This document discusses key aspects of a business's cost structure and revenue streams. It introduces the importance of understanding costs for a sustainable business model. The document then covers:
1) Questions to evaluate key costs derived from the business model, including important expenses from key resources, activities, and how activities drive costs.
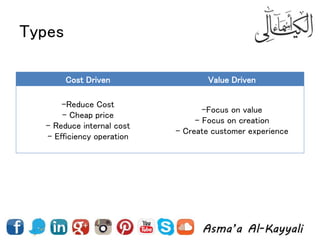
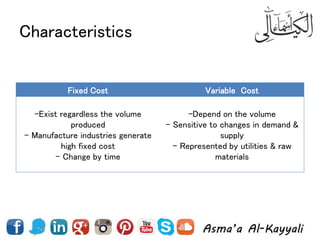
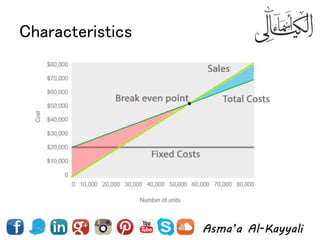
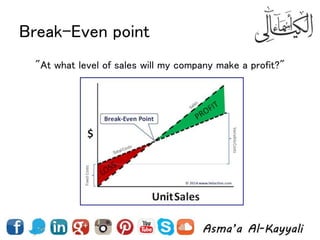
2) Types of costs like fixed, variable, and how costs are influenced by business value propositions.
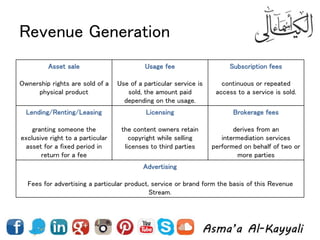
3) Revenue streams can come from transactions, recurring payments, and different pricing strategies.
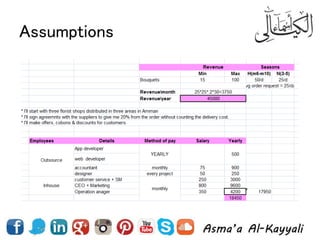
4) Financial statements are important for shareholders and investors to understand business progress and viability.