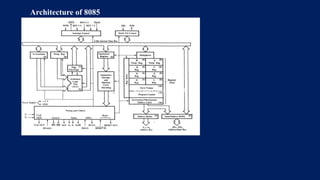
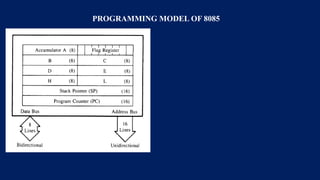
The document details the architecture of the 8085 microprocessor, highlighting essential components such as the ALU, timing and control unit, general purpose and special registers, and more. It explains the functions of key registers, including the accumulator, program counter, and stack pointer, as well as the role of the ALU in performing arithmetic and logical operations. Additionally, the document describes how the timing and control unit coordinates operations within the CPU.