The document discusses various line coding techniques used in digital communication. It describes 6 main types of line codes:
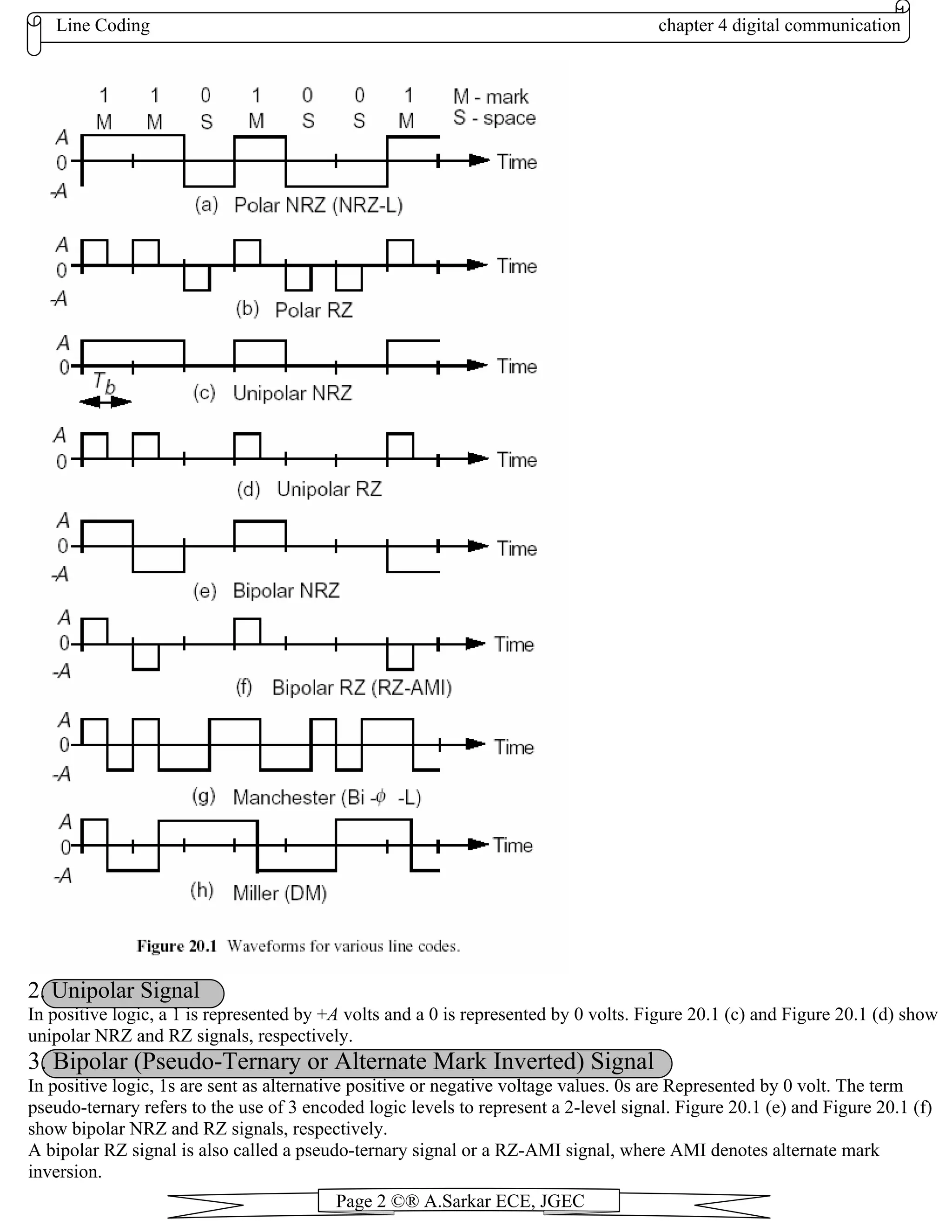
1) Polar signal - Represents 1 as +A volts and 0 as -A volts. Allows easy generation but requires dual supply voltages.
2) Unipolar signal - Represents 1 as +A volts and 0 as 0 volts. Easy generation from single supply but wastes power.
3) Bipolar signal - Alternates between positive and negative voltages for 1s. Represents 0 as 0 volts. Detects single errors.
4) Manchester coding - Encodes 1 as +A volts for half pulse then -A volts. Encodes 0 as opposite. Ensures
![Line Coding chapter 4 digital communication
Page 1 ©® A.Sarkar ECE, JGEC
Line Coding
Introduction
Line coding involves converting a sequence of 1s and 0s to a time-domain signal (a sequence of pulses) suitable for
transmission over a channel. The following primary factors should be considered when choosing or designing a line code.
1. Self-synchronization. Timing information should be built into the time-domain signal so that the timing information
can be extracted for clock synchronization. A long string of consecutive 1s and 0s should not cause a problem in clock
recovery.
2. Transmission power and bandwidth efficiency. The transmitted power should be as small as possible, and the
transmission bandwidth needs to be sufficiently small compared to the channel bandwidth so that inter-symbol
interference will not be a problem.
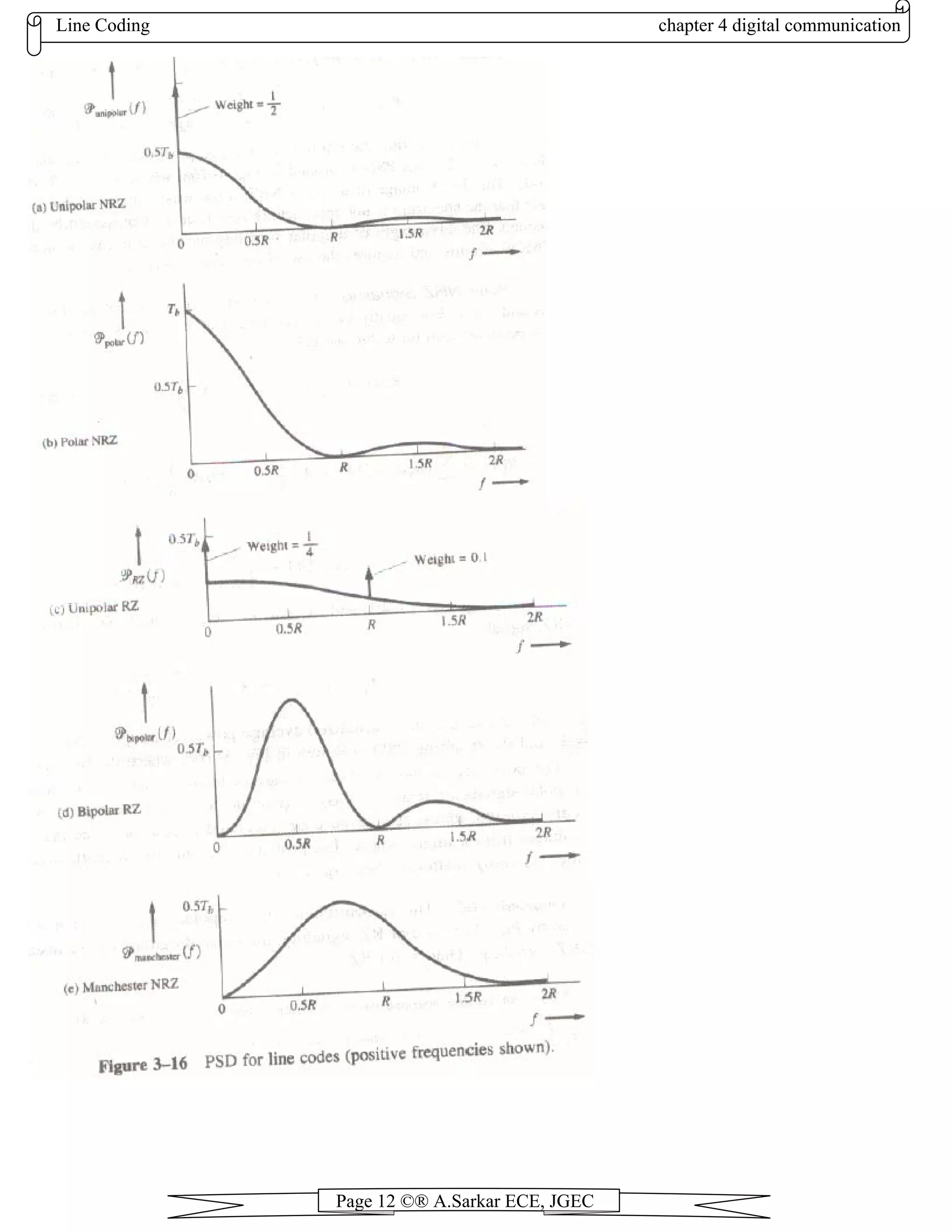
3. Favorable Power Spectral Density. The spectrum of the time-domain signal should be suitable for the transmission
channel. For example, if a channel is ac coupled, it is desirable to have zero power spectral density near dc to avoid dc
wandering in the pulse stream.
4. Low probability of error. When the received signal is corrupted by noise, the receiver can easily recover the un-coded
signal with low error probability.
5. Error detection and correction capability. The line code should have error detection capability, and preferably have
error correction capability.
6. Transparency. It should be possible to transmit every signal sequence correctly regardless of the patterns of 1s and 0s.
If the data are coded so that the coded signal is received faithfully, the code is transparent. Given a sequence of pulses,
there are two possible waveform formats that we can use to send a pulse of duration Tb seconds over a channel. The duty
cycle of the pulse can be used to define these two waveform formats.
If the transmitted pulse waveform is maintained for the entire duration of the pulse, this is called non-return-to-zero
(NRZ) format.
If the transmitted pulse waveform only occupies a fraction of the pulse duration, this is called return-to-zero (RZ) format.
Classification of Line Waveforms [1]
There are many types of line codes and we shall only discuss a few of them here. The waveforms for the line code may
be further classified according to the rule that is used to assign voltage levels to represent the binary data.
1. Polar Signal
In positive logic, a 1 is represented by +A volts and a 0 is represented by -A volts. Figure 20.1 (a) and Figure 20.1 (b)
show polar NRZ and RZ signals, respectively. A polar NRZ signal is also called a NRZ-L (L for level) signal because a
high voltage level corresponds to a positive logic level [3]. Alternatively, we could have used negative logic, where a 1 is
represented by -A volts and a 0 is represented by +A volts.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter4-130808051138-phpapp02/75/Chapter4-1-2048.jpg)
![Line Coding chapter 4 digital communication
Page 3 ©® A.Sarkar ECE, JGEC
4. Manchester (Split-phase, Twinned-Binary) Coding
Manchester coding was developed by Manchester University. In positive logic, a 1 is represented by +A volts over a half-
pulse period followed by -A volts over a half-pulse period. A 0 is represented by -A volts over a half-pulse period
followed by +A volts over a half-pulse period. This is shown in Figure 20.1 (g). Other names in use for Manchester
coding are split-phase and twinned-binary coding. Sometimes it is called bi-phase-level (Bi- φ-L)
A Manchester signal can be generated by multiplying a polar NRZ signal by a synchronized square-wave clock having a
period Tb [4]. It can also be generated by exclusive-ORing a polar NRZ signal with a synchronized but inverted square-
wave clock having a period Tb.
5. Miller (delay modulation) Coding
A transition occurs at the mid-point of each symbol interval for a 1. For a 1 followed by a 1, no transition occurs at the
symbol interval. No transition occurs at the mid-point of each symbol interval for a 0. For a 0 followed by a 0, a
transition occurs at the symbol interval. For a 0 followed by a 1 or a 1 followed by a 0, no transition occurs at the symbol
interval. This is shown in Figure 20.1 (h). Miller coding is also called delay modulation.
Power spectral densities of various line codes
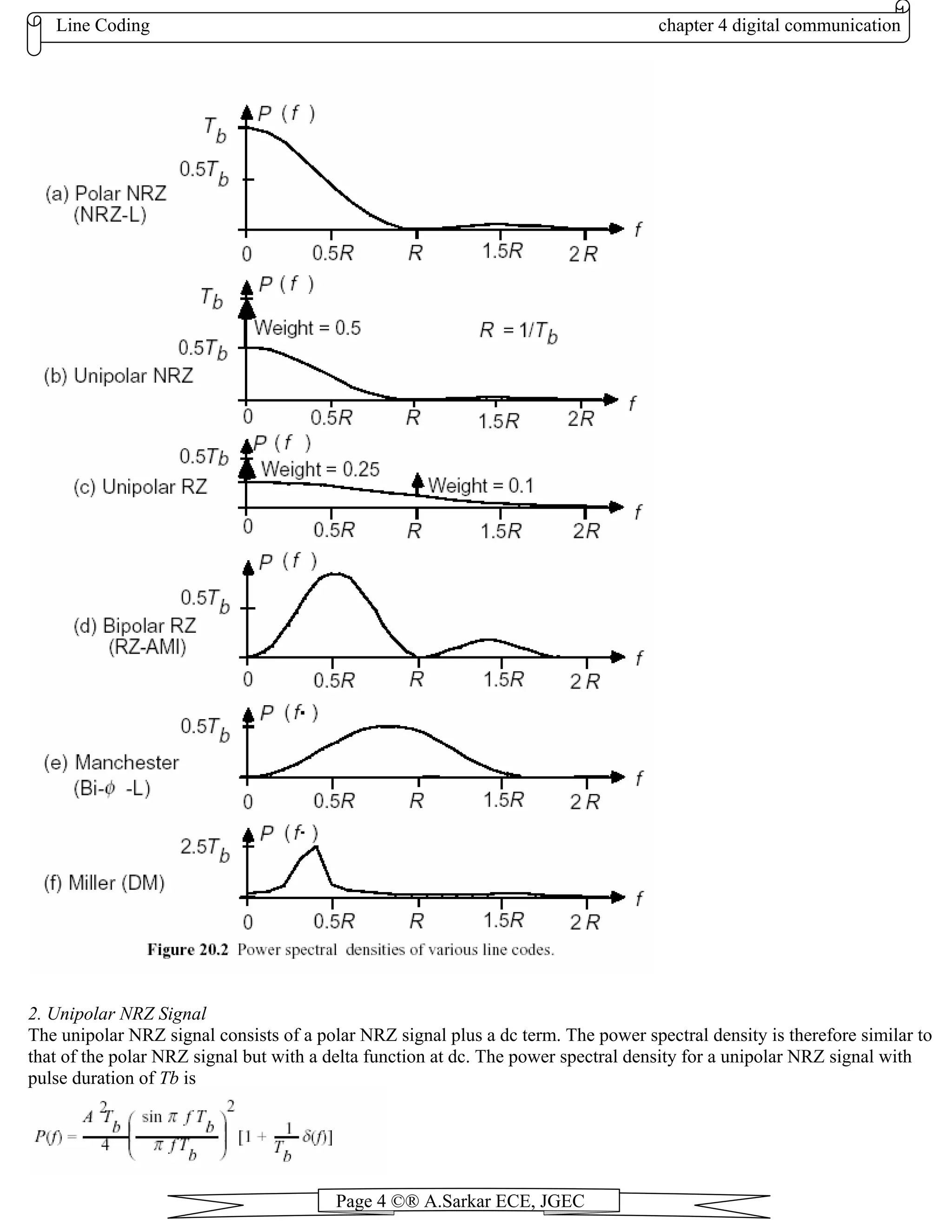
1. Polar NRZ Signal (NRZ-L)
The power spectral density for a polar NRZ signal with a pulse duration of Tb is
Figure 20.2 (a) shows the power spectral density of the polar NRZ signal where A is set to 1 so that the normalized
average power of the signal is unity.
Advantages of Polar NRZ Signal (NRZ-L):
Relatively easy to generate the signal but requires dual supply voltages.
Bit error probability performance is superior to other line encoding schemes.
Disadvantages of Polar NRZ Signal (NRZ-L):
It has a large power spectral density near dc.
Poor clock recovery - a string of 1s or 0s will cause a loss of clock signal.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter4-130808051138-phpapp02/75/Chapter4-3-2048.jpg)

![Line Coding chapter 4 digital communication
Page 6 ©® A.Sarkar ECE, JGEC
Disadvantage of Manchester (Split-phase, Twined-Binary) Coding:
Null bandwidth is twice that of the polar NRZ (NRZ-L), unipolar NRZ, or bipolar RZ (RZ-AMI) signals.
6. Miller Coding
Advantages of Miller Coding :
Attractive for magnetic recording and PSK signalling includes [5]:
1. Majority of signal energy lies in frequencies less than 0.5 of the symbol rate R = 1/Tb.
2. Small spectrum at dc facilitates carrier tracking, and important in tape recording with poor dc response.
3. Small spectrum at dc, lower magnetic-tape recording speed can be used (higher packing density is possible).
4. Insensitive to 180o phase ambiguity common to NRZ-L and Manchester coding.
5. Bandwidth requirements are approximately half those needed by Manchester coding.
The clock frequency is embedded in the code for all symbol sequences [6].
Disadvantage of Miller Coding:
Small spectrum at dc may not be acceptable for some transmission channels
In general, there is no optimum waveform choice for all digital transmission systems. Return-to-zero (RZ) waveforms
may be attractive when the bandwidth is available. Because RZ waveforms always have two level transitions per symbol
interval, symbol timing recovery can easily be achieved. For bandwidth-efficient systems, non-return-to- zero (NRZ)
waveforms are more attractive. However, long strings of ones or zeros should be avoided to allow accurate recovery of
symbol timing.
Polar or unipolar signals are found in most digital circuits, but they may have a nonzero dc level. Bipolar and Manchester
signals will always have a zero dc level regardless of the data sequence.
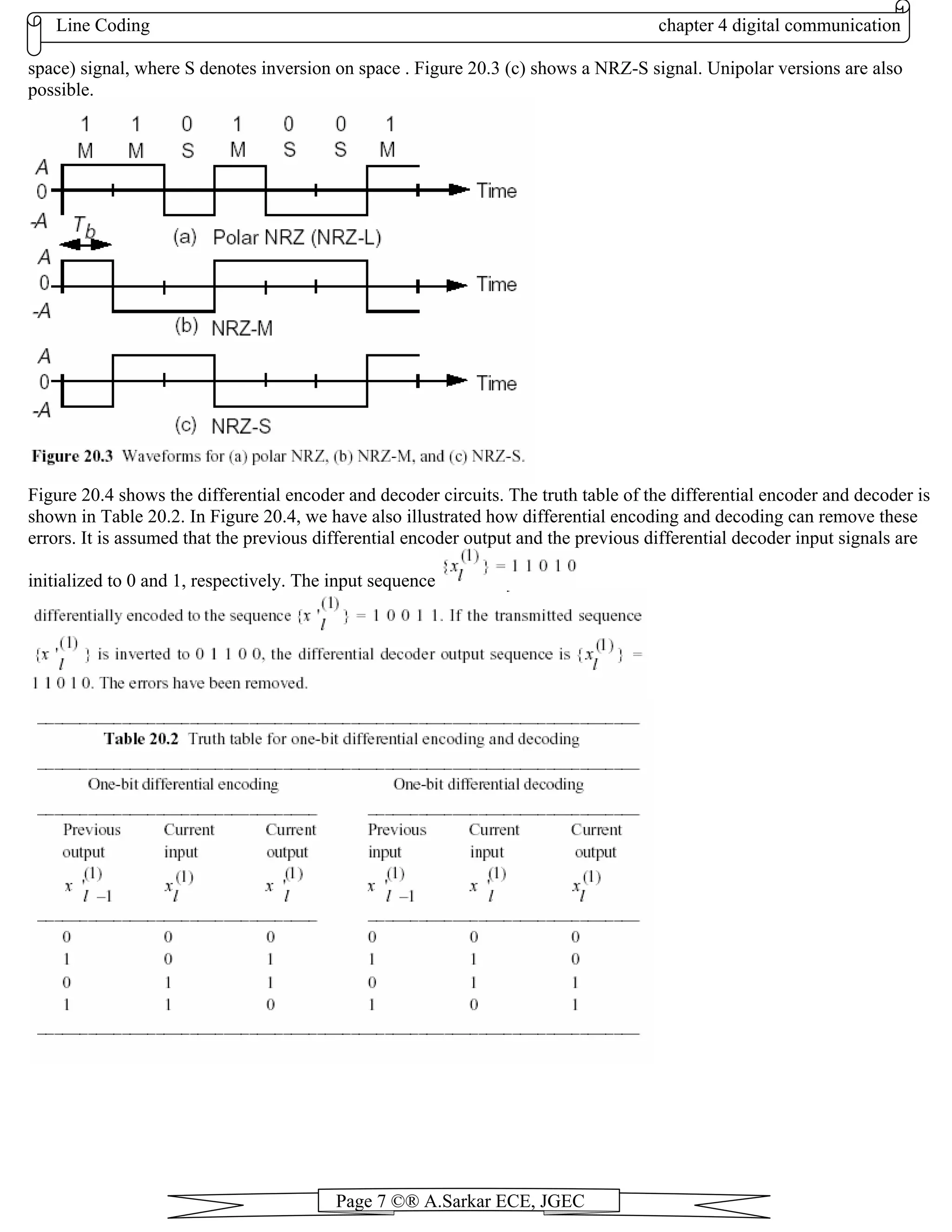
Differential Coding
The differential form of encoding is actually more the result of a coding technique than it is a line waveform. When serial
data are passed through many circuits along a transmission channel, the waveform is often unintentionally inverted. For
example, if we employ a polar signal and reverse the two leads at a connection point of a twisted-pair transmission
channel, the entire data sequence will be inverted and every symbol will be in error.
Differential coding can solve this problem. We can insert a differential encoder before the line encoder at the
transmitter and a differential decoder after the line decoder at the receiver to remove these errors. The differential
encoding operation can be viewed as a rotation of the previous differential encoder output signals in accordance with the
current differential encoder input signals. The differential decoder is performing the reverse operation. The encoding
rules are: A 1 is represented by a change in level between two consecutive symbol times. A 0 is represented by no
change. This kind of differential form of encoding has been called NRZ-M (M for mark) signal, where M denotes
inversion on mark . Figure 20.3 (b) shows a NRZ-M signal. If a 1 is represented by no change in level between two
consecutive symbol times and a 0 is represented by a change, this differential waveform has been called NRZ-S (S for](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter4-130808051138-phpapp02/75/Chapter4-6-2048.jpg)
![Line Coding chapter 4 digital communication
Page 8 ©® A.Sarkar ECE, JGEC
PSD of a digital signal:-
we now derive a general formulae for the PSD of digital signals. A general result can be obtained in terms of
autocorrelation of the data an.
The polar signal may be modeled as
)()( ∑
∞
−∞=
−=
n
bn nTtfatx ….(1)
where f(t) is the sampling pulse or symbol pulse shape. Tb is the duration of one bit.i.e the time that it takes to
send 1 bit. {an} is a set of random variables that represent the binary data. It is given that the random variables
are independent. Clearly each one is discretely distributed at an =±1 and P(an=1)=P(an=-1)=1/2.
The PSD for x(t) will be evaluated first by obtaining XT(f) . we can obtain XT(t) by truncating eqn (1)
)()( ∑−=
−=
N
Nn
bnT nTtfatx
where T/2= (N+1/2)Tb then
XT(f)=F[xt(t)]= …(2)
bb jwnT
N
Nn
n
jwnT
N
Nn
n
N
Nn
bn eafFefFanTtfFa −
−=
−
−=−=
∑∑∑ ==− )()()]([
Where F(f)= F[f(t)]
Now we know that PSD for a random process x(t) is given by
)
])([
(lim)(
2
T
fX
fP T
T
x
∞>−
= where ∫−
−
=
2/
2/
2
)()(
T
T
ftj
T dtetxfX π
when we substitute (2) into above eqn we find that PSD is](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter4-130808051138-phpapp02/75/Chapter4-8-2048.jpg)