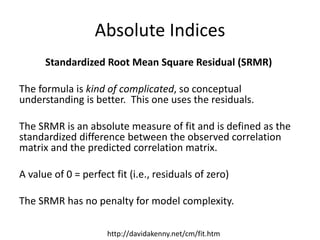
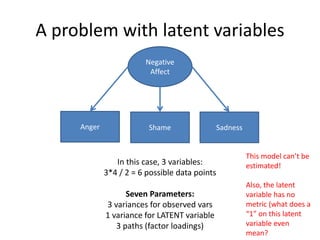
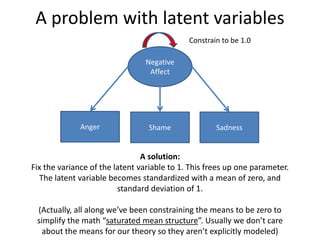
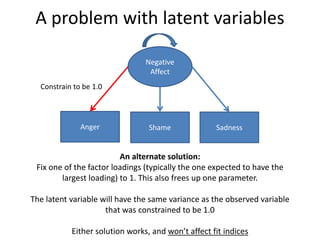
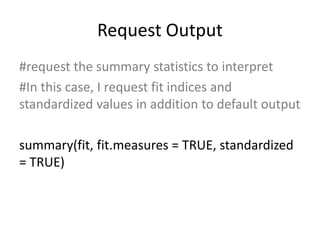
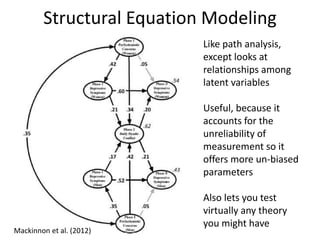
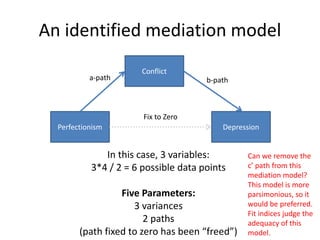
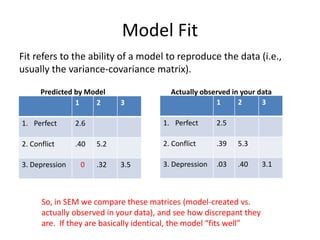
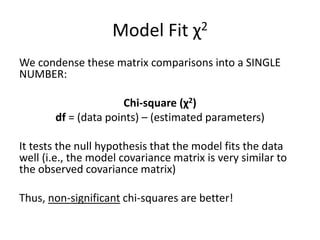
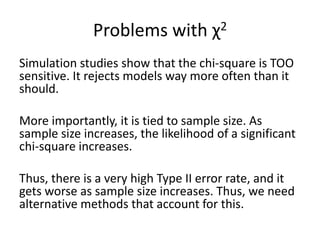
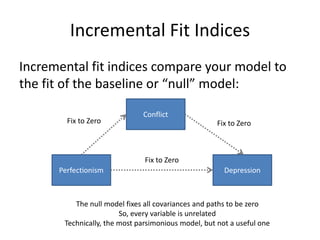
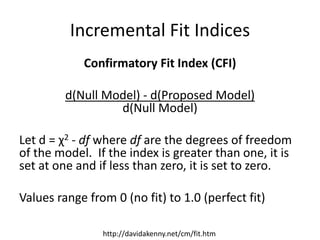
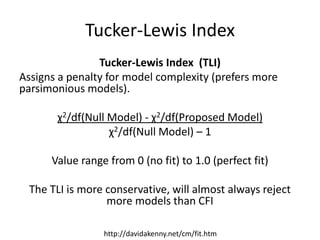
The document provides an overview of structural equation modeling (SEM), explaining its advantages over ordinary least squares regression, such as maximum likelihood estimation and the ability to analyze complex relationships among variables. It introduces key concepts like exogenous and endogenous variables, mediation, path analysis, and model fit indices, including chi-square, CFI, TLI, RMSEA, and SRMR. Additionally, it discusses issues related to latent variables and provides a practical example of conducting a confirmatory factor analysis using R.



![Parsimonious Indices
Root Mean Square Approximation of Error (RMSEA)
Similar to the others, except that it doesn’t actually
compare to the null model, and (like TLI) offers a
penalty for more complex models:
√(χ2 - df)
√[df(N - 1)]
Can also calculate a 90% CI for RMSEA
http://davidakenny.net/cm/fit.htm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introsem-150216093420-conversion-gate01/85/Basics-of-Structural-Equation-Modeling-26-320.jpg)