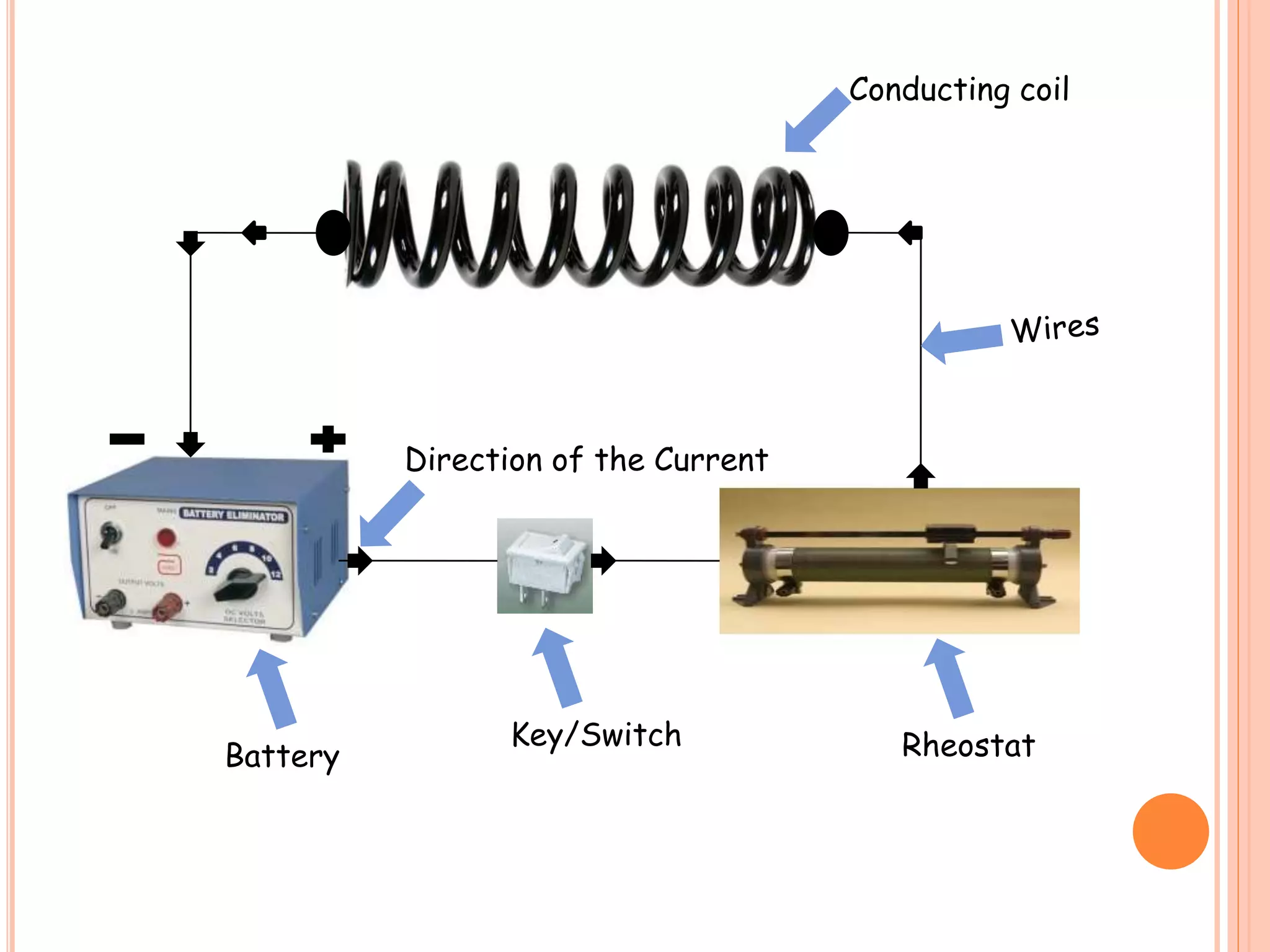
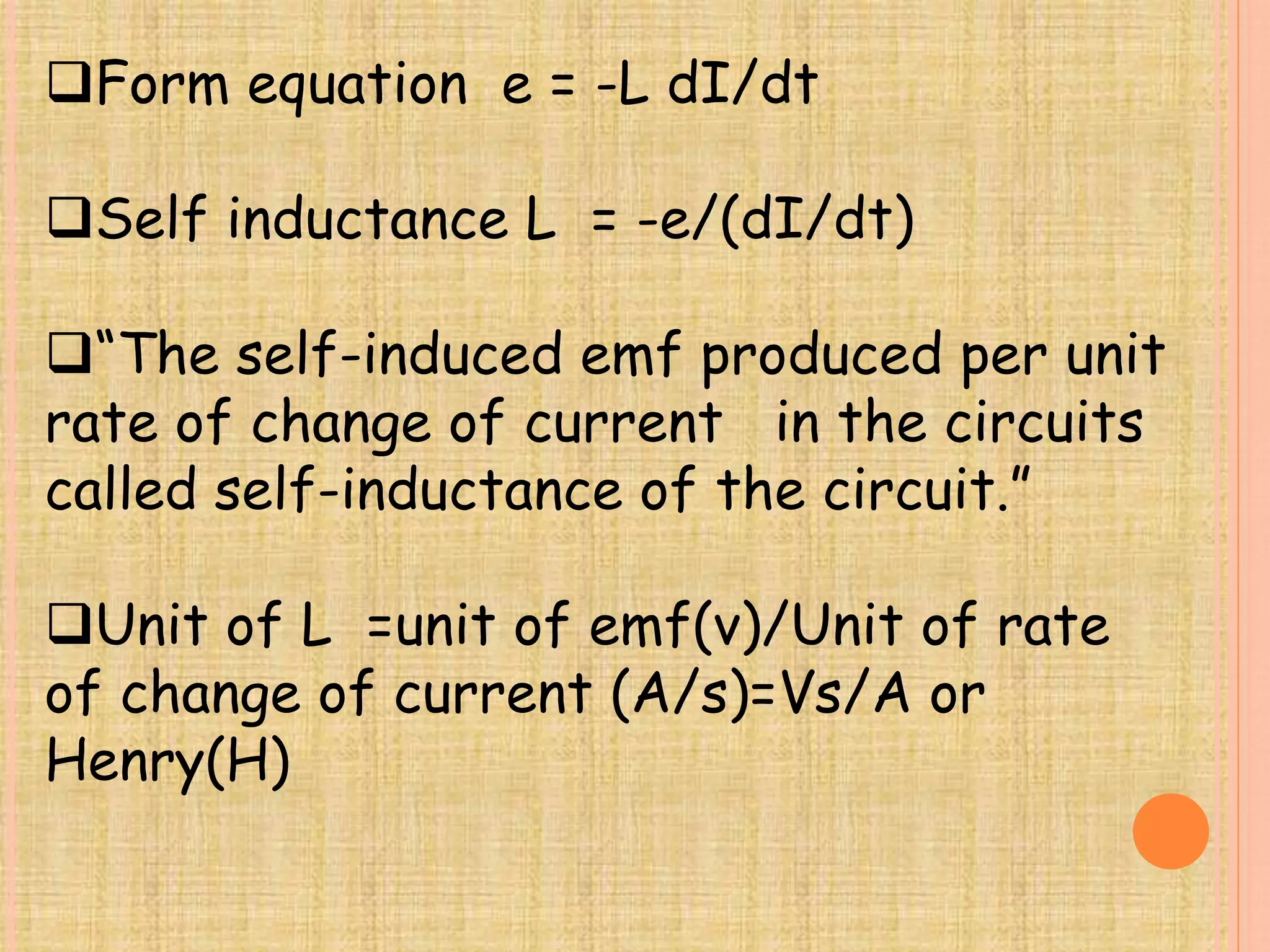
When a current passes through an insulated coil, it produces a magnetic field and links flux within the coil. This causes self-induction, where changing the current induces an electromotive force (emf) back in the coil. The self-inductance (L) of a coil depends on its shape, number of turns, and the material inside. It represents the flux linked per unit of current and does not depend on the current itself. Lenz's law applies, so the induced self emf opposes the change that created it.