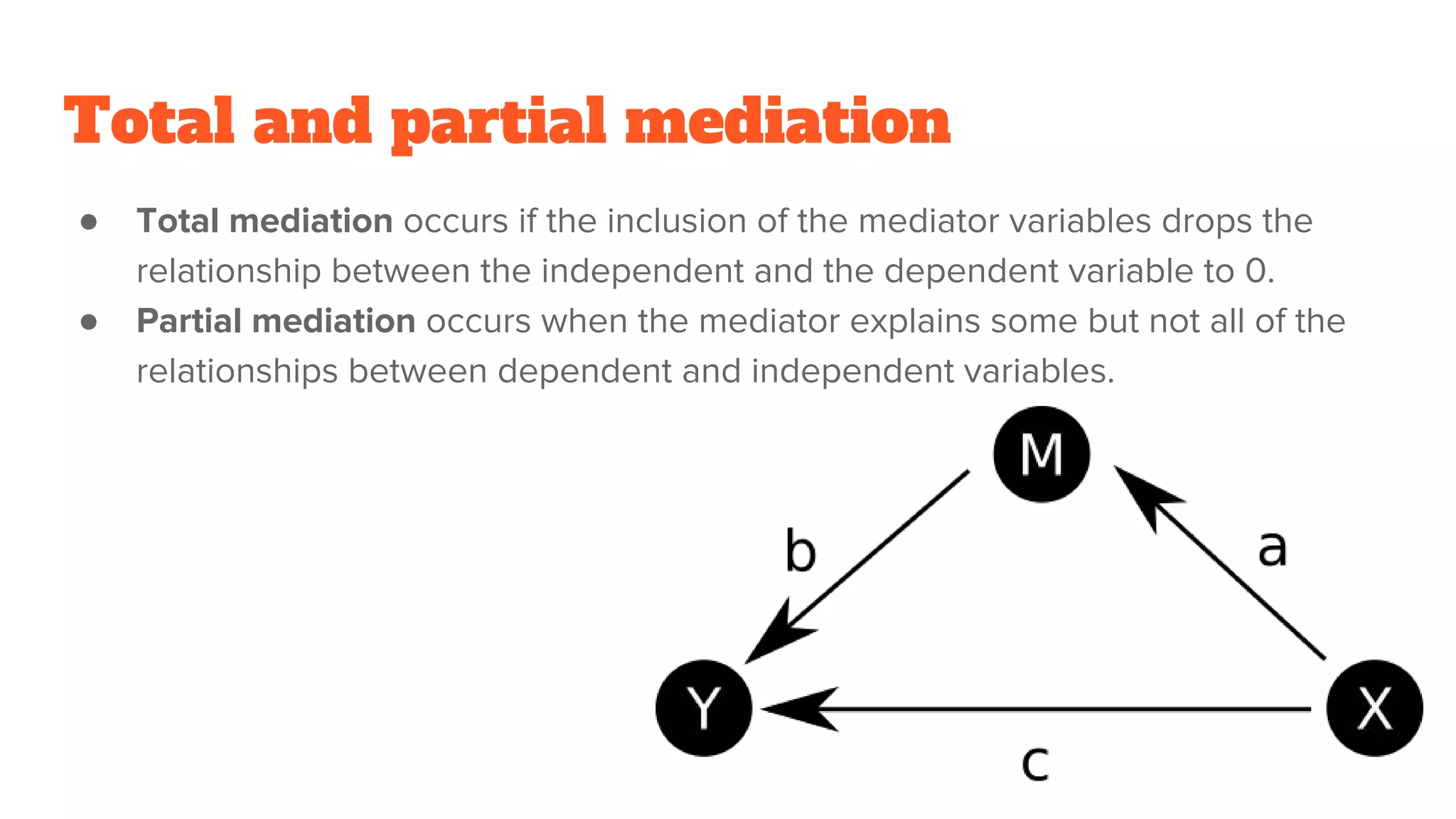
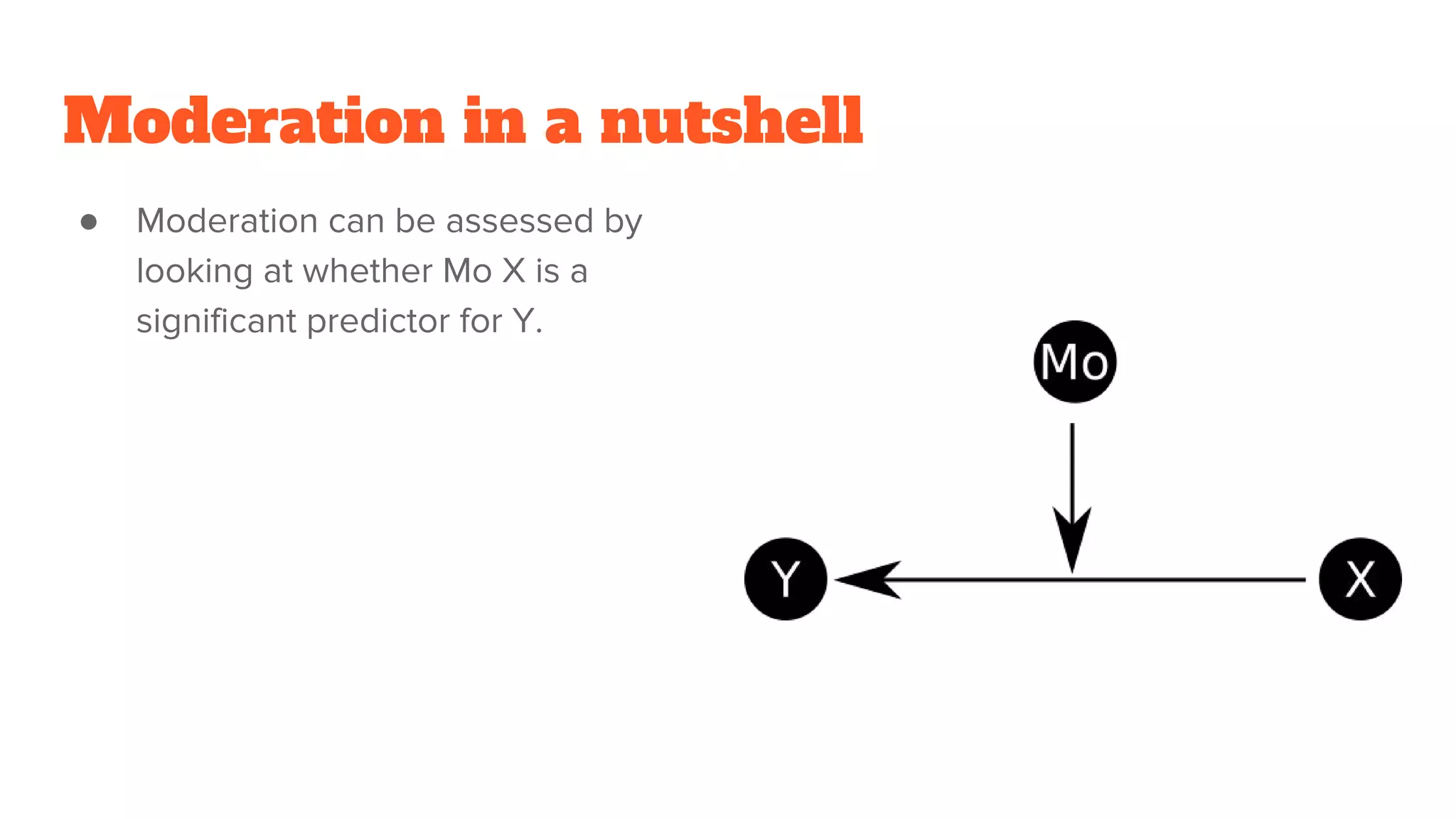
Mediation analysis is used to determine if a mediator variable explains the relationship between an independent and dependent variable. Baron and Kenny developed steps for mediation analysis including showing the independent variable predicts the dependent variable, predicts the mediator, and that the mediator predicts the dependent variable while reducing the effect of the independent variable. Total mediation occurs when the mediator fully explains the relationship, while partial mediation means the mediator only partially explains it. Limitations include needing strong theory to support mediators and being unable to manipulate mediators, while temporal precedence of variables and accounting for confounds can strengthen mediation analysis.