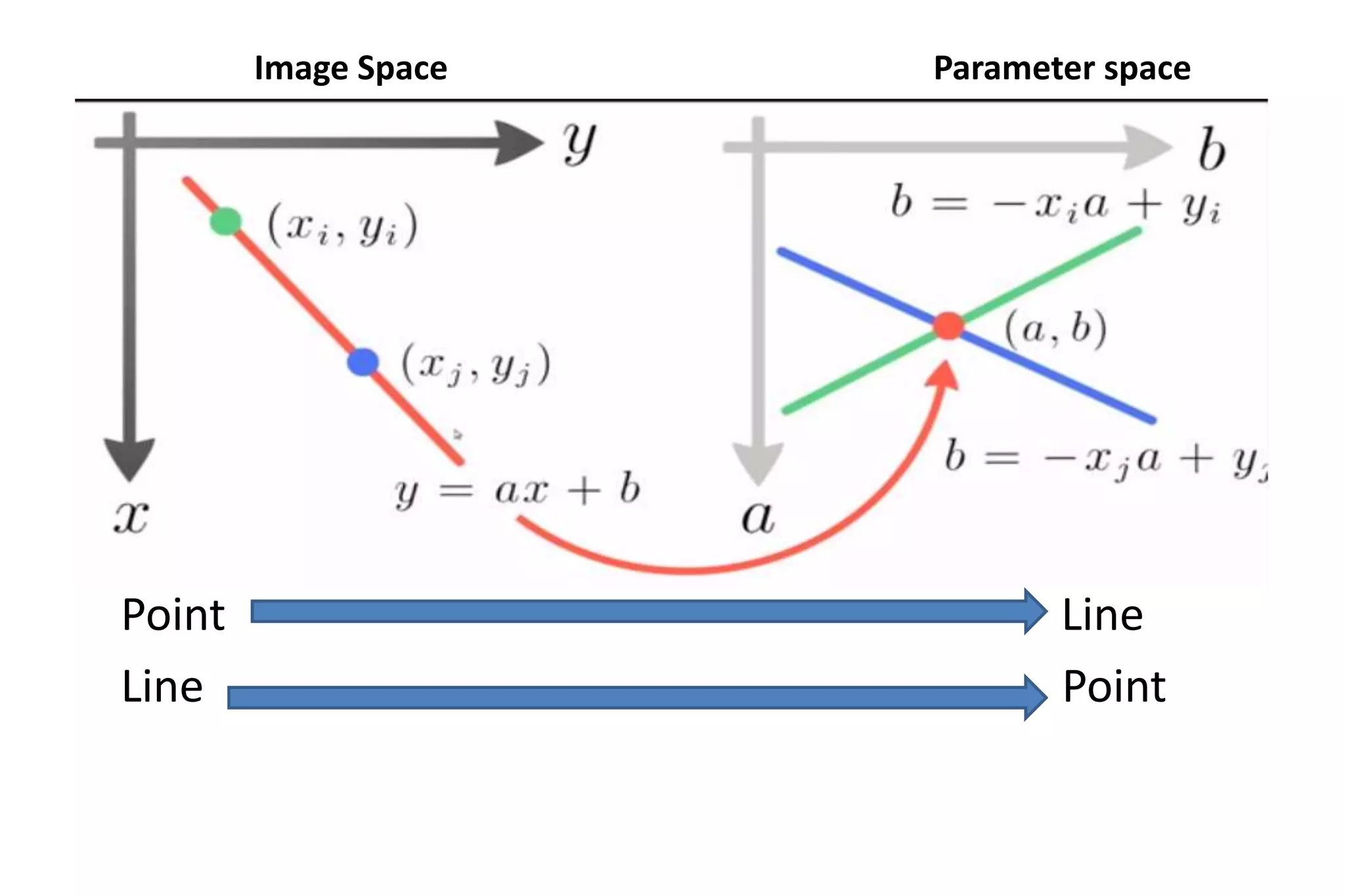
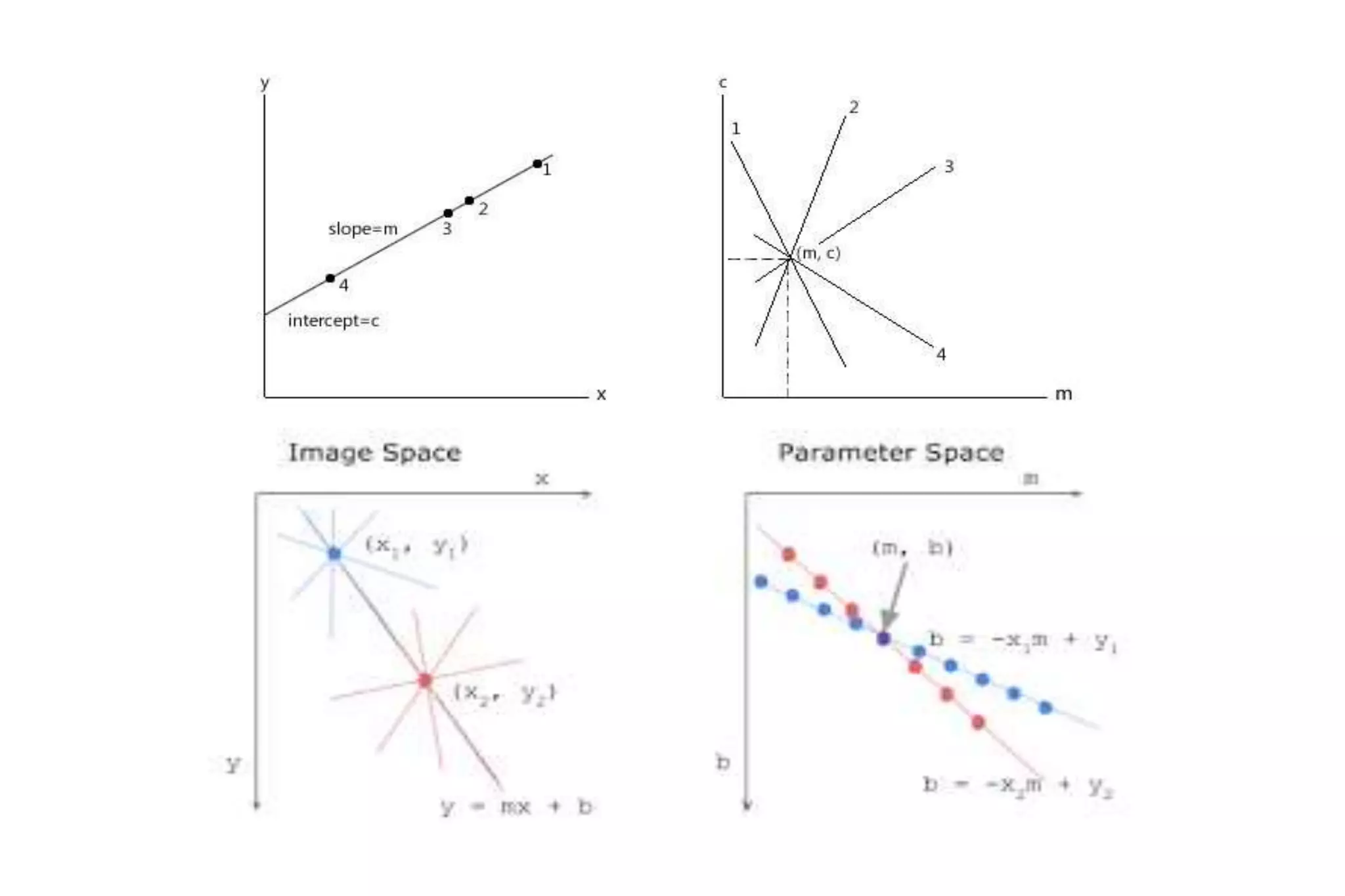
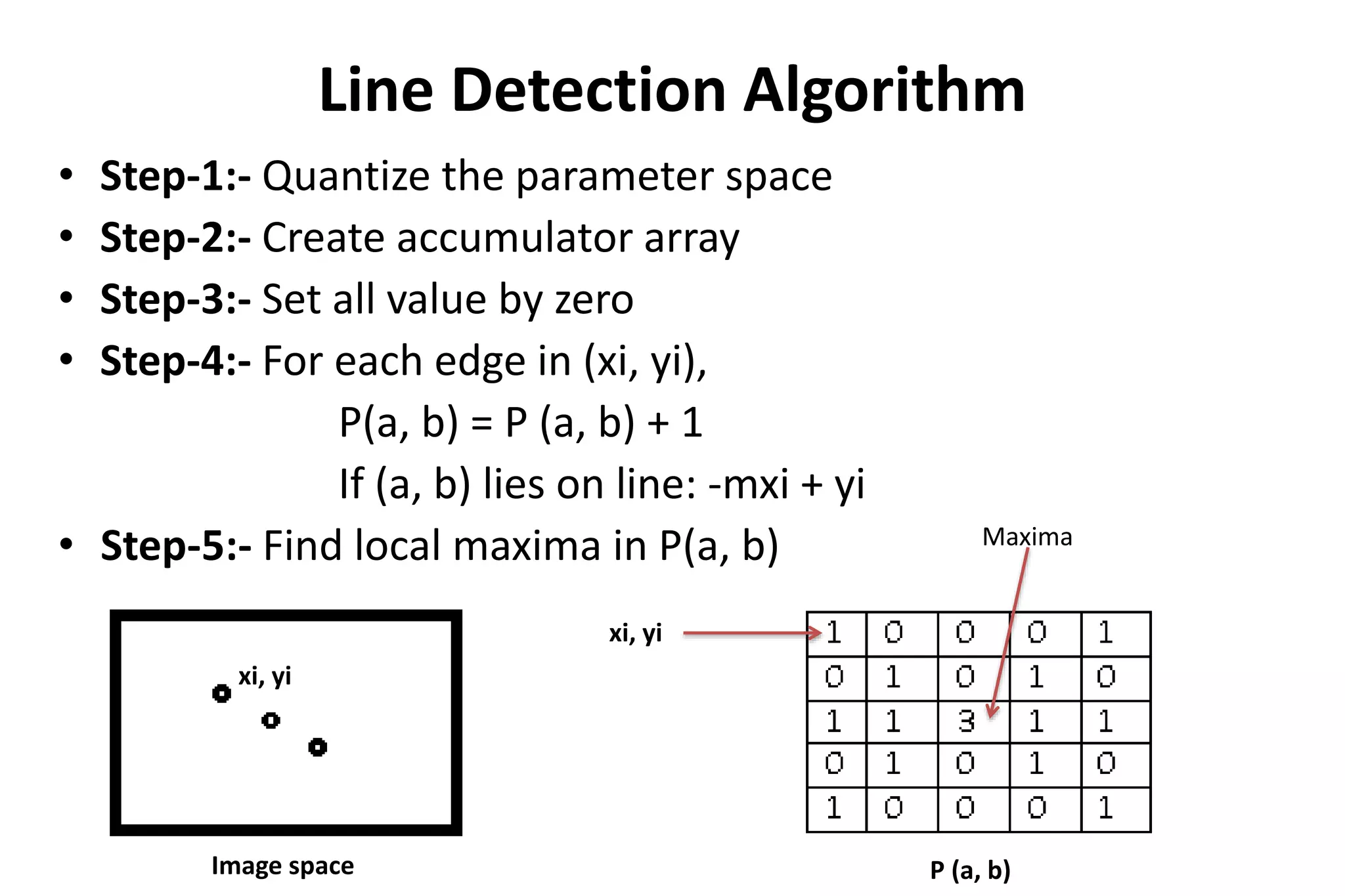
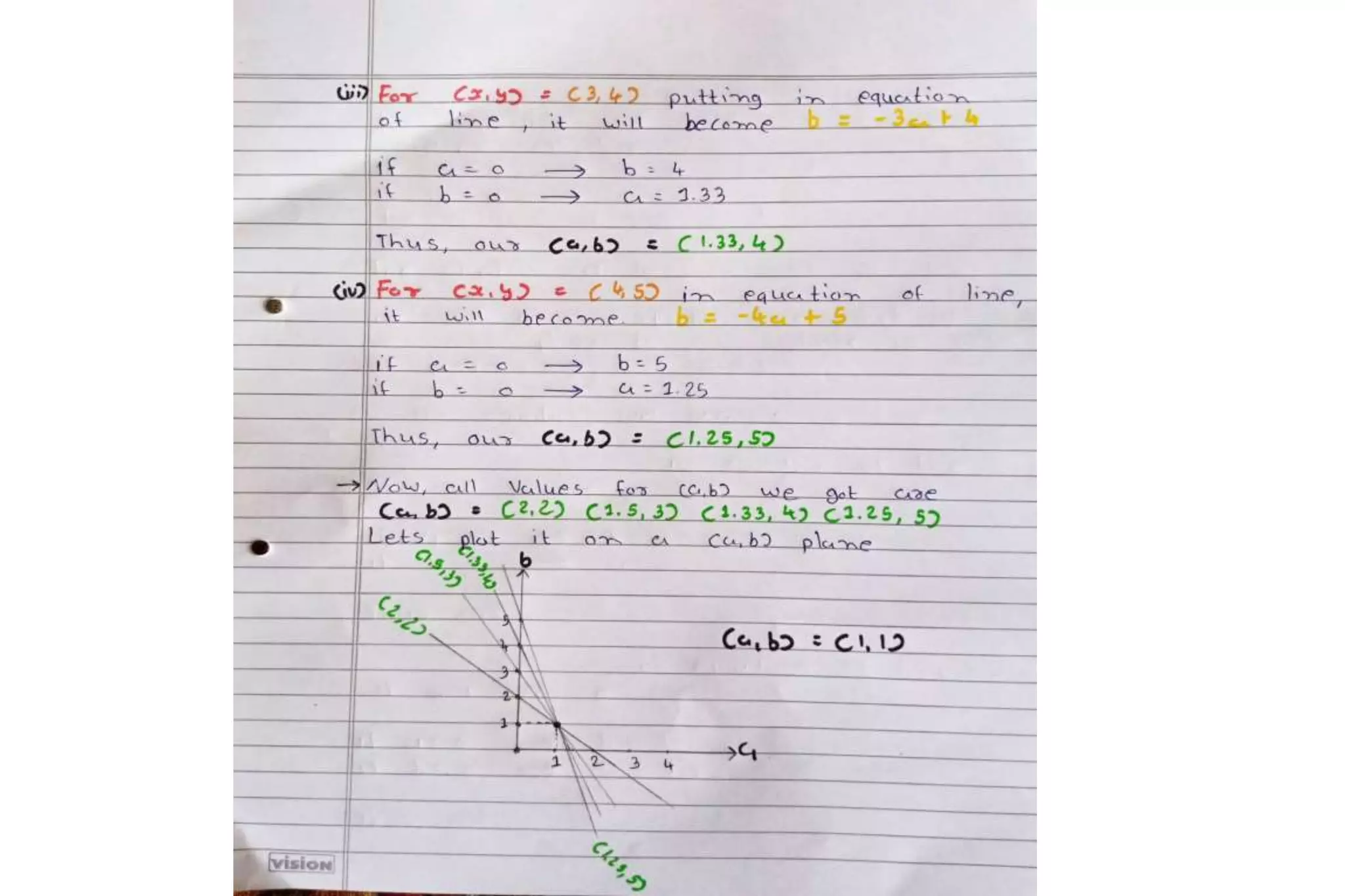
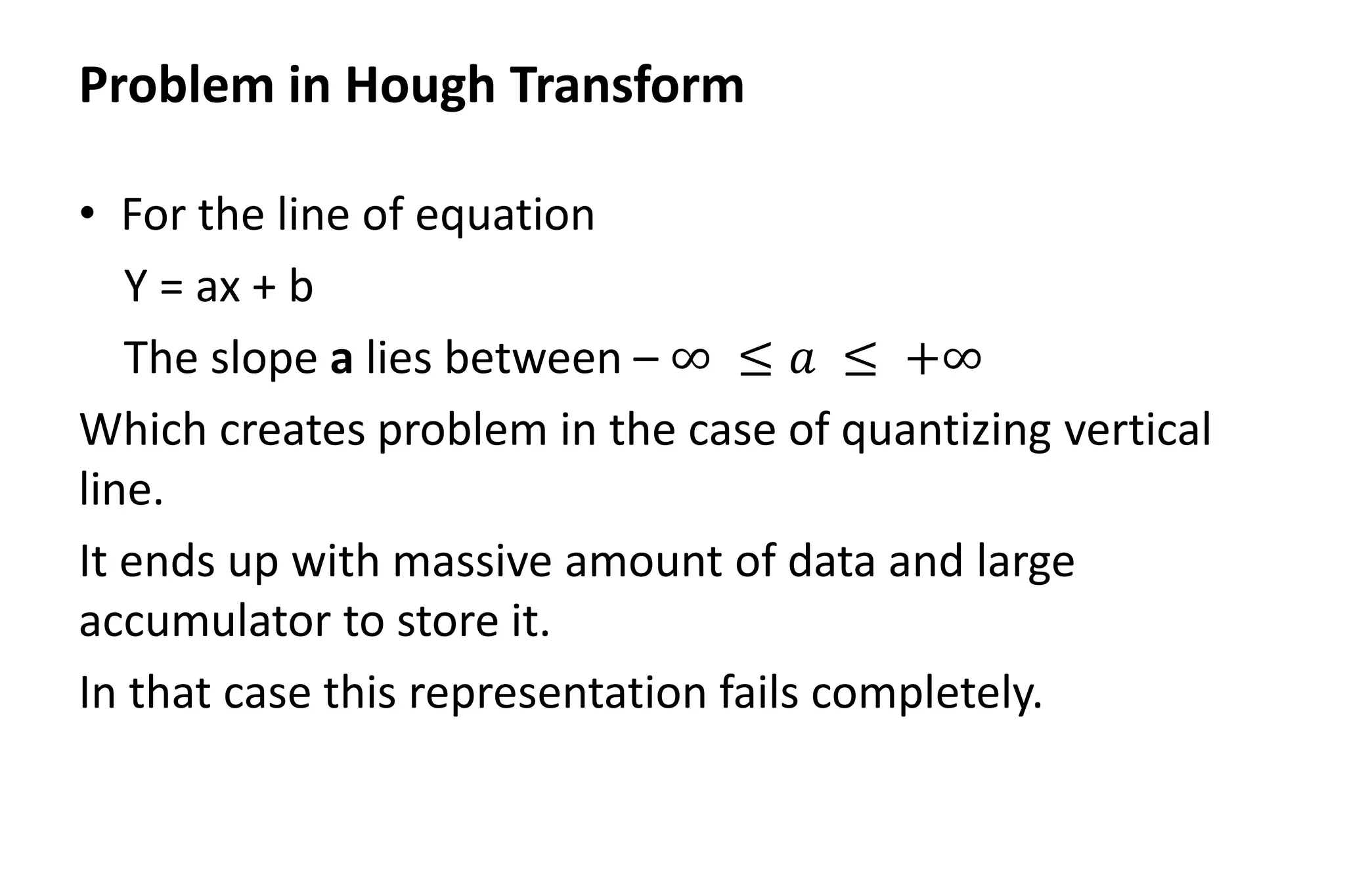
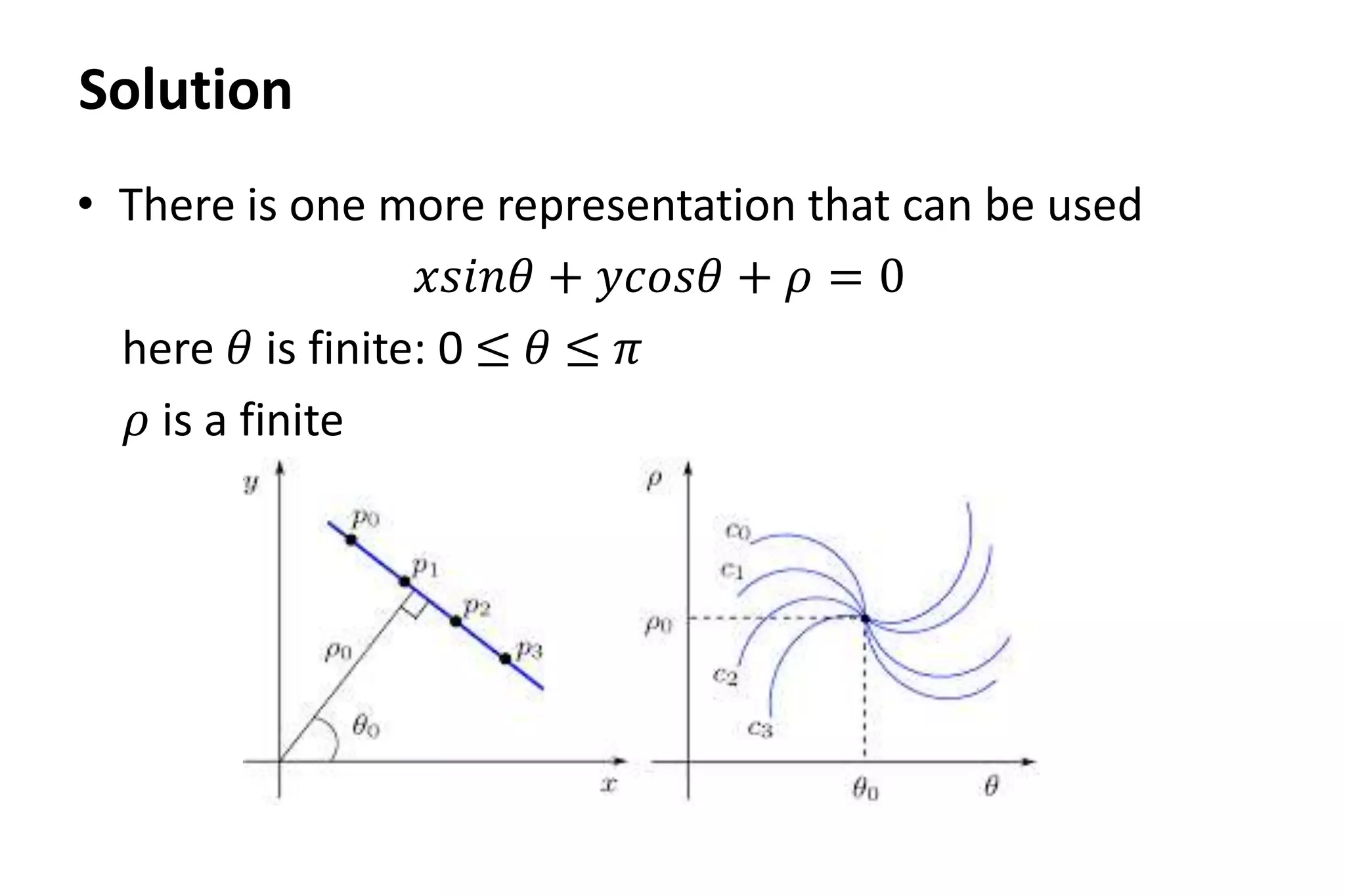
The Hough transform is a feature extraction technique used in image analysis and computer vision to detect shapes and patterns, like lines, circles, and curves. It works by having each edge point in an image vote for a set of possible shape parameters, which are then compiled into a histogram in a parameter space. Local maxima in this space correspond to the most likely shapes in the image. Specifically for line detection, the Hough transform represents a line using its slope (a) and intercept (b), with each edge point voting for all lines passing through it in the parameter space. The algorithm then finds local maxima in this space to detect the lines present in the image. The Hough transform is robust to noise, gaps,