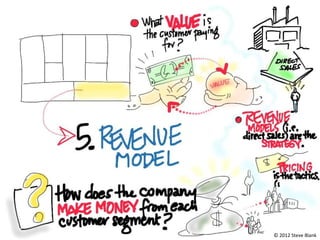
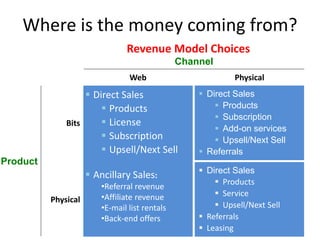
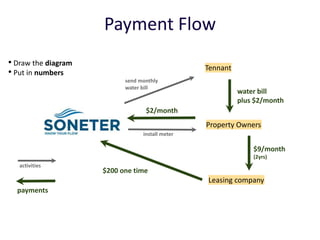
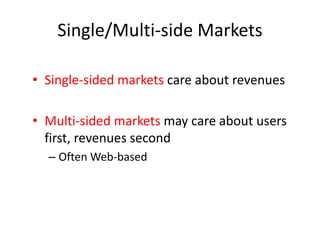
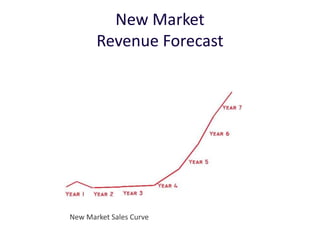
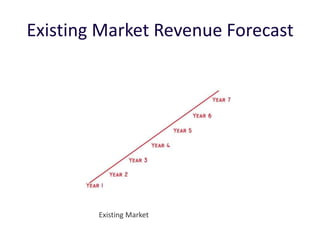
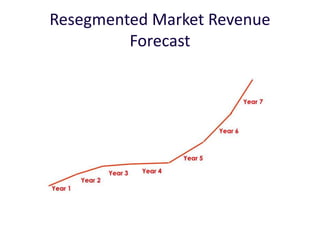
The document discusses revenue models and pricing strategies for startups. It explains that the two key questions are what the revenue model is and how to price the product within that model. Revenue models describe how a company generates cash from customers, such as through direct sales, subscriptions, or licensing. Pricing models determine how to set prices for different customer segments using approaches like cost-plus, value-based, or competitive pricing. The document also covers issues like distribution channels, market types, and demand curves and their impact on revenue streams.