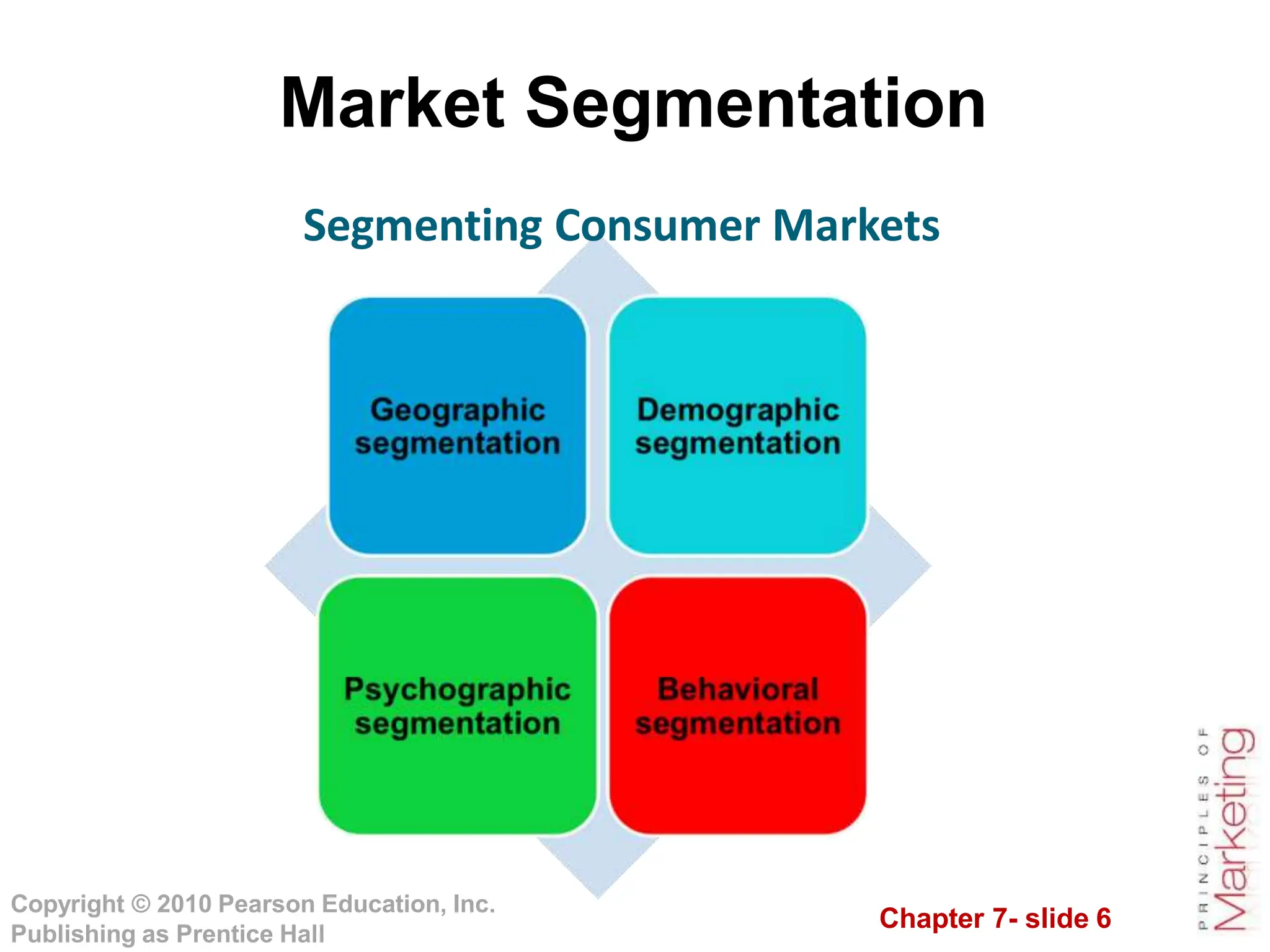
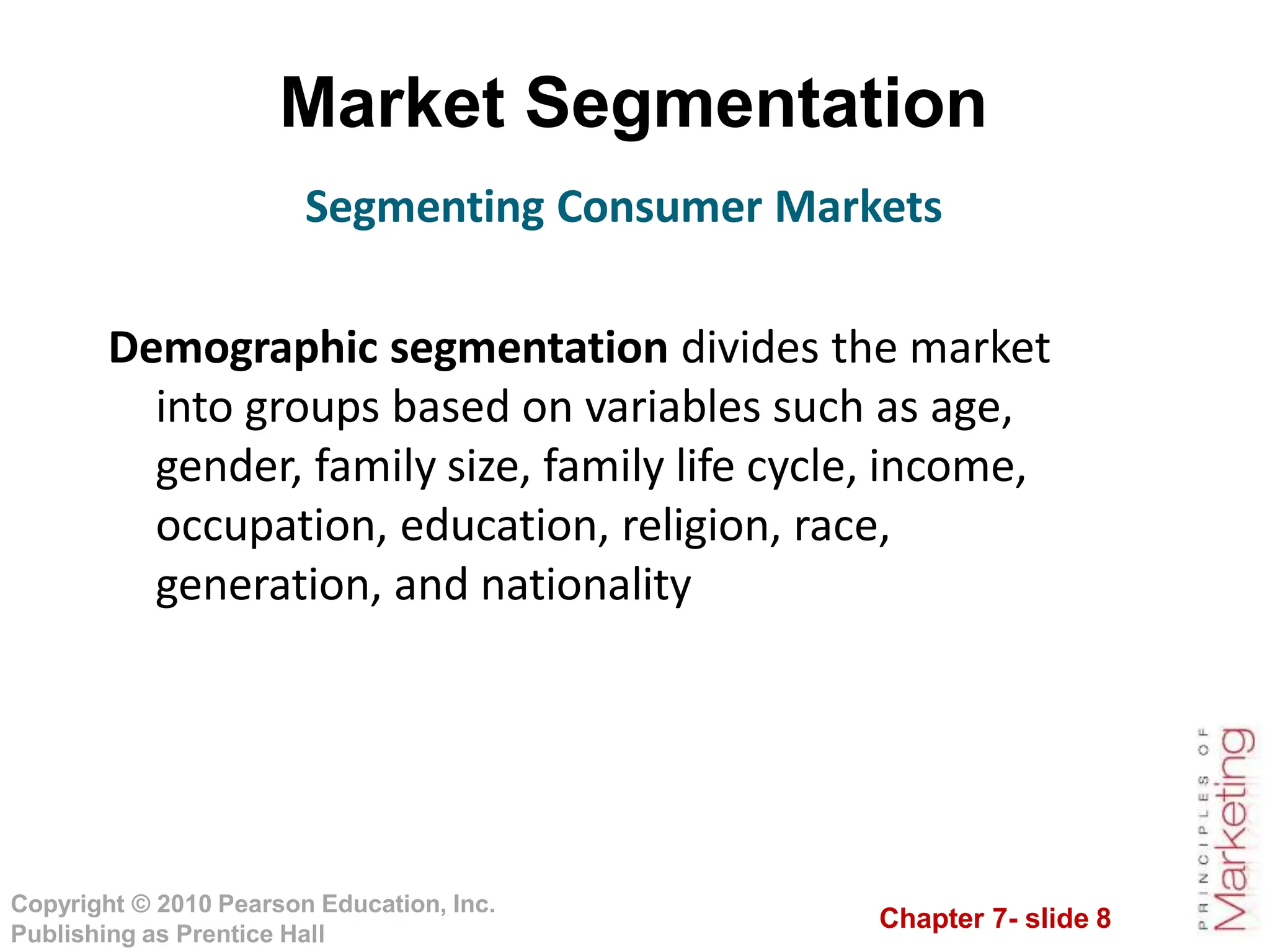
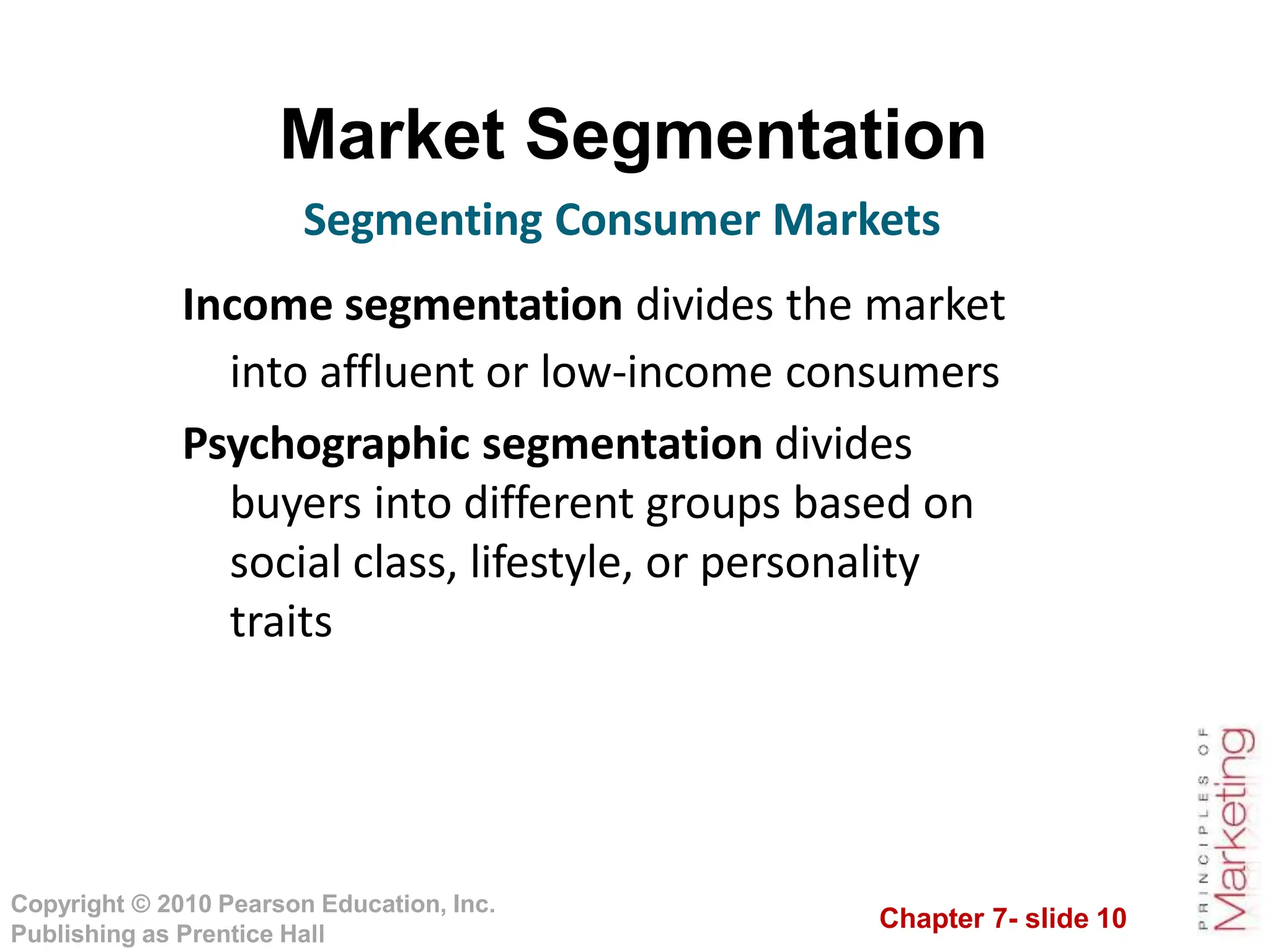
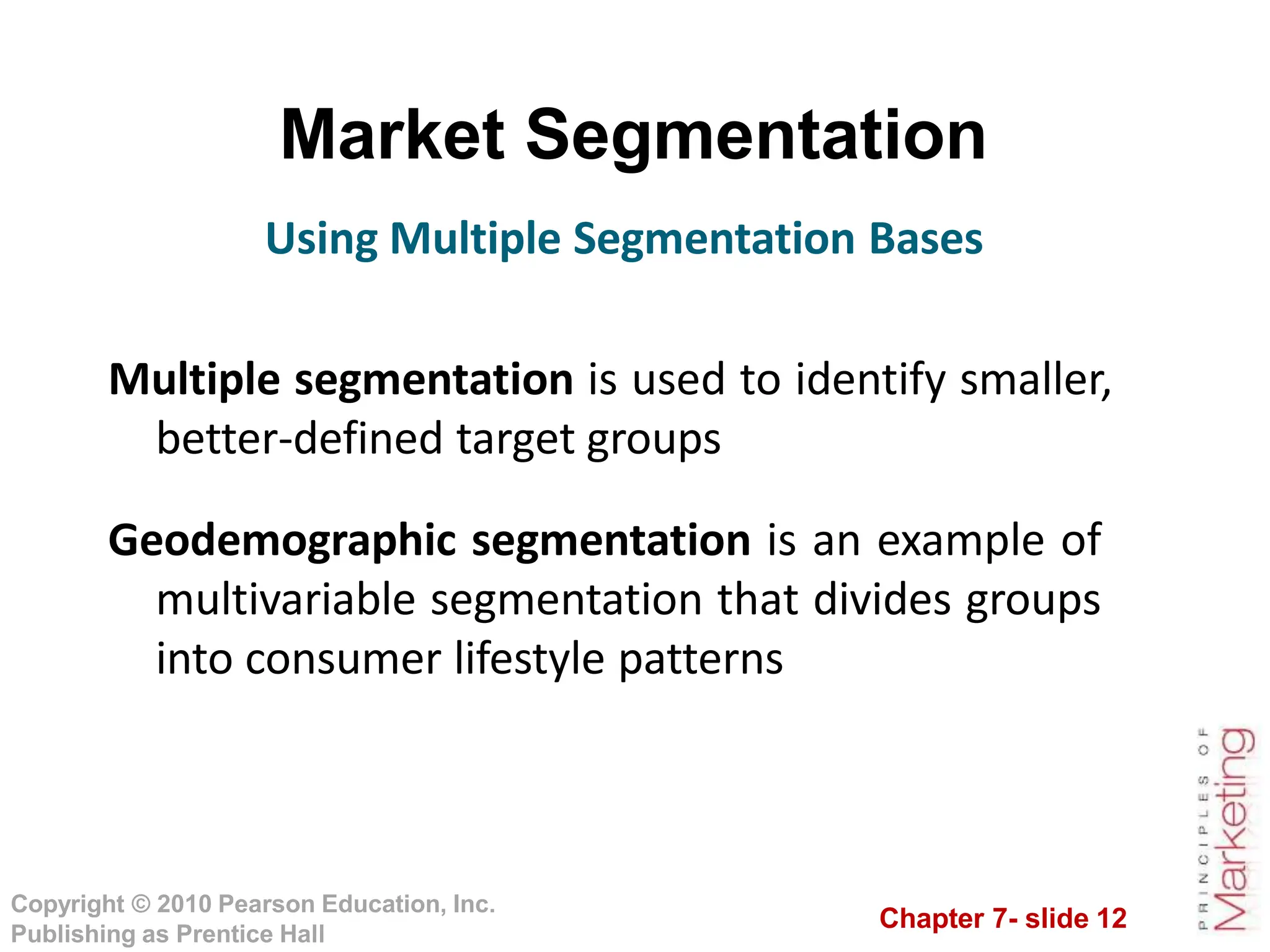
This document summarizes key topics from Chapter 7 on customer-driven marketing strategies. The chapter discusses market segmentation, targeting, differentiation and positioning. It describes how companies segment markets based on geographic, demographic, psychographic and behavioral factors. Effective segmentation requires segments to be measurable, accessible, substantial, differentiable and actionable. The chapter also covers selecting target markets, and different targeting strategies like undifferentiated, differentiated, concentrated and micromarketing. It emphasizes identifying competitive advantages to build product positioning through superior value. Overall, the chapter provides an overview of developing customer-driven marketing strategies through segmentation, targeting and positioning.