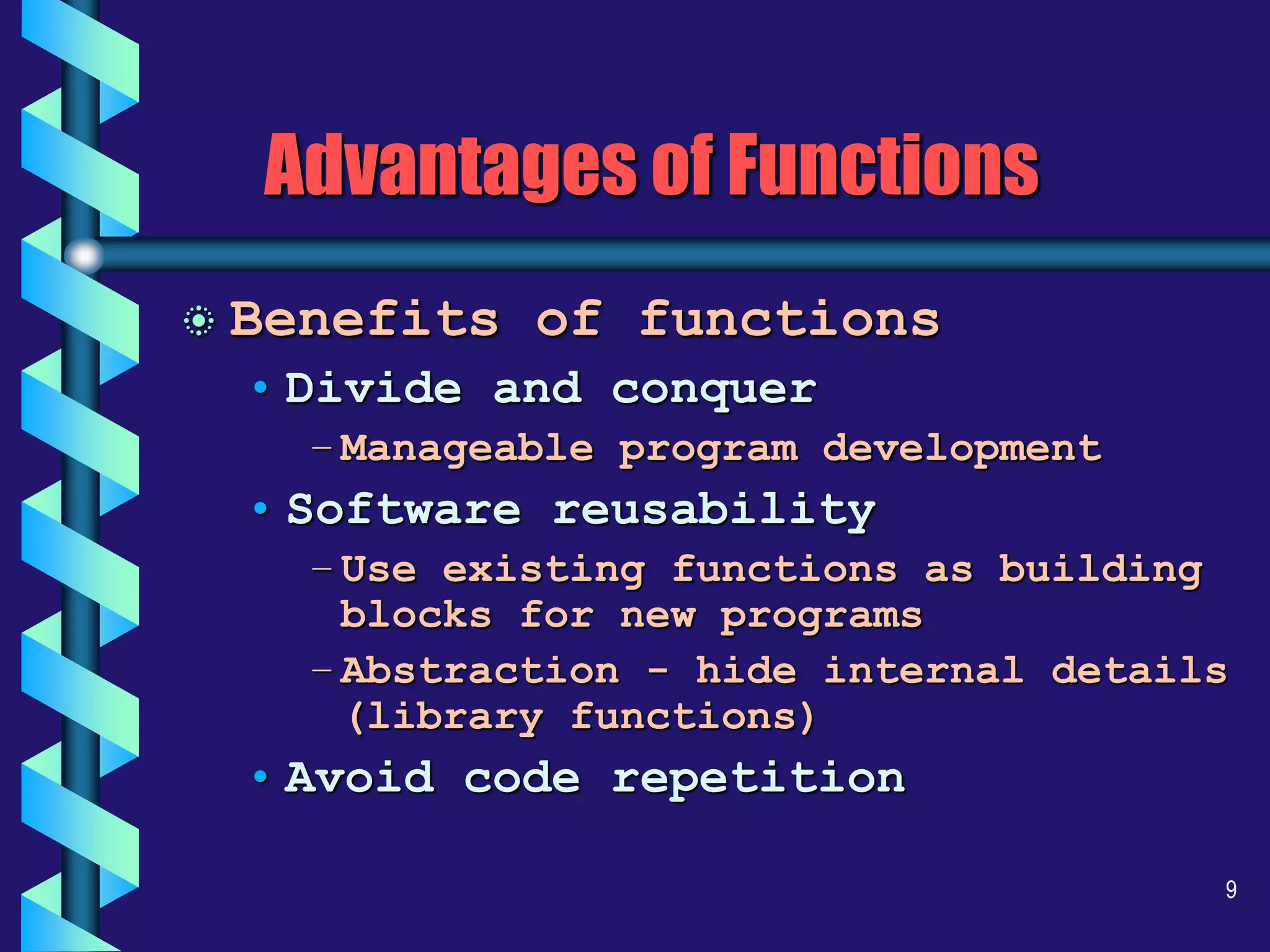
The document discusses functions in C programming. It defines what functions are and their advantages, such as modularity, reusability and avoiding code repetition. It covers different types of functions based on arguments and return values. Additionally, it discusses function definitions, prototypes, scope, storage classes, recursion, call by value vs reference and examples of functions.