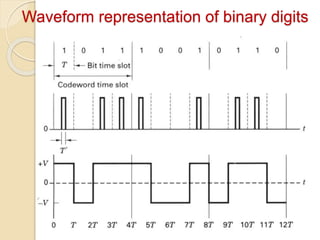
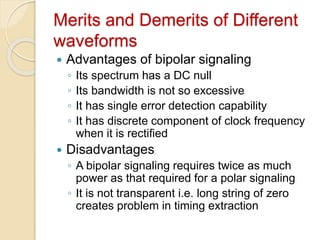
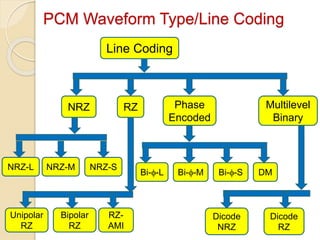
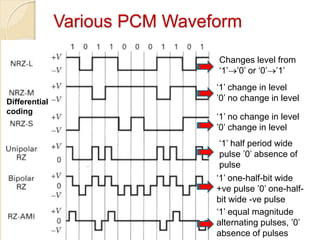
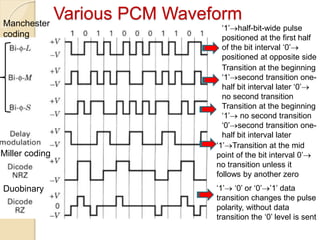
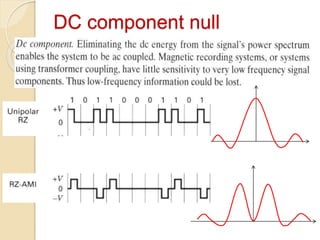
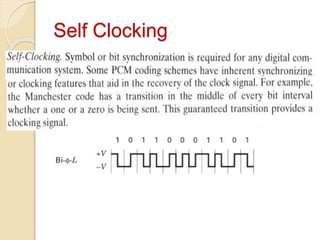
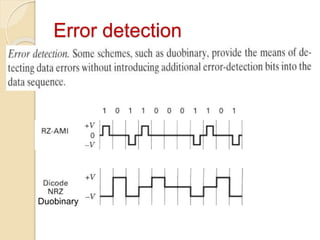
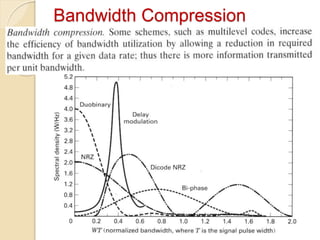
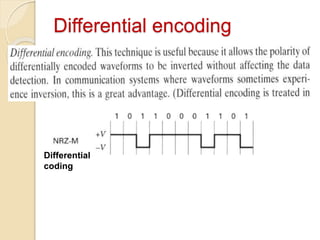
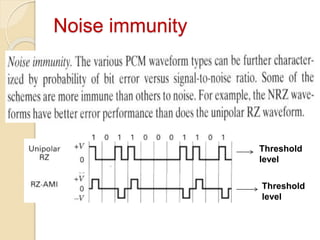
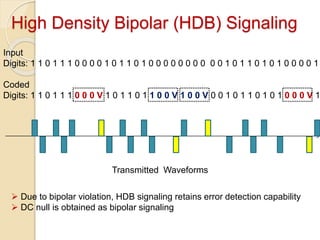
The document discusses various line coding techniques for pulse code modulation (PCM), emphasizing different waveform types such as unipolar, polar, and bipolar, along with their respective merits and demerits. It explains the importance of aspects like noise immunity, bandwidth efficiency, and error detection in these signaling methods, specifically highlighting high-density bipolar (HDB) signaling that addresses non-transparency issues. The document also includes an example of HDB signaling encoding to illustrate its operational principles.