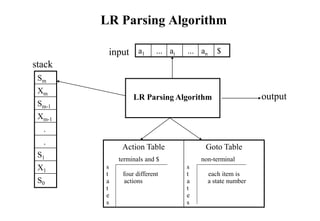
LR parsing is a powerful shift-reduce parsing technique that is both efficient and handles a wide range of grammars. LR parsers work by maintaining a stack and scanning input from left to right. They determine the next action to take by consulting parsing tables generated from the grammar. LR parsing avoids backtracking and can detect syntactic errors as early as possible. The most general form of LR parsing is LR(k) which uses k tokens of lookahead, while practical parsers often use LR(1) or variants like LALR(1) which have smaller and more efficiently constructed tables.




![Actions of A LR-Parser
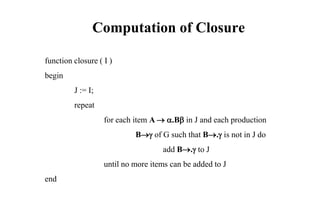
1. shift s -- shifts the next input symbol and the state s onto the stack
( So X1 S1 ... Xm Sm, ai ai+1 ... an $ ) ( So X1 S1 ... Xm Sm ai s, ai+1 ... an $ )
2. reduce A (or rn where n is a production number)
– pop 2|| (=r) items from the stack;
– then push A and s where s=goto[sm-r,A]
( So X1 S1 ... Xm Sm, ai ai+1 ... an $ ) ( So X1 S1 ... Xm-r Sm-r A s, ai ... an $ )
– Output is the reducing production reduce A
3. Accept – Parsing successfully completed
4. Error -- Parser detected an error (an empty entry in the action table)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lr-parsing-230804113549-cde6cabf/85/LR-Parsing-ppt-6-320.jpg)
![Reduce Action
• pop 2|| (=r) items from the stack; let us assume that = Y1Y2...Yr
• then push A and s where s=goto[sm-r,A]
( So X1 S1 ... Xm-r Sm-r Y1 Sm-r+1 ...Yr Sm, ai ai+1 ... an $ )
( So X1 S1 ... Xm-r Sm-r A s, ai ... an $ )
• In fact, Y1Y2...Yr is a handle.
X1 ... Xm-r A ai ... an $ X1 ... Xm Y1...Yr ai ai+1 ... an $](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lr-parsing-230804113549-cde6cabf/85/LR-Parsing-ppt-7-320.jpg)
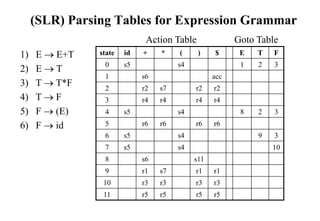
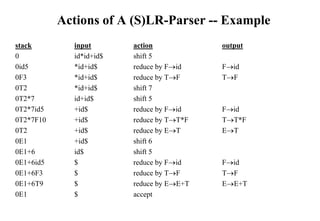





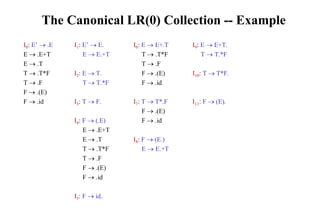
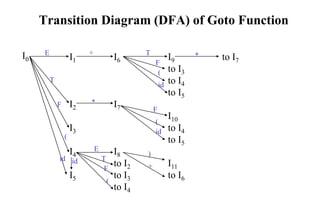
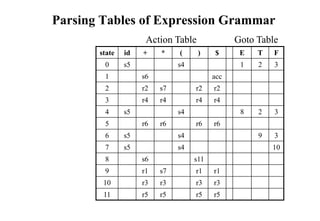
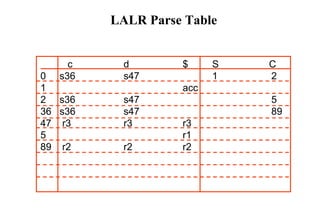
![Constructing SLR Parsing Table
(of an augumented grammar G’)
1. Construct the canonical collection of sets of LR(0) items for G’. C{I0,...,In}
2. Create the parsing action table as follows
• If a is a terminal, A.a in Ii and goto(Ii,a)=Ij then action[i,a] is shift j.
• If A. is in Ii , then action[i,a] is reduce A for all a in FOLLOW(A) where
AS’.
• If S’S. is in Ii , then action[i,$] is accept.
• If any conflicting actions generated by these rules, the grammar is not SLR(1).
3. Create the parsing goto table
• for all non-terminals A, if goto(Ii,A)=Ij then goto[i,A]=j
4. All entries not defined by (2) and (3) are errors.
5. Initial state of the parser contains S’.S](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lr-parsing-230804113549-cde6cabf/85/LR-Parsing-ppt-18-320.jpg)


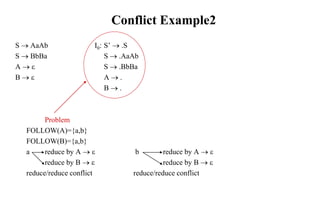
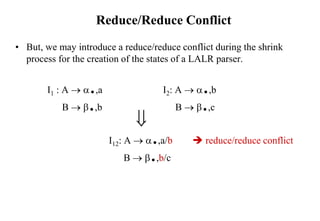
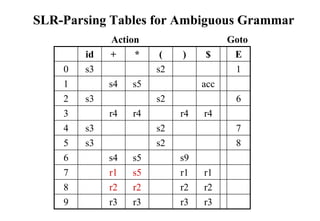
![Conflict Example
S L=R I0: S’ .S I1:S’ S. I6:S L=.R I9: S L=R.
S R S .L=R R .L
L *R S .R I2:S L.=R L .*R
L id L .*R R L. L .id
R L L .id
R .L I3:S R.
I4:L *.R I7:L *R.
Problem R .L
FOLLOW(R)={=,$} L .*R I8:R L.
= shift 6 L .id
reduce by R L
shift/reduce conflict I5:L id.
Action[2,=] = shift 6
Action[2,=] = reduce by R L
[ S L=R *R=R] so follow(R) contains, =](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lr-parsing-230804113549-cde6cabf/85/LR-Parsing-ppt-22-320.jpg)

![LR(1) Item
• To avoid some of invalid reductions, the states need to carry more information.
• Extra information is put into a state by including a terminal symbol as a second
component in an item.
• A LR(1) item is:
A .,a where a is the look-head of the LR(1) item
(a is a terminal or end-marker.)
• Such an object is called LR(1) item.
– 1 refers to the length of the second component
– The lookahead has no effect in an item of the form [A .,a], where is not .
– But an item of the form [A .,a] calls for a reduction by A only if the next input
symbol is a.
– The set of such a’s will be a subset of FOLLOW(A), but it could be a proper subset.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lr-parsing-230804113549-cde6cabf/85/LR-Parsing-ppt-25-320.jpg)





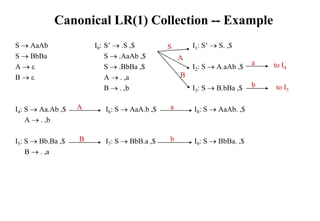
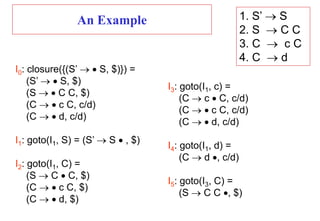
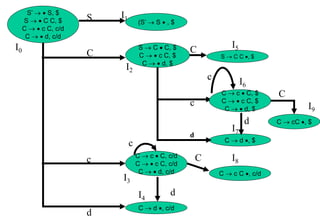
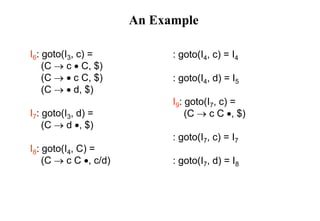
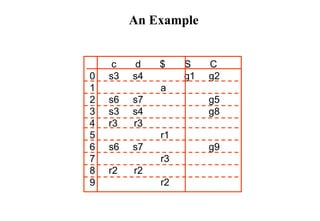

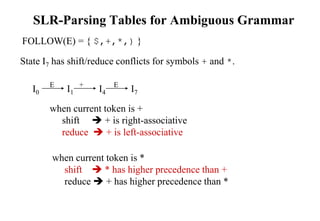
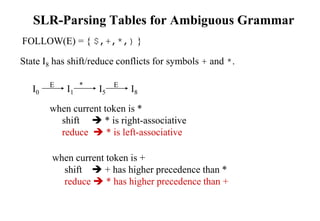
![Construction of LR(1) Parsing Tables
1. Construct the canonical collection of sets of LR(1) items for G’.
C{I0,...,In}
2. Create the parsing action table as follows
• If a is a terminal, A.a,b in Ii and goto(Ii,a)=Ij then action[i,a] is shift j.
• If A.,a is in Ii , then action[i,a] is reduce A where AS’.
• If S’S.,$ is in Ii , then action[i,$] is accept.
• If any conflicting actions generated by these rules, the grammar is not LR(1).
3. Create the parsing goto table
• for all non-terminals A, if goto(Ii,A)=Ij then goto[i,A]=j
4. All entries not defined by (2) and (3) are errors.
5. Initial state of the parser contains S’.S,$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lr-parsing-230804113549-cde6cabf/85/LR-Parsing-ppt-38-320.jpg)






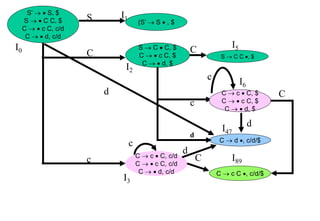
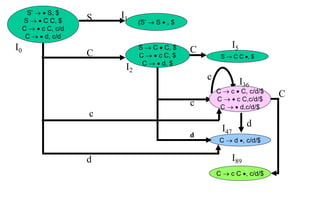






![Panic Mode Error Recovery in LR Parsing
• Scan down the stack until a state s with a goto on a particular
nonterminal A is found. (Get rid of everything from the stack before this
state s).
• Discard zero or more input symbols until a symbol a is found that can
legitimately follow A.
– The symbol a is simply in FOLLOW(A), but this may not work for all situations.
• The parser stacks the nonterminal A and the state goto[s,A], and it
resumes the normal parsing.
• This nonterminal A is normally is a basic programming block (there can
be more than one choice for A).
– stmt, expr, block, ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lr-parsing-230804113549-cde6cabf/85/LR-Parsing-ppt-58-320.jpg)

