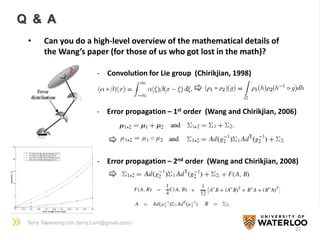
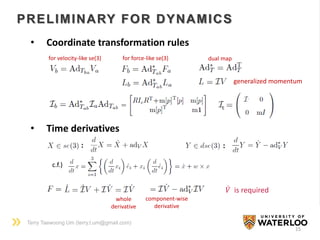
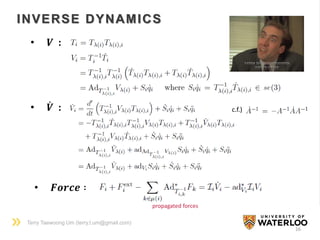
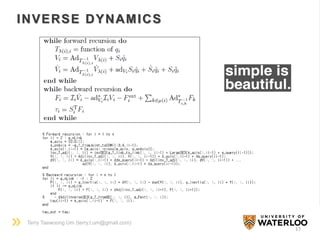
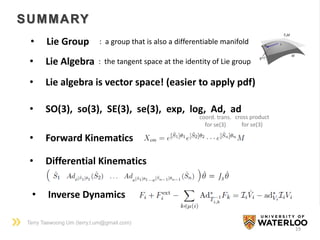
The document discusses the application of Lie group and Lie algebra concepts in robot mechanics, focusing on motion representation, kinematics, and dynamics. Key topics include differential manifolds, forward kinematics, and inverse dynamics, utilizing the product of exponentials and the Jacobian for angular velocity. The summary also highlights the differences between Lie groups and other notational systems for describing rigid body dynamics.


![Terry Taewoong Um (terry.t.um@gmail.com)
MOTIVATION
4
• Coordinate-free approach
http://arxiv.org/pdf/1404.1100.pdf
- Which coordinate should we choose?
- Let’s remove the dependency on the choice of reference frames!
→ Use the right representation for motion → Lie group & Lie algebra
[Newton-Euler formulation]
- Geodesic : a shortest path b/w two points
- Euler angle-based trajectory is not a geodesic!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groupmeetingliegroup150715-150715215659-lva1-app6892/85/Lie-Group-Formulation-for-Robot-Mechanics-4-320.jpg)
![Terry Taewoong Um (terry.t.um@gmail.com)
6
- General Linear Group, GL(n)
: 𝑛 × 𝑛 invertible matrices with matrix multiplication
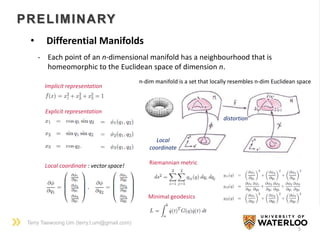
PRELIMINARY
- Special Linear Group, SL(n) : GL(n) with determinant 1
- Orthogonal Group, O(n) : 𝑄 ∈ 𝐺𝐿 𝑛 𝑄 𝑇
𝑄 = 𝑄𝑄 𝑇
= 𝐼}
• Lie Group : a group that is also a differentiable manifold
e.g.)
• Lie Algebra : the tangent space at the identity of Lie group
a vector space with Lie bracket operation [x, y]
- Lie bracket
Non-commutative
Lie group
Lie algebra](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groupmeetingliegroup150715-150715215659-lva1-app6892/85/Lie-Group-Formulation-for-Robot-Mechanics-6-320.jpg)
![Terry Taewoong Um (terry.t.um@gmail.com)
7
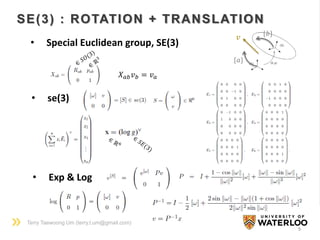
SO(3) : ROTATION
• Special Orthogonal group, SO(3)
𝑅 𝑇
𝑅 = 𝑅𝑅 𝑇
= 𝐼det 𝑅 = 1
• Lie algebra of SO(3) : so(3)
𝑅 𝑎𝑏 = [𝑥 𝑎 𝑦𝑎 𝑧 𝑎]
𝑥
𝑦
𝑧
𝑥 of {b} w.r.t. {a}
- You can express SO(3) with the rotation axis & angle!
http://goo.gl/uqilDV
so(3) : skew-symm. matrices
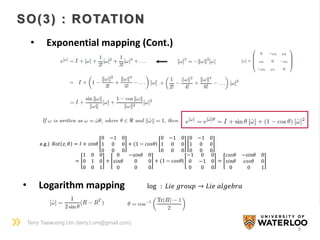
• Exponential mapping
exp ∶ 𝑠𝑜 3 → 𝑆𝑂(3) exp ∶ 𝑠𝑒 3 → 𝑆𝐸(3)
exp ∶ 𝐿𝑖𝑒 𝑎𝑙𝑔𝑒𝑏𝑟𝑎 → 𝐿𝑖𝑒 𝑔𝑟𝑜𝑢𝑝
𝑅 𝑎𝑏 𝑣 𝑏 = 𝑣 𝑎](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groupmeetingliegroup150715-150715215659-lva1-app6892/85/Lie-Group-Formulation-for-Robot-Mechanics-7-320.jpg)
![Terry Taewoong Um (terry.t.um@gmail.com)
10
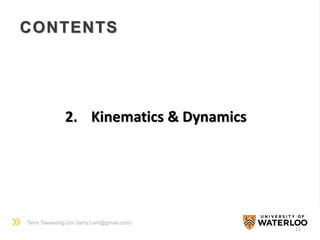
ADJOINT MAPPING
• Lie Algebra : the tangent space at the identity of Lie group
a vector space with Lie bracket operation [x, y]
• Small adjoint mapping
• Large adjoint mapping
cross product
For so(3),
For se(3),
For so(3),
For se(3),
coordinate change](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groupmeetingliegroup150715-150715215659-lva1-app6892/85/Lie-Group-Formulation-for-Robot-Mechanics-10-320.jpg)
![Terry Taewoong Um (terry.t.um@gmail.com)
12
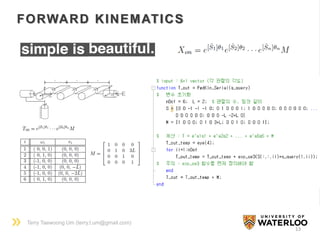
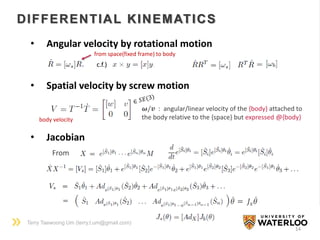
FORWARD KINEMATICS
• Product of Exponential (POE) Formula
- D-H Convention
- POE formula from robot configuration
h = pitch (m/𝑟𝑎𝑑) (0 for rev. joint)
q = a point on the axis
variableconstant
c.f.)
A seen from {0}
𝑅 𝑎𝑏 𝑣 𝑏 = 𝑣 𝑎
𝑇𝑎𝑏 𝑣 𝑏 = 𝑣 𝑎
𝐴𝑑 𝑇 𝑎𝑏
[𝐴] 𝑏= [𝐴] 𝑎
Coord. change
SE(3) from {0} to {n} at home position](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groupmeetingliegroup150715-150715215659-lva1-app6892/85/Lie-Group-Formulation-for-Robot-Mechanics-12-320.jpg)

![Terry Taewoong Um (terry.t.um@gmail.com)
20
Q & A
• What are the benefits/drawbacks of using Lie group for rigid
body dynamics?
• What are the key differences between Lie groups and other 6D
formulations (e.g., Featherstone's spatial notation)?
[Featherstone's cross operation]
skew-symmetric
Lie bracket](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groupmeetingliegroup150715-150715215659-lva1-app6892/85/Lie-Group-Formulation-for-Robot-Mechanics-20-320.jpg)
![Terry Taewoong Um (terry.t.um@gmail.com)
21
Q & A
[From Featherstone's book]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groupmeetingliegroup150715-150715215659-lva1-app6892/85/Lie-Group-Formulation-for-Robot-Mechanics-21-320.jpg)