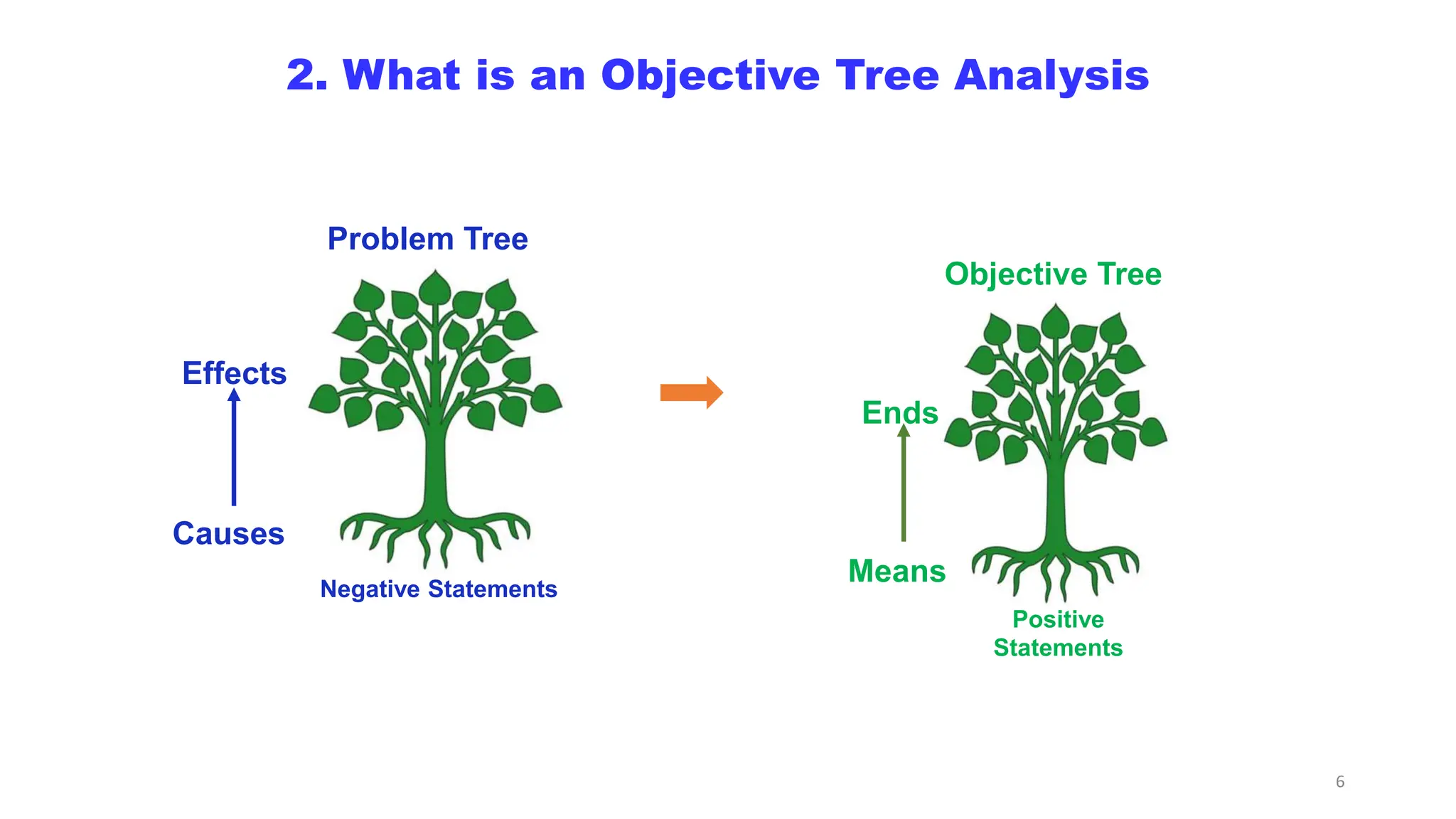
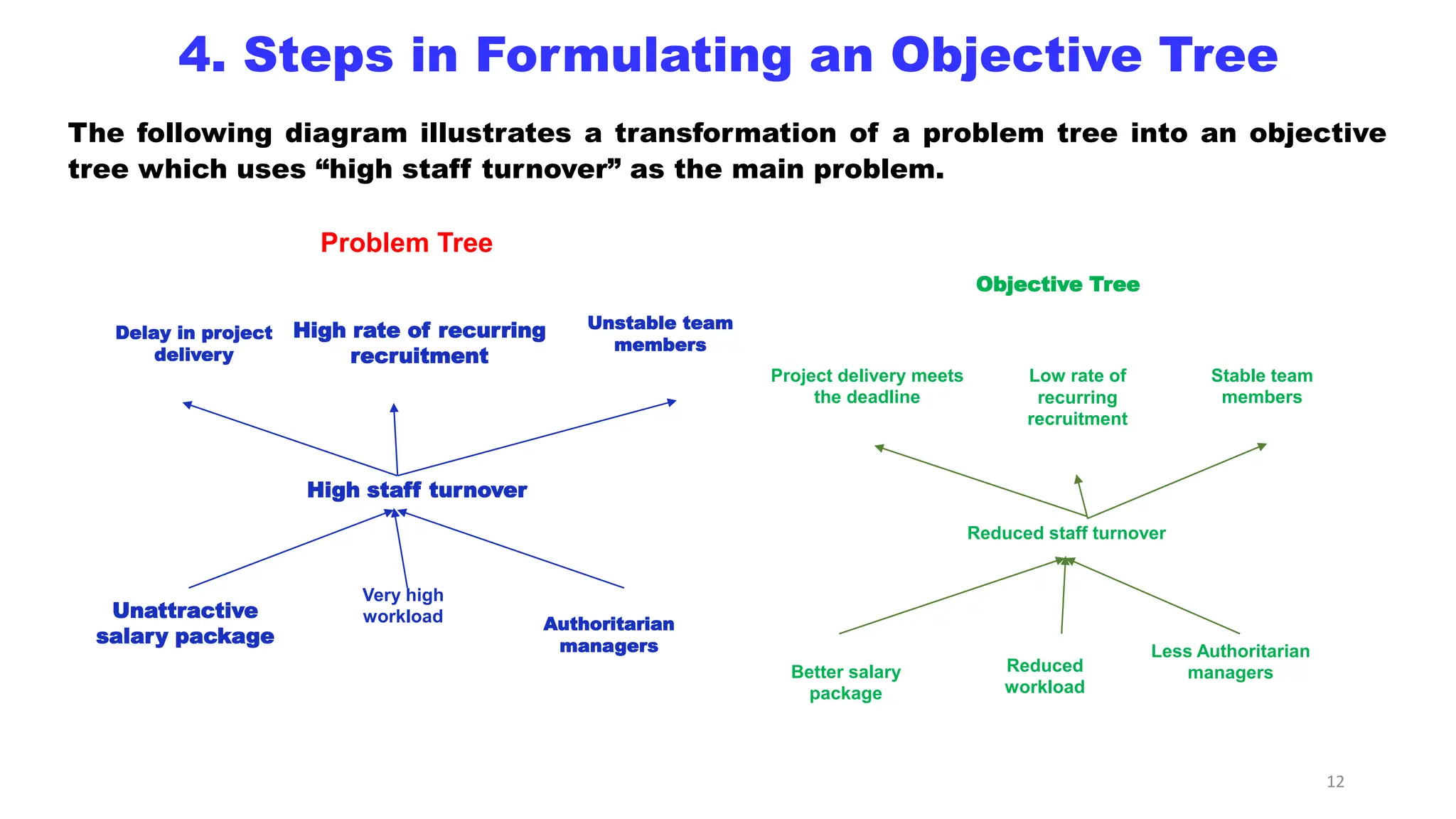
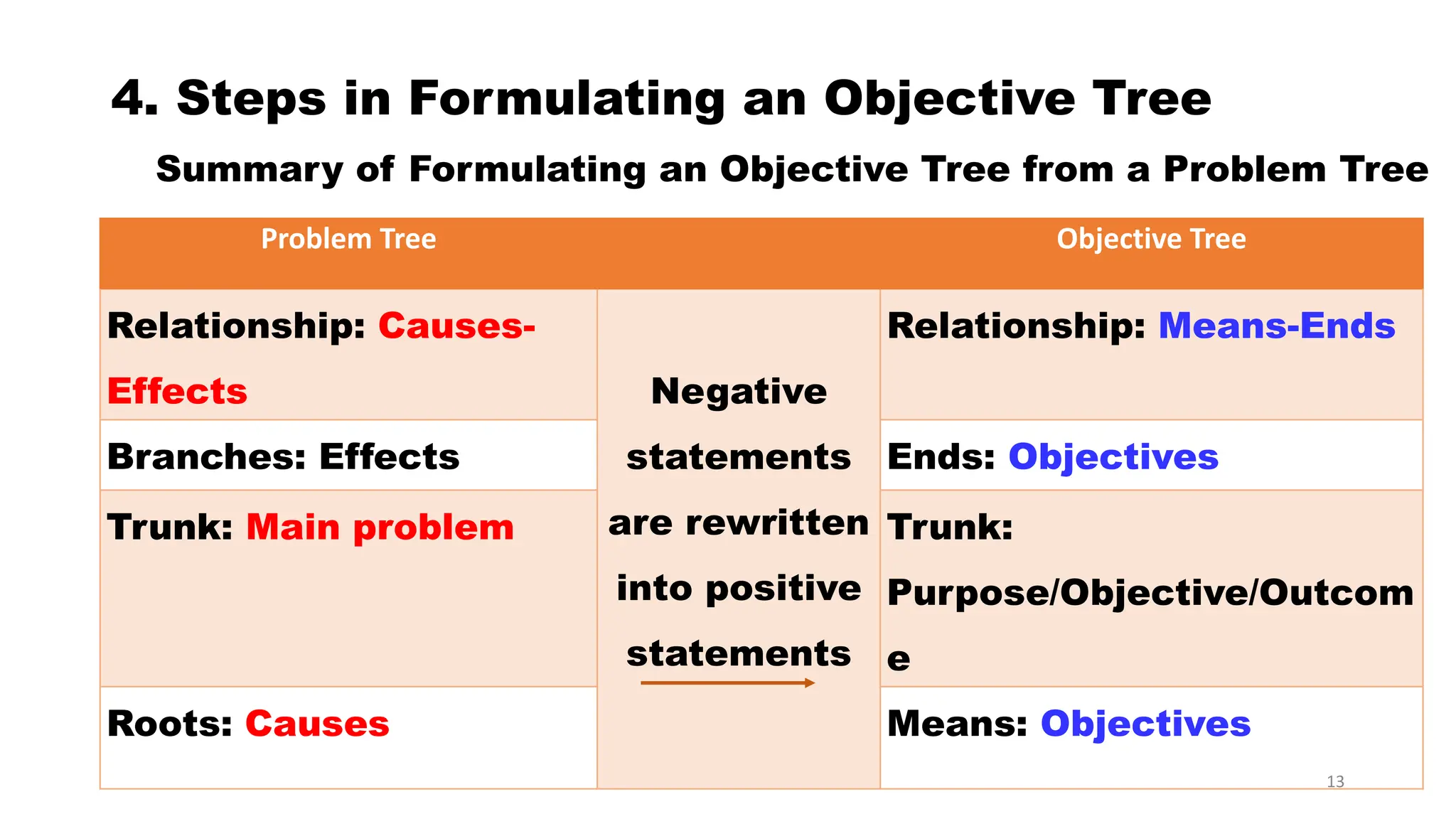
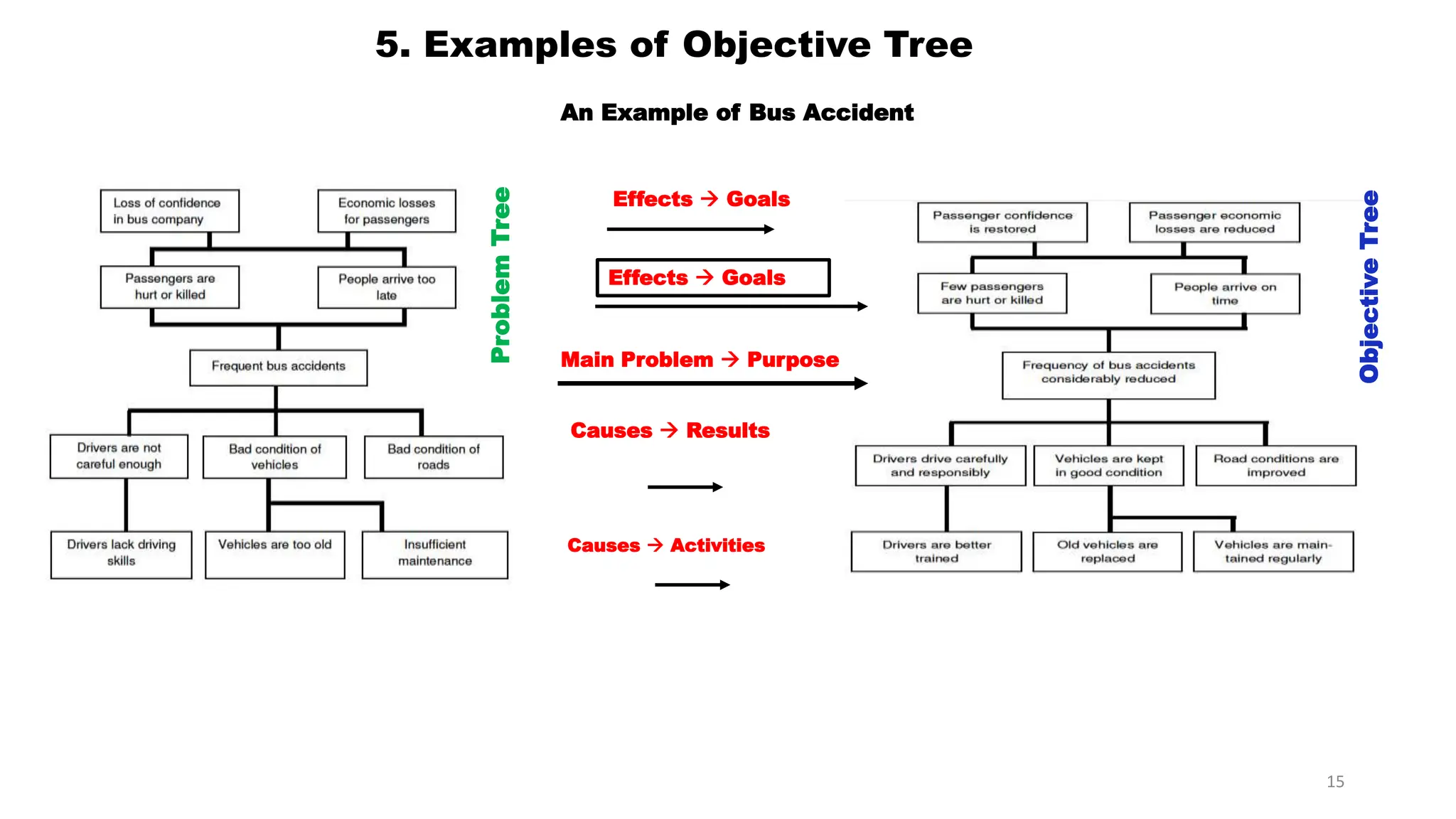
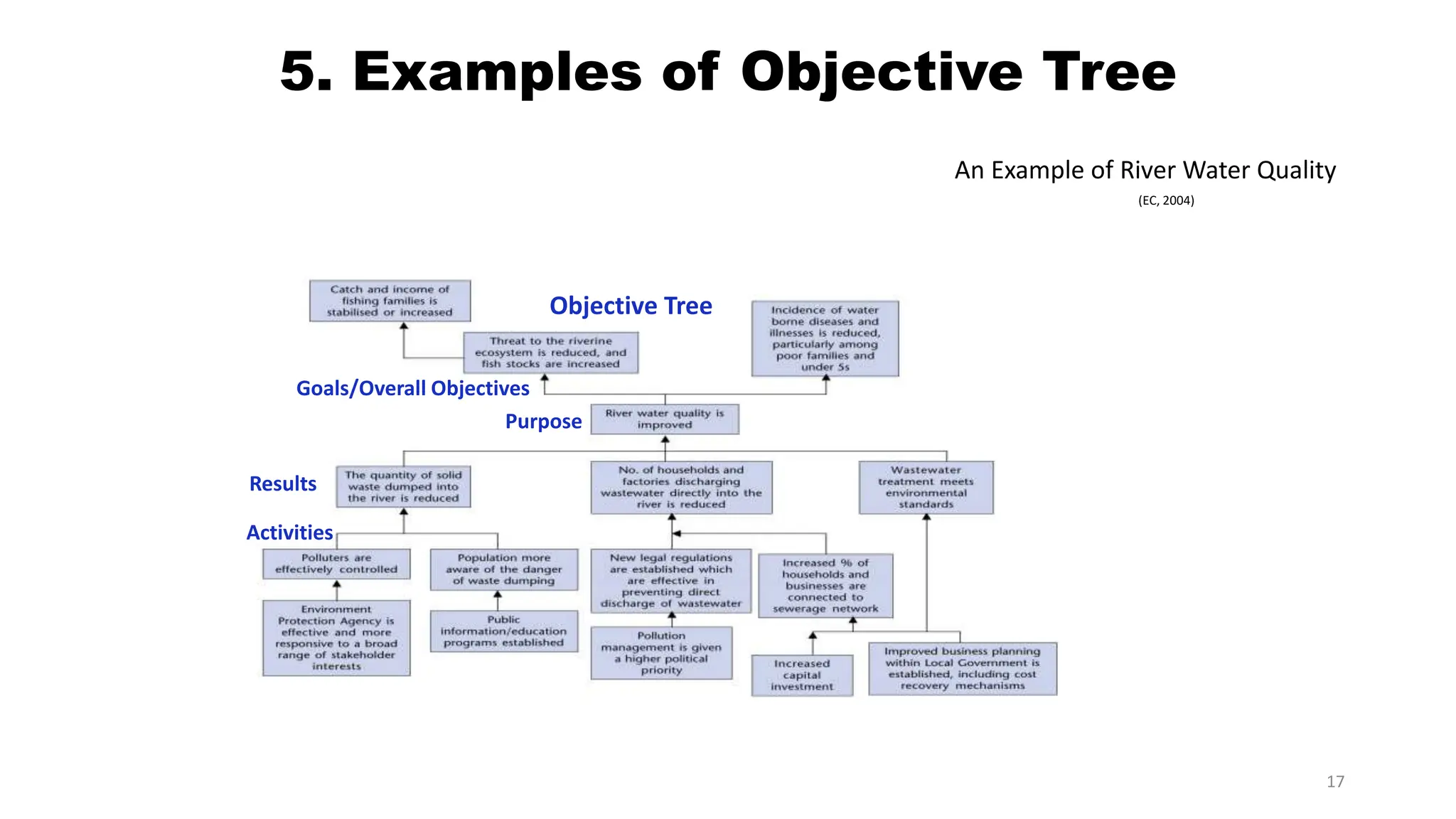
This document discusses objective tree analysis, which involves transforming a problem tree into a set of objectives by rewriting negative problem statements as positive future goals. An objective tree shows the hierarchy of objectives and means-end relationships through a diagram. The steps for formulating an objective tree are: 1) rewrite problems positively, 2) check validity of relationships, 3) revise if needed. Two examples of objective trees are provided - one for bus accidents and one for river water quality. The objective tree provides an overview of the desired future situation and how objectives can be achieved.