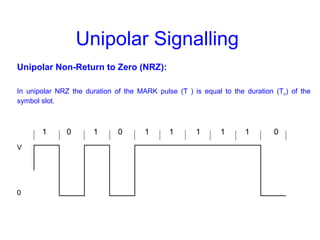
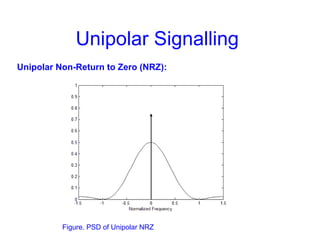
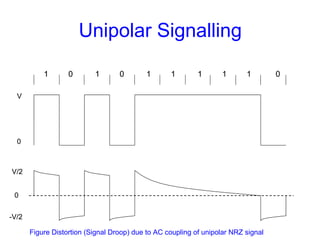
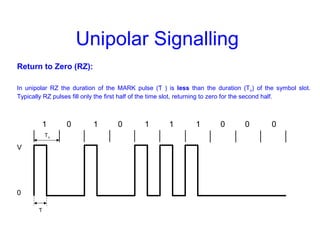
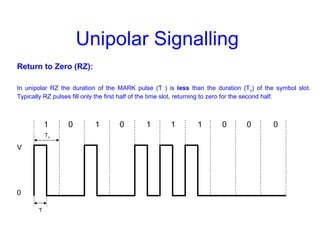
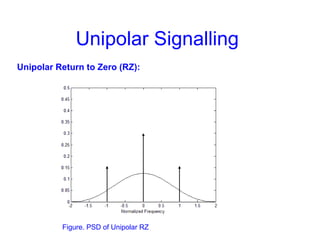
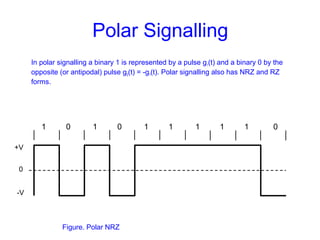
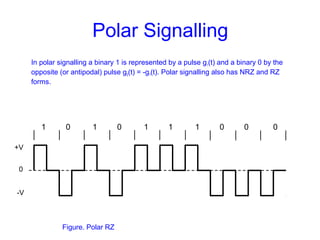
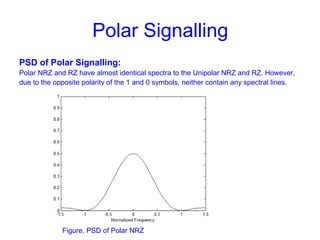
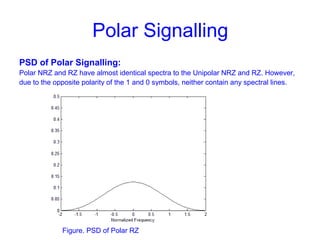
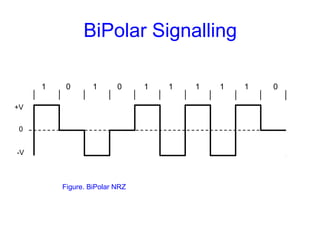
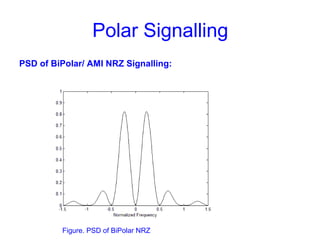
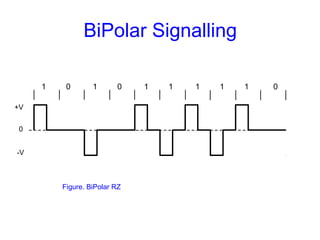
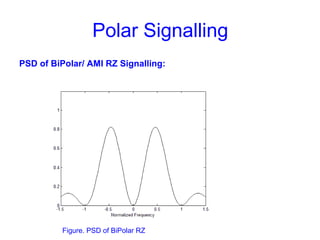
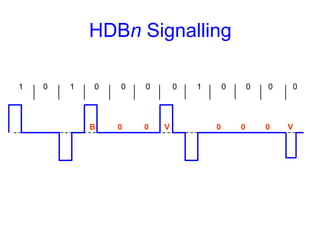
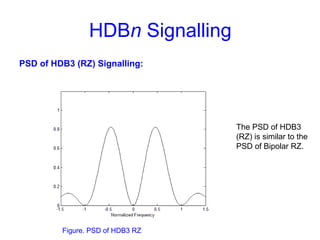
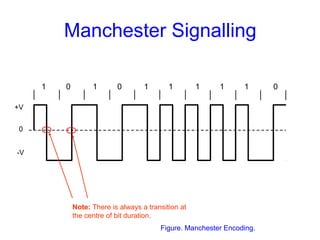
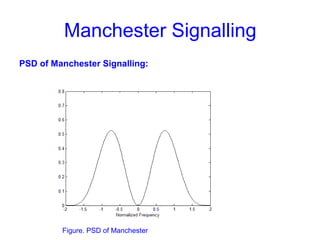
This document provides information about different types of line coding used to transmit binary data over communication channels. It discusses unipolar, polar, bipolar, HDBn, and Manchester line coding. For each type it provides the pulse representation for 1s and 0s, advantages, disadvantages, and power spectral density plots. It explains that line coding choices are made based on factors like bandwidth, error performance, transparency, and suitability for transmission over AC coupled lines.