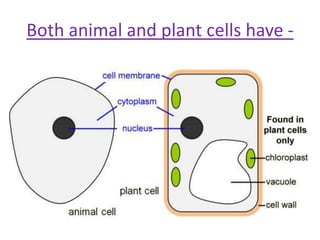
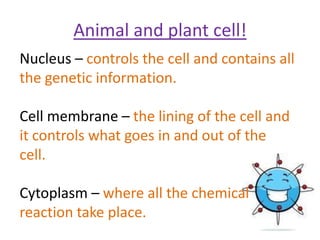
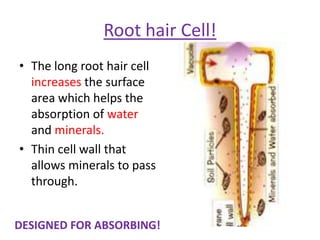
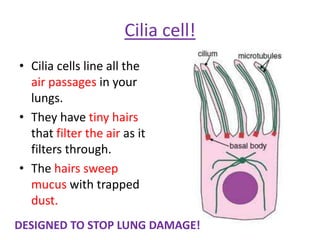
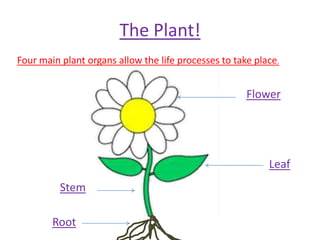
The document outlines key features and functions of plant and animal cells, highlighting the seven life processes essential for living organisms. It identifies specialized cells, such as sperm, ovum, palisade, root hair, and cilia cells, each adapted for specific functions. Additionally, it describes the four main plant organs—flower, stem, root, and leaf—detailing their roles in reproduction, support, nutrient transport, and photosynthesis.