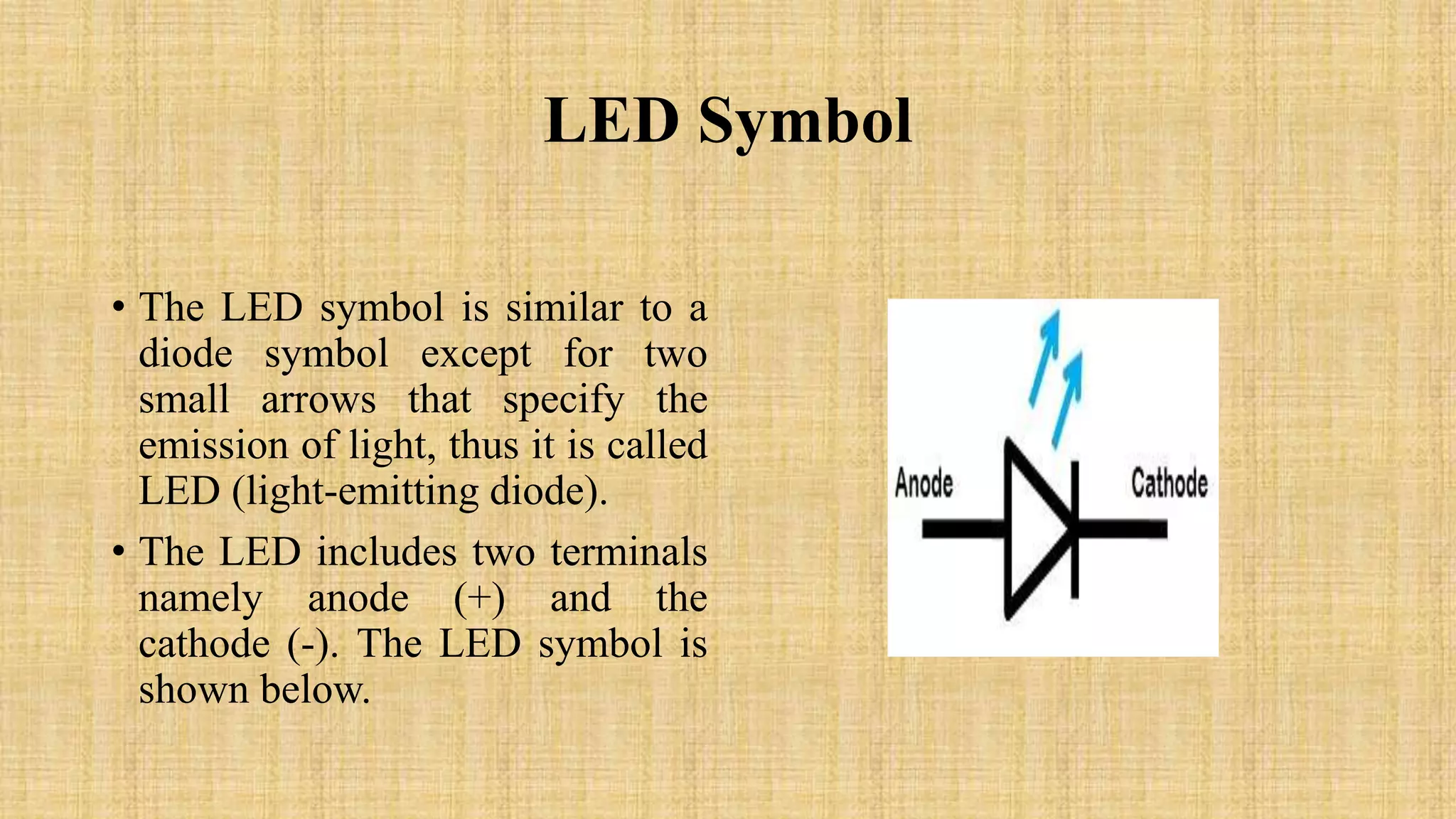
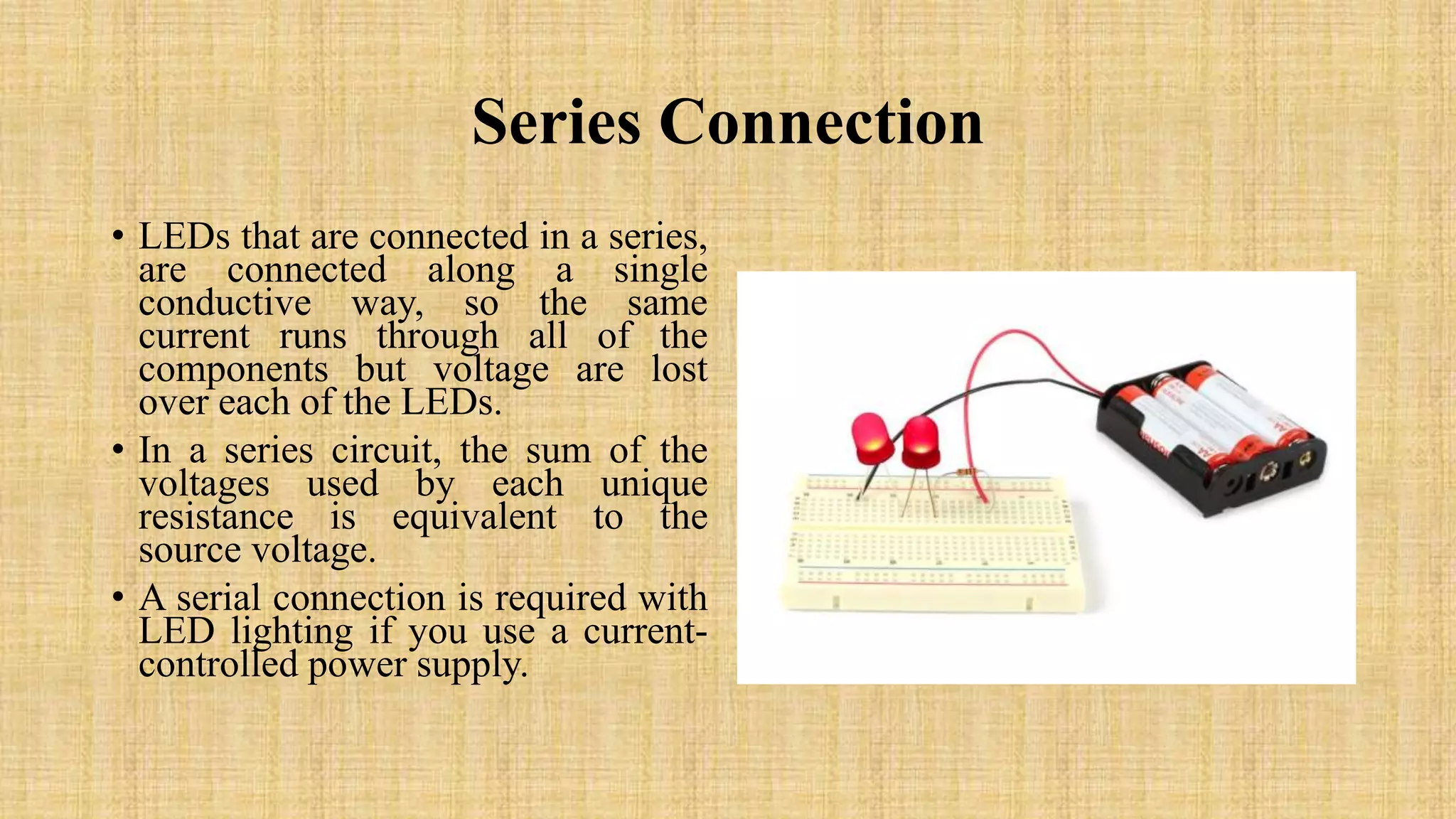
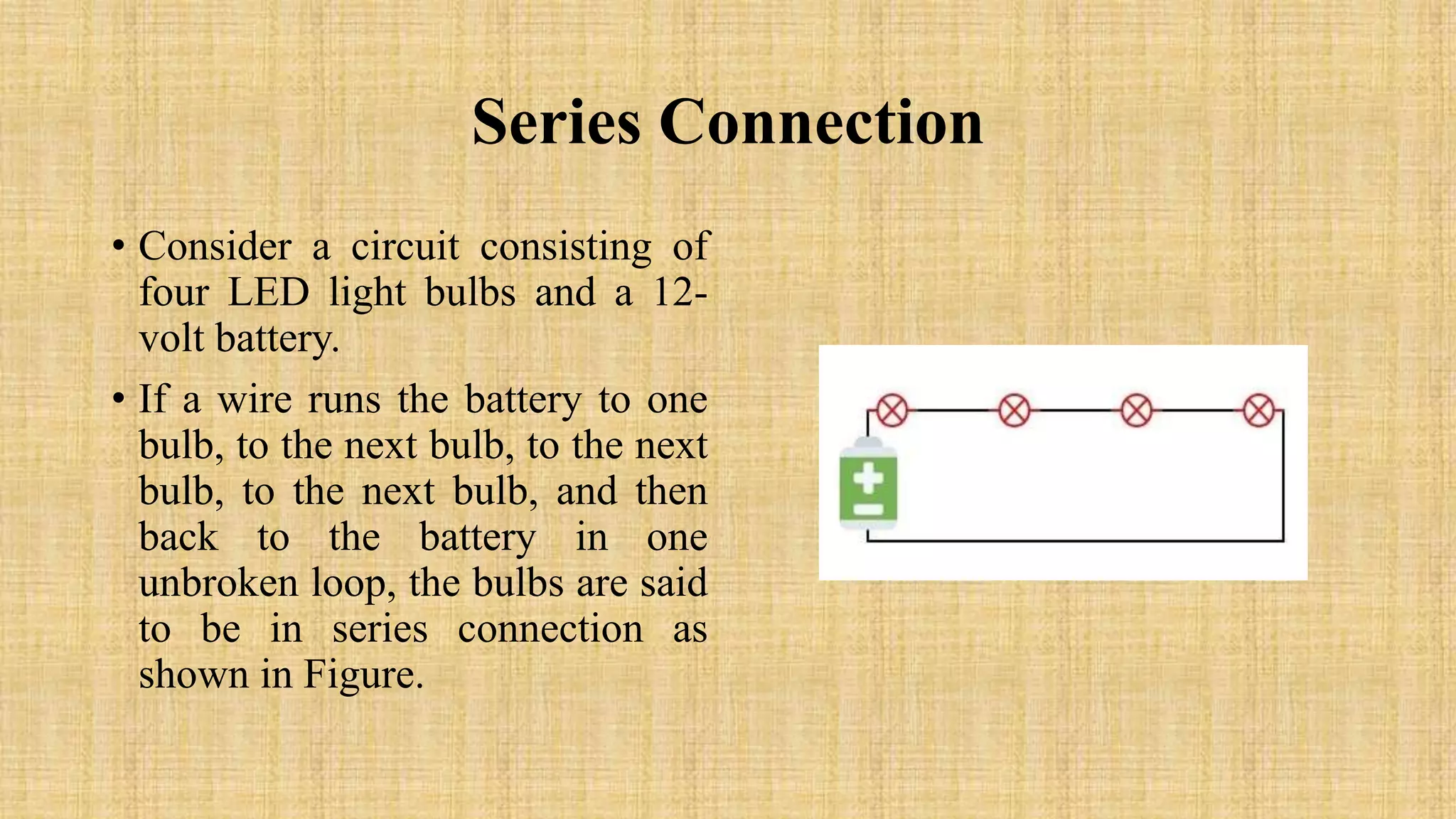
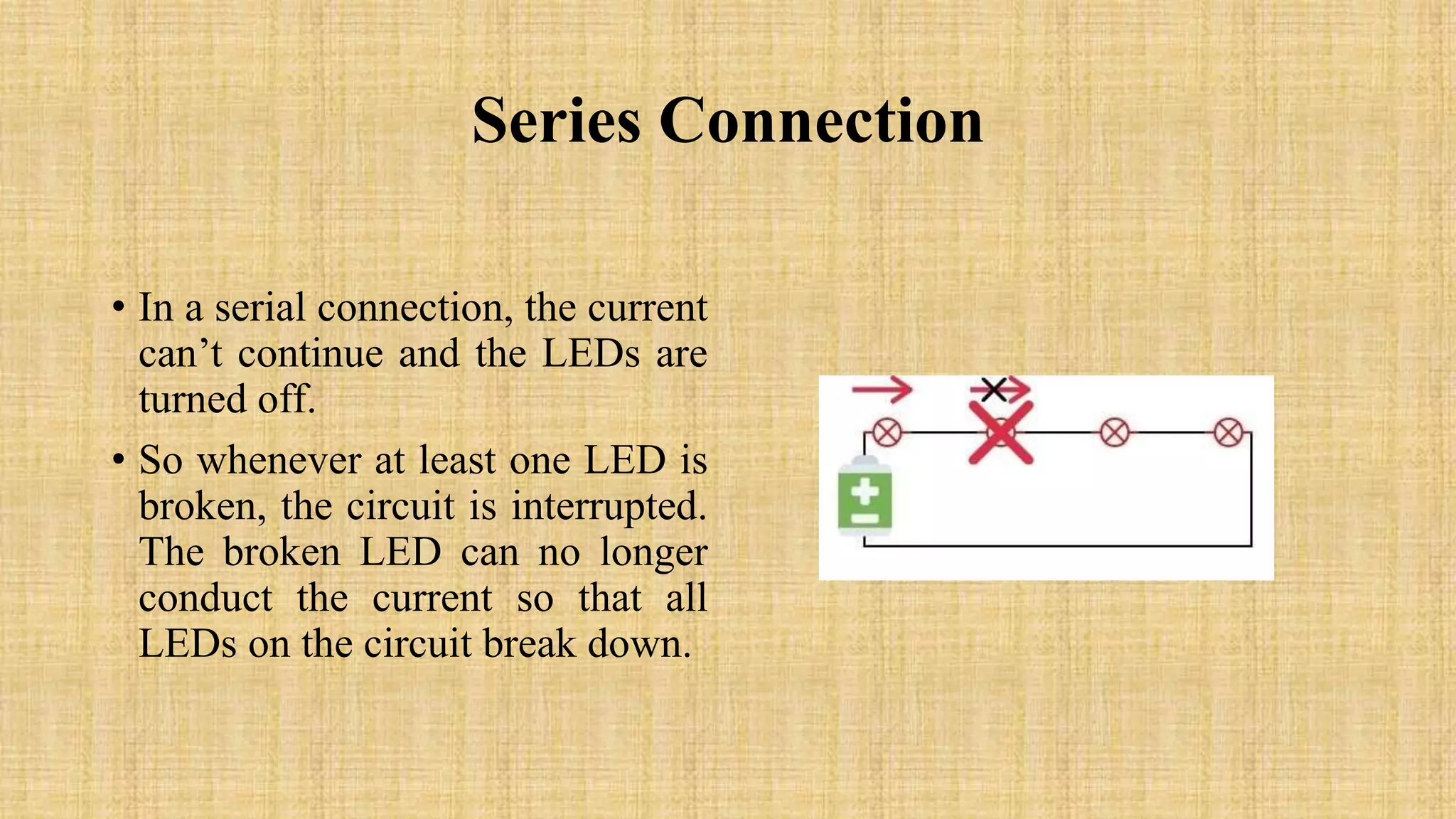
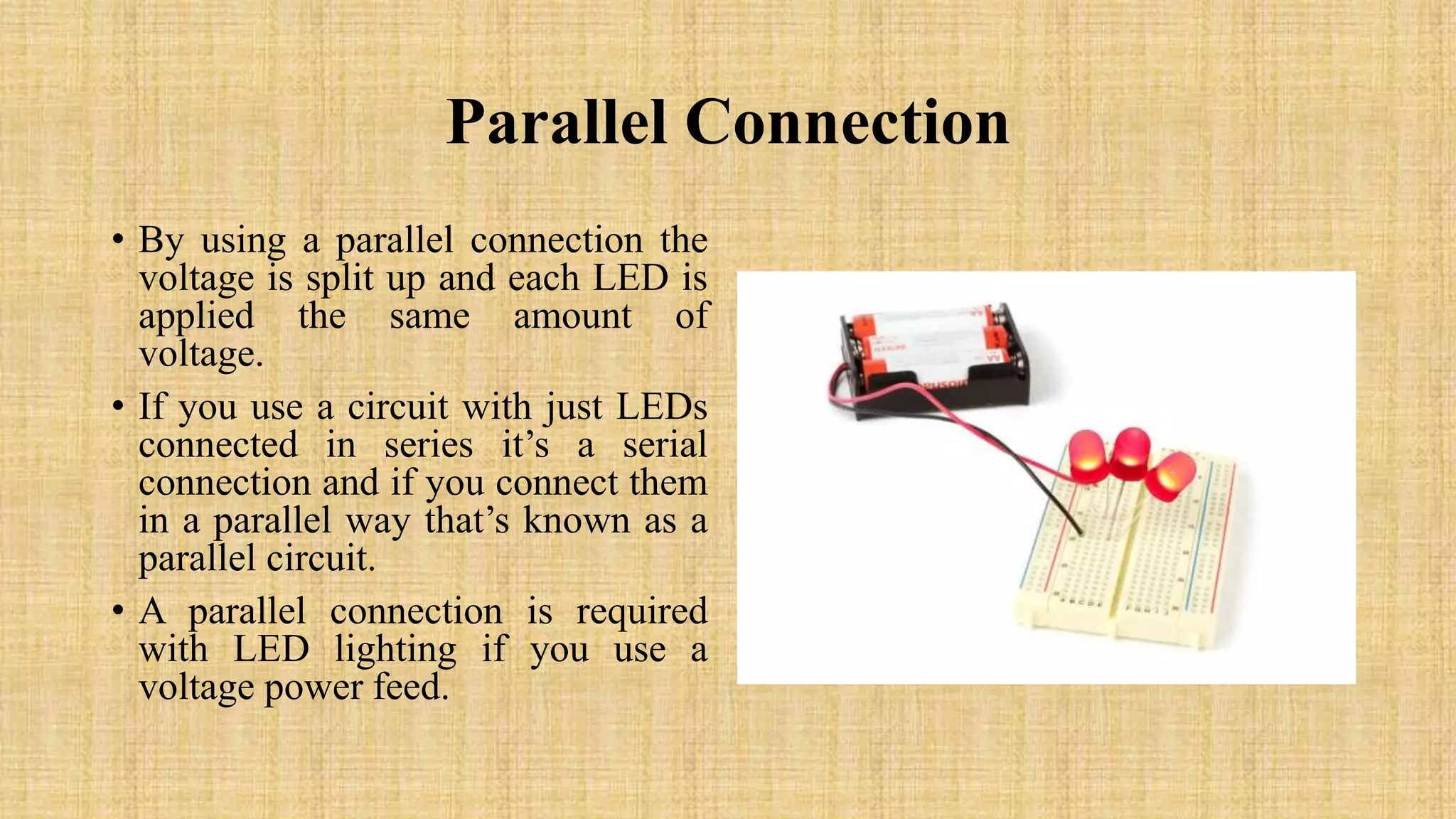
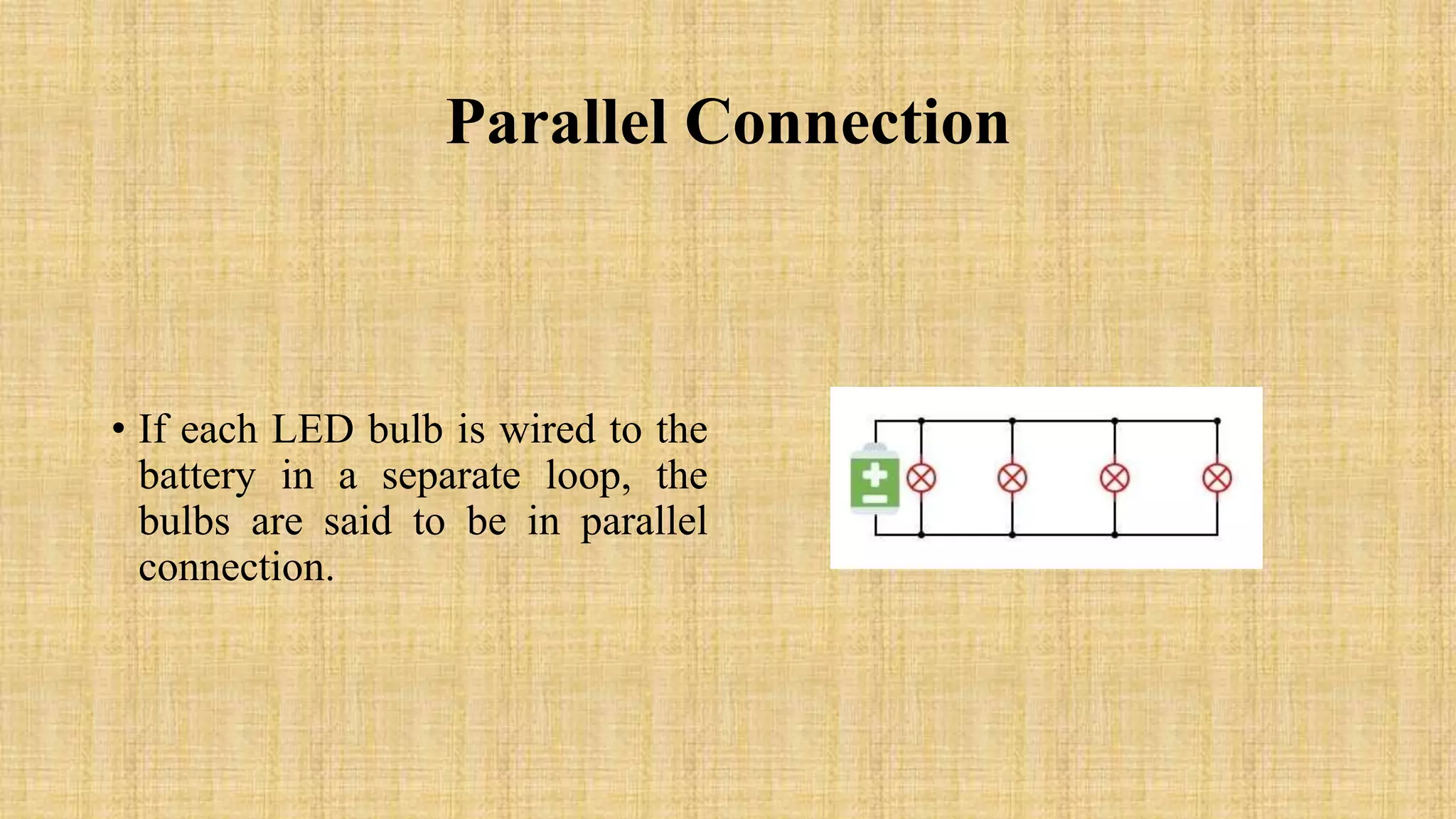
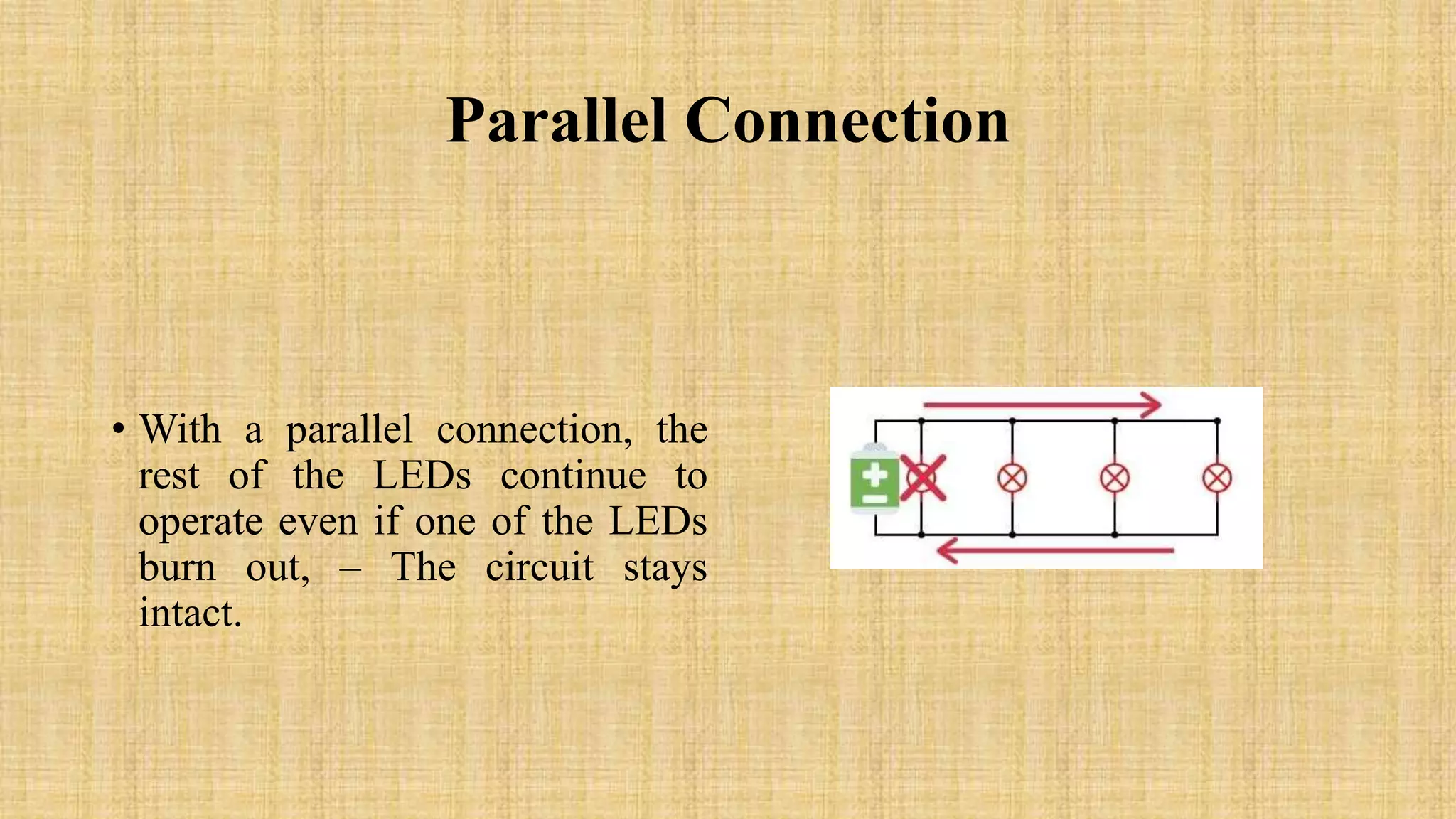
This document discusses LEDs and how they can be connected in series or parallel circuits. It provides information on LED components, symbols, and how they work. When connected in series, all LEDs experience the same current but voltages are lost across each one. A parallel connection splits the voltage so each LED receives the same voltage. The key advantages are that a series circuit remains intact if one LED fails, while a parallel circuit can have individual LEDs burn out without affecting the others. Applications of LEDs include lighting, electronics displays, and traffic signals.