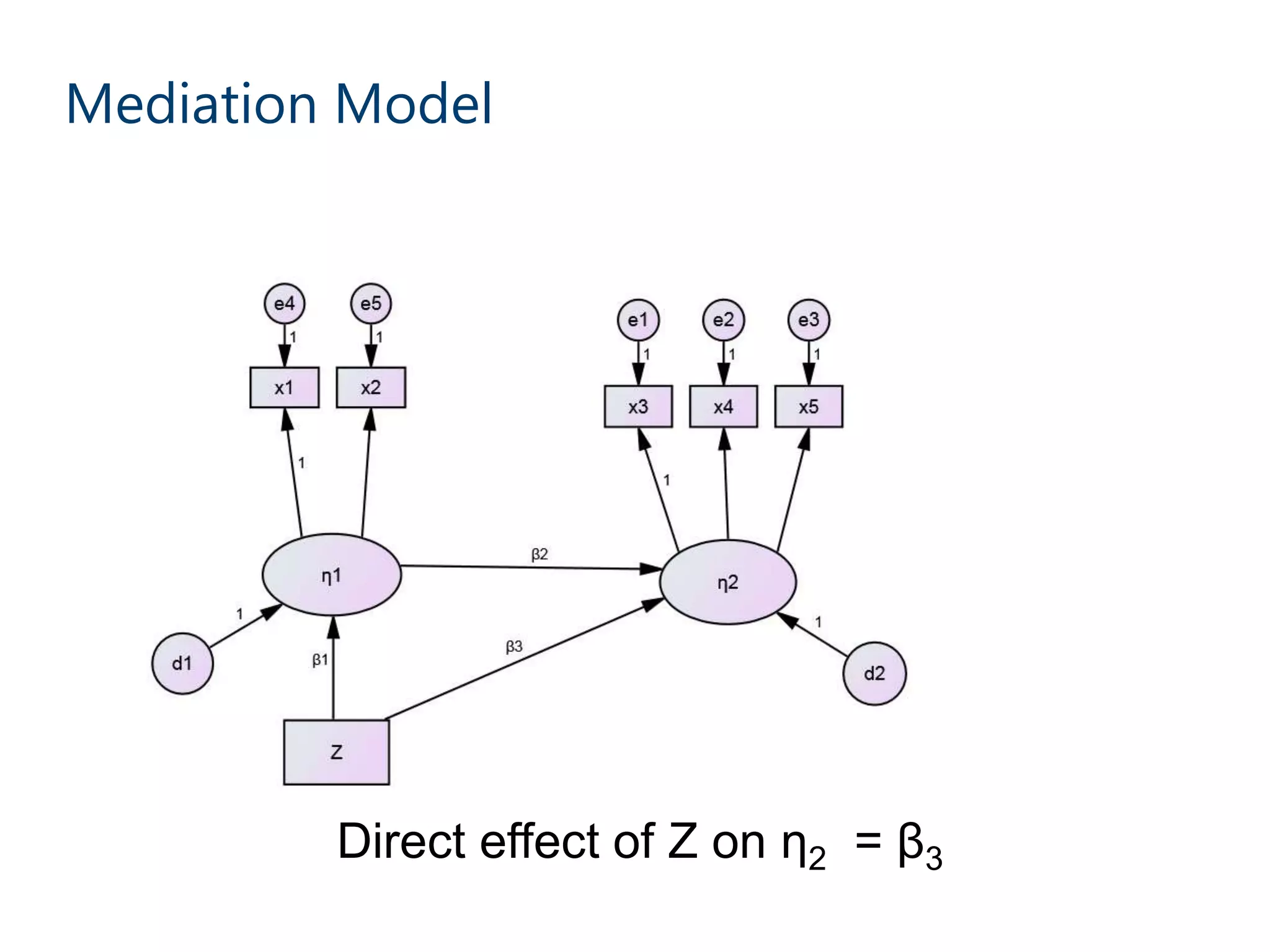
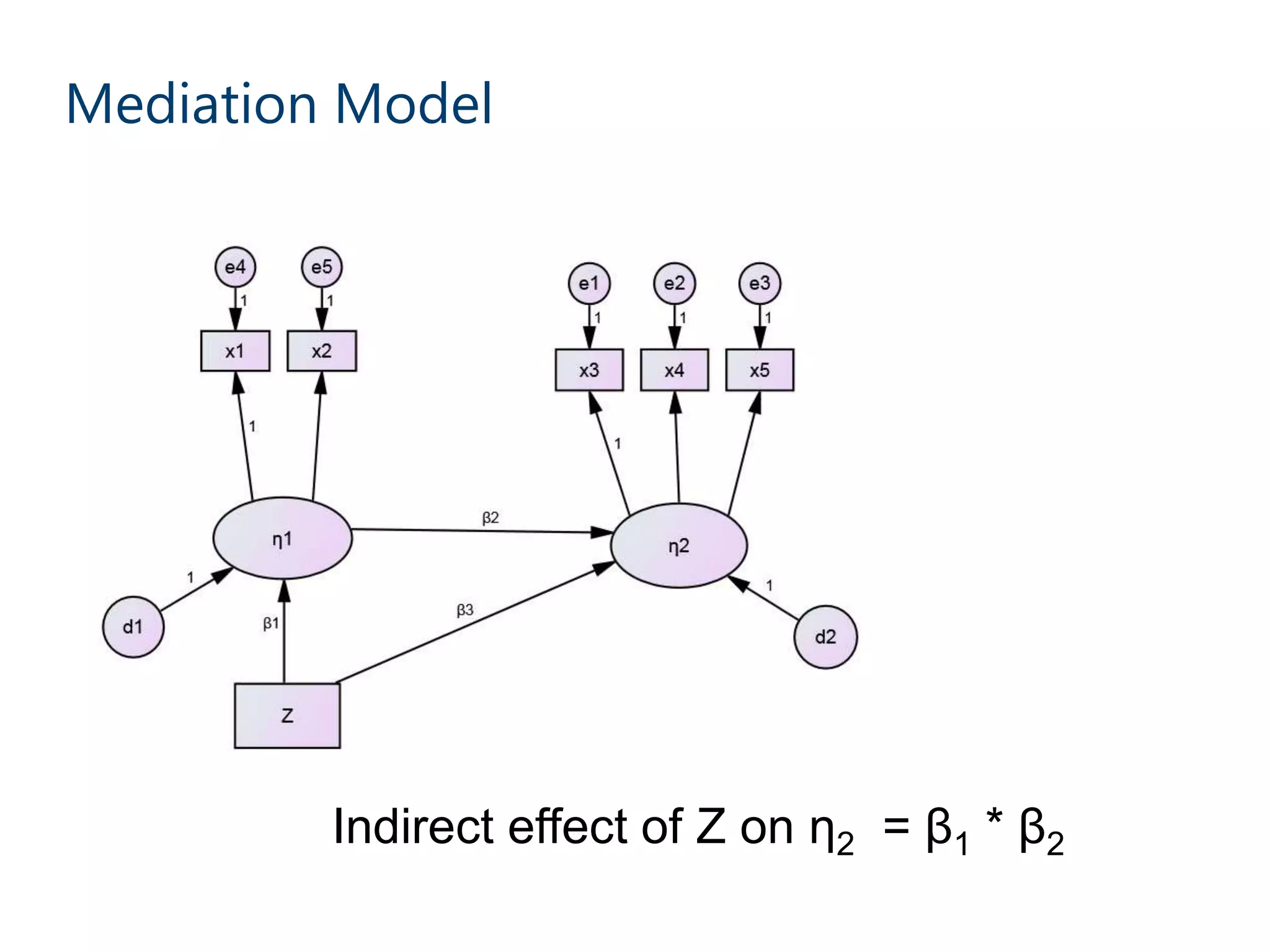
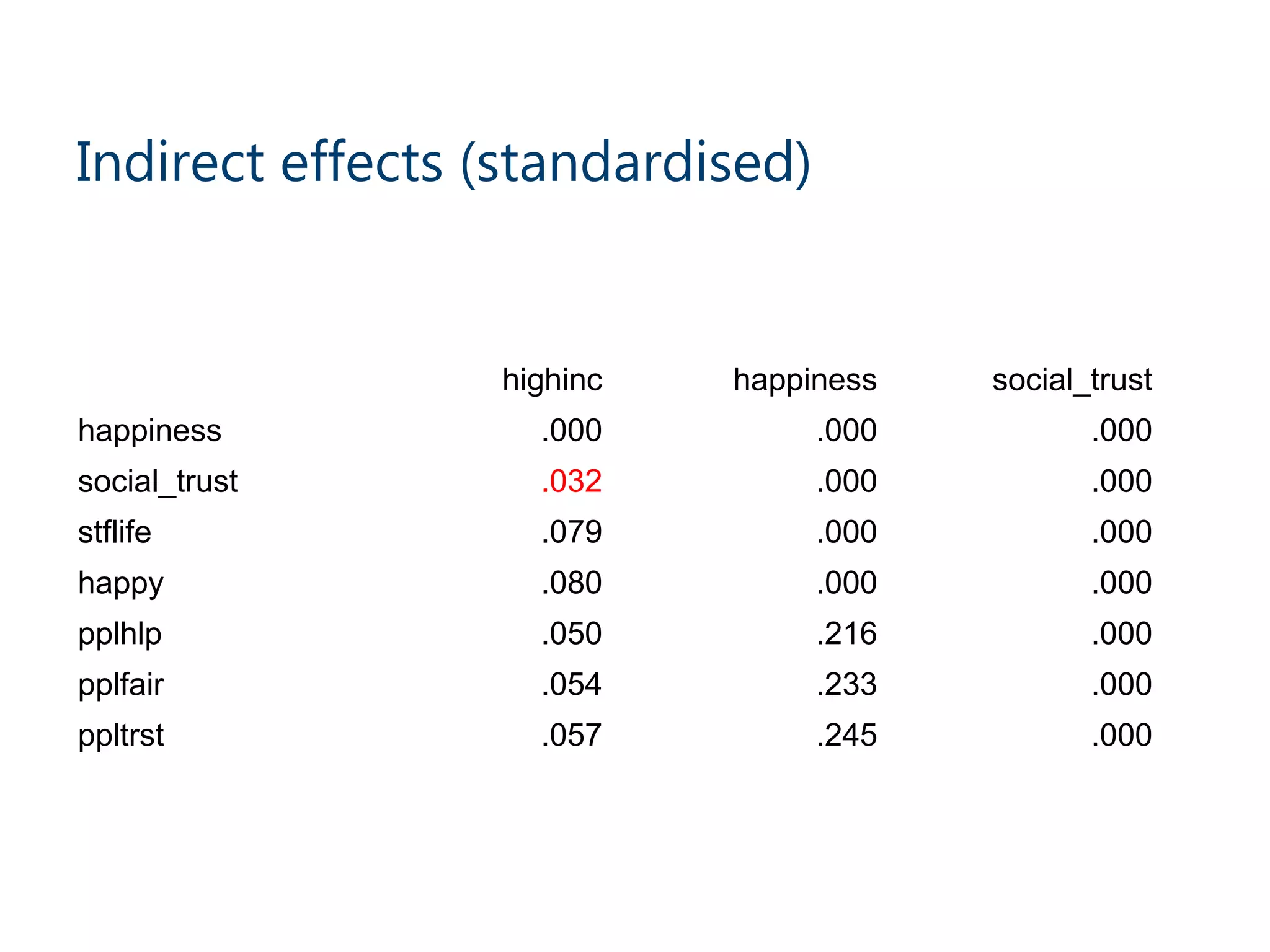
This document discusses mediation models and how they can be used to analyze direct, indirect, and total effects. It explains that ordinary least squares (OLS) models estimate direct effects but mediation models are needed to examine indirect and total effects. A perfect mediation occurs when the direct effect is non-significant after including the mediator, while partial mediation means the direct effect is significantly lower after including the mediator. Bootstrapping methods can generate confidence intervals for mediated paths. The document provides an example analyzing how income relates to happiness and trust. It finds partial mediation and reports specific indirect effects and their significance levels. The document notes limitations of this approach and discusses newer counterfactual based methods like g-computation.