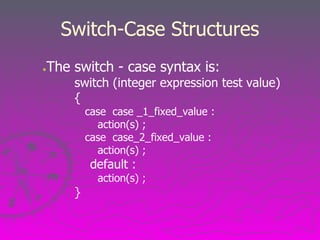
This document discusses switch-case statements in C programming. It explains that switch-case statements provide a way to implement decision making when a variable is tested for multiple possible integral values. Each case represents a different action. The document provides the syntax of switch-case statements and explains that all code within a matched case will execute until a break statement. It includes an example program that uses a switch-case statement to output a message based on a letter grade input.