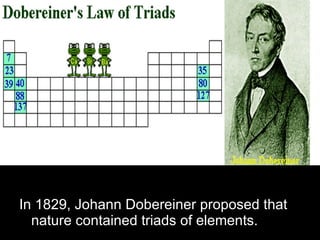
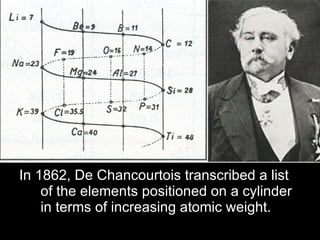
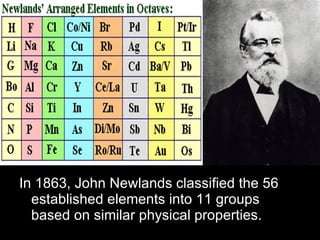
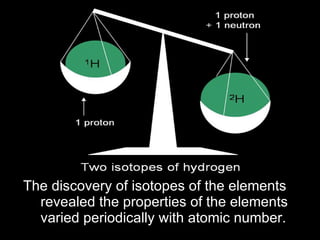
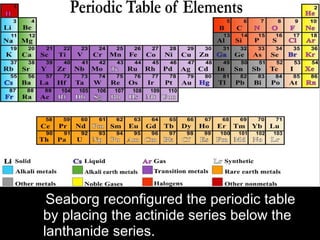
The development of the periodic table occurred over many decades as scientists discovered elements and recognized patterns in their properties. Early proposals included Dobereiner's law of triads in 1829 and Newlands' law of octaves in 1863. However, Dmitri Mendeleev is considered the father of the periodic table for his 1869 table that predicted undiscovered elements. Later, noble gases like argon were discovered and placed on the table. The modern periodic table was influenced by discoveries of atomic structure and isotopes that explained the periodic recurrence of properties.