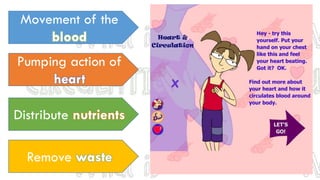
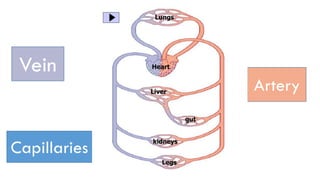
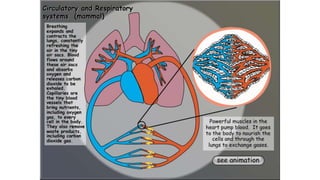
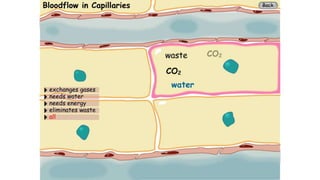
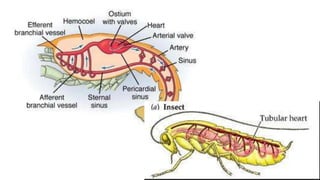
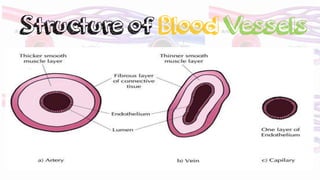
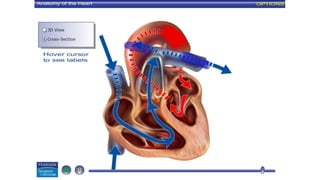
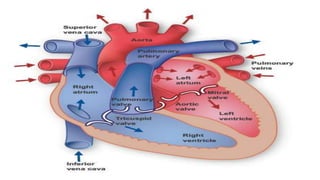
The circulatory system transports blood throughout the body to deliver oxygen and nutrients to cells and remove waste. It includes the heart, which pumps blood through vessels. There are three main types of blood vessels - arteries, which carry blood away from the heart; veins, which carry blood back to the heart; and capillaries, which connect arteries and veins and allow exchange of materials with body cells. The circulatory system moves blood in a double circulation from the heart to the lungs and back, and from the heart to all body tissues before returning to the heart.
![K W H L
What do I
know?
What do I
want to find
out?
How can I
find out
what I want
to learn?
What did I
learn?
[at the end of
the lesson]
Skills I
expect to use](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1structureandfunction-circulatorysystem-140718072518-phpapp01/85/Lesson-1-Circulatory-System-Grade-9-2-320.jpg)








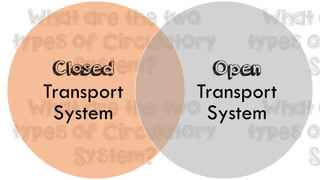

![WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE?
Closed
- Vertebrates and few
invertebrates
- Have heart and blood vessels
- Does not fill body cavities
- Blood kept in blood vessels
- Heart pumps blood
Open
- Invertebrates
- Do not have true heart or
capillaries
- Blood is pumped in hemocoel
[cavity]
- Blood + interstitial fluid =
hemolymph](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1structureandfunction-circulatorysystem-140718072518-phpapp01/85/Lesson-1-Circulatory-System-Grade-9-21-320.jpg)
![[1] [2] [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1structureandfunction-circulatorysystem-140718072518-phpapp01/85/Lesson-1-Circulatory-System-Grade-9-24-320.jpg)



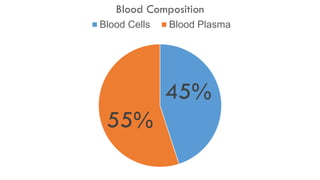
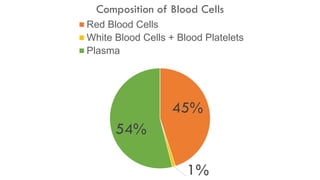

![RED BLOOD CELLS [ERYTHROCYTES]
[biconcave] [no nucleus]
[unable to repair]
[120 days body]
[10 days blood]
[Hemoglobin red] [carry O2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1structureandfunction-circulatorysystem-140718072518-phpapp01/85/Lesson-1-Circulatory-System-Grade-9-36-320.jpg)
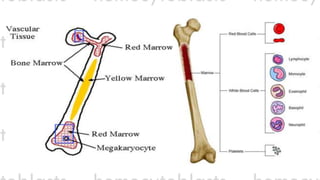

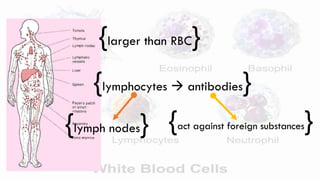
![WHITE BLOOD CELLS [LEUKOCYTES]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson1structureandfunction-circulatorysystem-140718072518-phpapp01/85/Lesson-1-Circulatory-System-Grade-9-39-320.jpg)