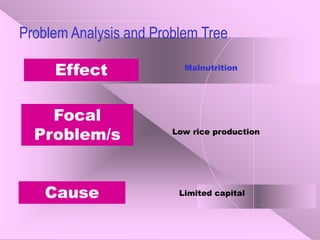
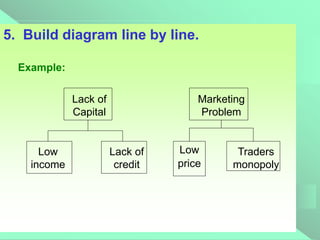
The document outlines the problem tree approach for problem analysis, detailing its definitions, objectives, and guidelines for creating a problem tree diagram. It emphasizes the method's utility in understanding the core and causal factors of problems, guiding intervention strategies, and aiding in program planning and evaluation. The document also includes a step-by-step procedure for constructing a problem tree diagram, highlighting the need for collaboration and effective facilitation.