The document provides an introduction to machine learning and deep learning, explaining core concepts, tasks such as classification, regression, and clustering, and performance measures. It emphasizes the importance of experience through labeled and unlabeled data, and discusses various models, including parametric and nonparametric approaches. Additionally, it covers techniques like regularization and dimension reduction to optimize machine learning performance.





![Terry Taewoong Um (terry.t.um@gmail.com)
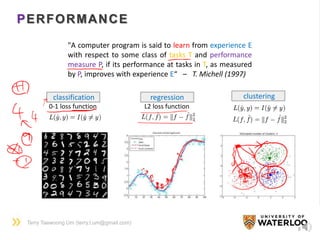
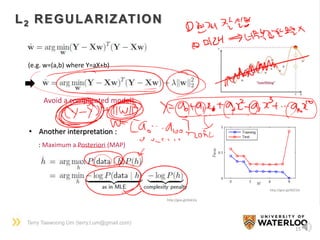
A TOY EXAMPLE
10
? Height(cm)
Weight
(kg)
[Input X]
[Output Y]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlsportsterry150622-copy-151029160304-lva1-app6892/85/Machine-learning-10-320.jpg)
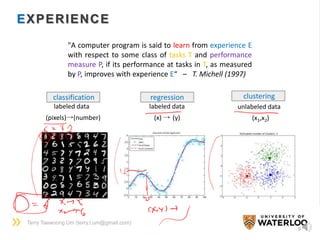
![Terry Taewoong Um (terry.t.um@gmail.com)
11
180 Height(cm)
Weight
(kg)
80
Y = aX+b
Model : Y = aX+b Parameter : (a, b)
[Goal] Find (a,b) which best fits the given data
A TOY EXAMPLE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlsportsterry150622-copy-151029160304-lva1-app6892/85/Machine-learning-11-320.jpg)
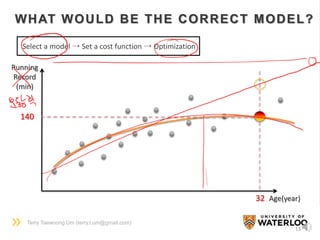
![Terry Taewoong Um (terry.t.um@gmail.com)
12
[Analytic Solution]
Least square problem
(from AX = b, X=A#b where
A# is A’s pseudo inverse)
Not always available
[Numerical Solution]
1. Set a cost function
2. Apply an optimization method
(e.g. Gradient Descent (GD) Method)
L
(a,b)
http://www.yaldex.com/game-
development/1592730043_ch18lev1sec4.html
Local minima problem
http://mnemstudio.org/neural-networks-
multilayer-perceptron-design.htm
A TOY EXAMPLE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlsportsterry150622-copy-151029160304-lva1-app6892/85/Machine-learning-12-320.jpg)
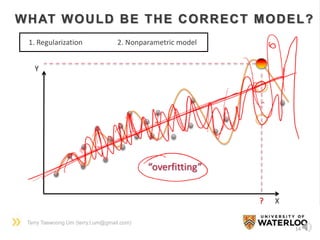
![Terry Taewoong Um (terry.t.um@gmail.com)
17
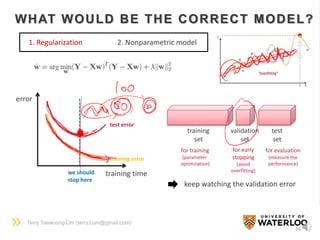
NONPARAMETRIC MODEL
• It does not assume any parametric models (e.g. Y = aX+b, Y=aX2+bX+c, etc.)
• It often requires much more samples
• Kernel methods are frequently applied for modeling the data
• Gaussian Process Regression (GPR), a sort of kernel method, is a widely-used
nonparametric regression method
• Support Vector Machine (SVM), also a sort of kernel method, is a widely-used
nonparametric classification method
kernel function
[Input space] [Feature space]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlsportsterry150622-copy-151029160304-lva1-app6892/85/Machine-learning-17-320.jpg)
![Terry Taewoong Um (terry.t.um@gmail.com)
18
SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE (SVM)
“Myo”, Thalmic Labs (2013)
https://youtu.be/oWu9TFJjHaM
[Linear classifiers] [Maximum margin]
Support vector Machine Tutorial, J. Weston, http://goo.gl/19ywcj
[Dual formulation] ( )
kernel function
kernel function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlsportsterry150622-copy-151029160304-lva1-app6892/85/Machine-learning-18-320.jpg)
![Terry Taewoong Um (terry.t.um@gmail.com)
20
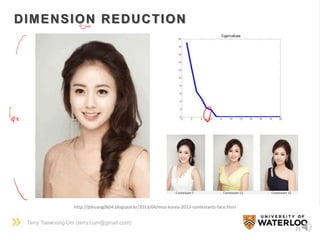
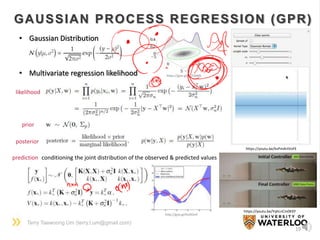
DIMENSION REDUCTION
[Original space] [Feature space]
low dim. high dim.
high dim. low dim.
𝑋 → ∅(𝑋)
• Principal Component Analysis
: Find the best orthogonal axes
(=principal components) which
maximize the variance of the data
Y = P X
* The rows in P are m largest eigenvectors
of
1
𝑁
𝑋𝑋 𝑇
(covariance matrix)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlsportsterry150622-copy-151029160304-lva1-app6892/85/Machine-learning-20-320.jpg)