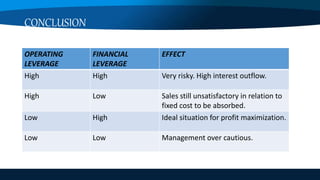
This document discusses the different types of leverage used in financial management. It defines leverage as a firm's ability to use fixed assets or funds to increase returns for owners. The three main types of leverage discussed are operating leverage, financial leverage, and combined leverage. Operating leverage refers to using fixed costs to earn more revenue. Financial leverage means using debt funds that have fixed interest charges. Combined leverage is the multiplier effect of using both operating and financial leverage, where a small sales change can greatly impact earnings per share. An example is provided to illustrate the calculations of degree of operating leverage, financial leverage, and combined leverage.