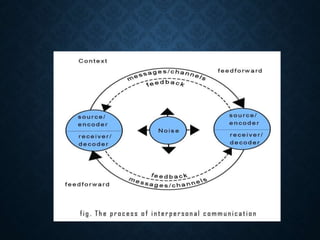
The document outlines the various levels of human communication, which include intrapersonal, interpersonal, group, public, mass, extrapersonal, and organizational communication. Each level is defined with examples and characteristics, highlighting how messages are conveyed and received in different contexts. Additionally, the document discusses the importance and challenges of group dynamics and organizational communication methods.