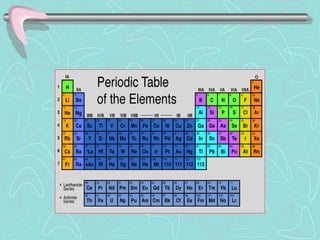
The document summarizes the key aspects and importance of the periodic table. It describes how the periodic table organizes the elements and provides order that was lacking prior to its creation. It explains that Dmitri Mendeleev created one of the first successful long form periodic tables by arranging elements by atomic mass, with similar reactive elements in the same columns. The periodic table is now organized by atomic number. Elements in the same group have similar properties because they have the same number of valence electrons. The document reviews the various families of elements and provides examples to illustrate their properties and importance.