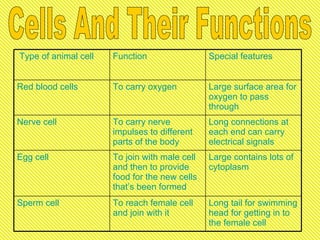
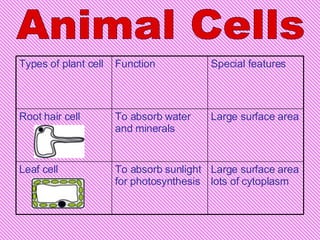
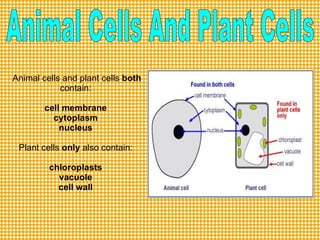
The document discusses several key biology concepts including life processes, photosynthesis, plant and animal cells, and cell structures and functions. It defines photosynthesis as the process by which plants, algae and some bacteria use sunlight, carbon dioxide and water to produce oxygen and energy-rich carbohydrates. It also describes the main structures of plant and animal cells including the cell wall, vacuole, chloroplasts and differences between them. Specialized cell types in plants and animals are outlined with their distinctive features that allow them to perform functions like photosynthesis, gas exchange and nerve signaling.