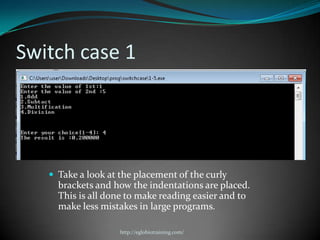
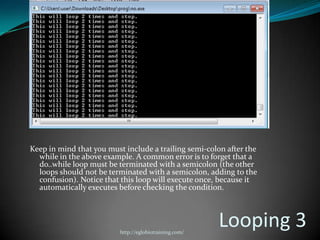
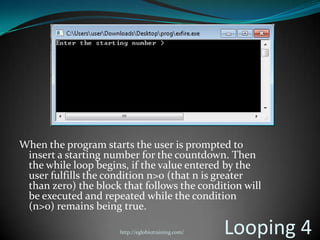
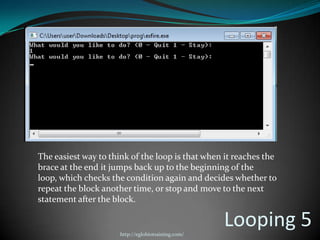
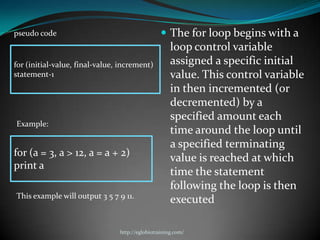
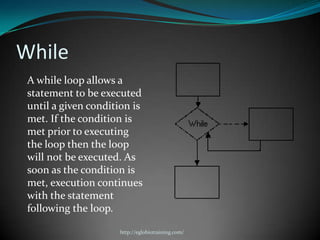
A computer program is a sequence of instructions that tells a computer to perform tasks. Programs are written by programmers in human-readable source code and then compiled into an executable form for the computer to run directly. Common programming languages include C++, Java, and Python. Switch-case statements allow programmers to write code that performs different actions depending on the value of a variable.






























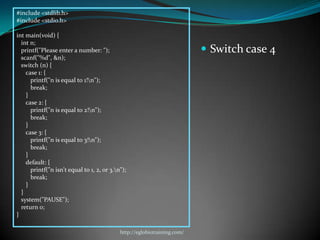
![#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
main()
{
int choice;
float x,y;
Switch case 1
printf("Enter the value of 1st:");
scanf("%f",&x);
printf("Enter the value of 2nd :");
scanf("%f",&y);
printf("1.Addn");
printf("2.Subtactn");
printf("3.Multificationn");
printf("4.Divisionn");
printf("nnnEnter your choice[1-4]: ");
scanf("%d",&choice);
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
printf("THE result is :%f",x+y);
break;
case 2:
printf("The result is :%f",x-y);
break;
case 3:
printf("The result is :%f",x*y);
break;
case 4:
printf("The result is :%f",x/y);
break;
default:
printf("unknown");
}
fflush(stdin);
getchar();
}
http://eglobiotraining.com/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/switchcaseandlooping-121012074703-phpapp01/85/Switch-case-and-looping-34-320.jpg)


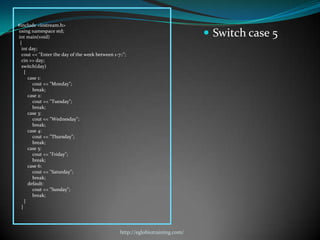


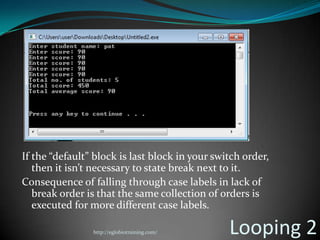
![#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x, score, tnum_stud, t_score, ave_score;
char student_name[20];
tnum_stud = 0, t_score = 0, ave_score = 0;
cout<< "Enter student name: ";
Looping 2
cin>>student_name;
cout<< "Enter score: ";
cin>> score;
t_score = t_score + score;
for (x = 1; x <= 4; x++)
{
cout<< "Enter score: ";
cin>> score;
t_score = t_score + score;
}
tnum_stud = x++;
ave_score = t_score/tnum_stud;
cout<< "Total no. of students: "
<<tnum_stud<<endl;
cout<< "Total score: " <<t_score<<endl;
cout<< "Total average score: "
<<ave_score<<endl;
tnum_stud = 0, t_score = 0, ave_score = 0;
cout<< "nnn";
system ("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
http://eglobiotraining.com/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/switchcaseandlooping-121012074703-phpapp01/85/Switch-case-and-looping-41-320.jpg)