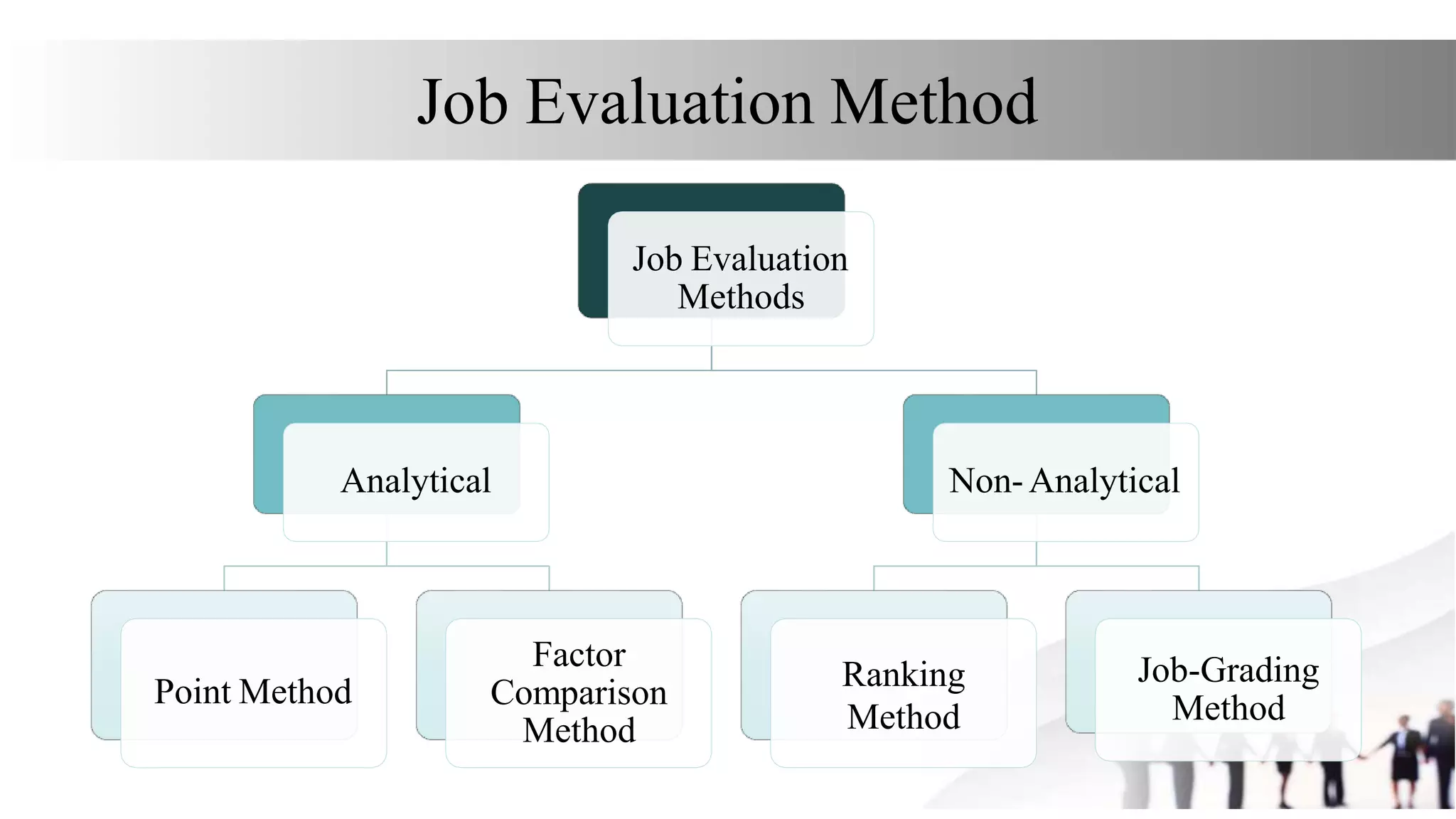
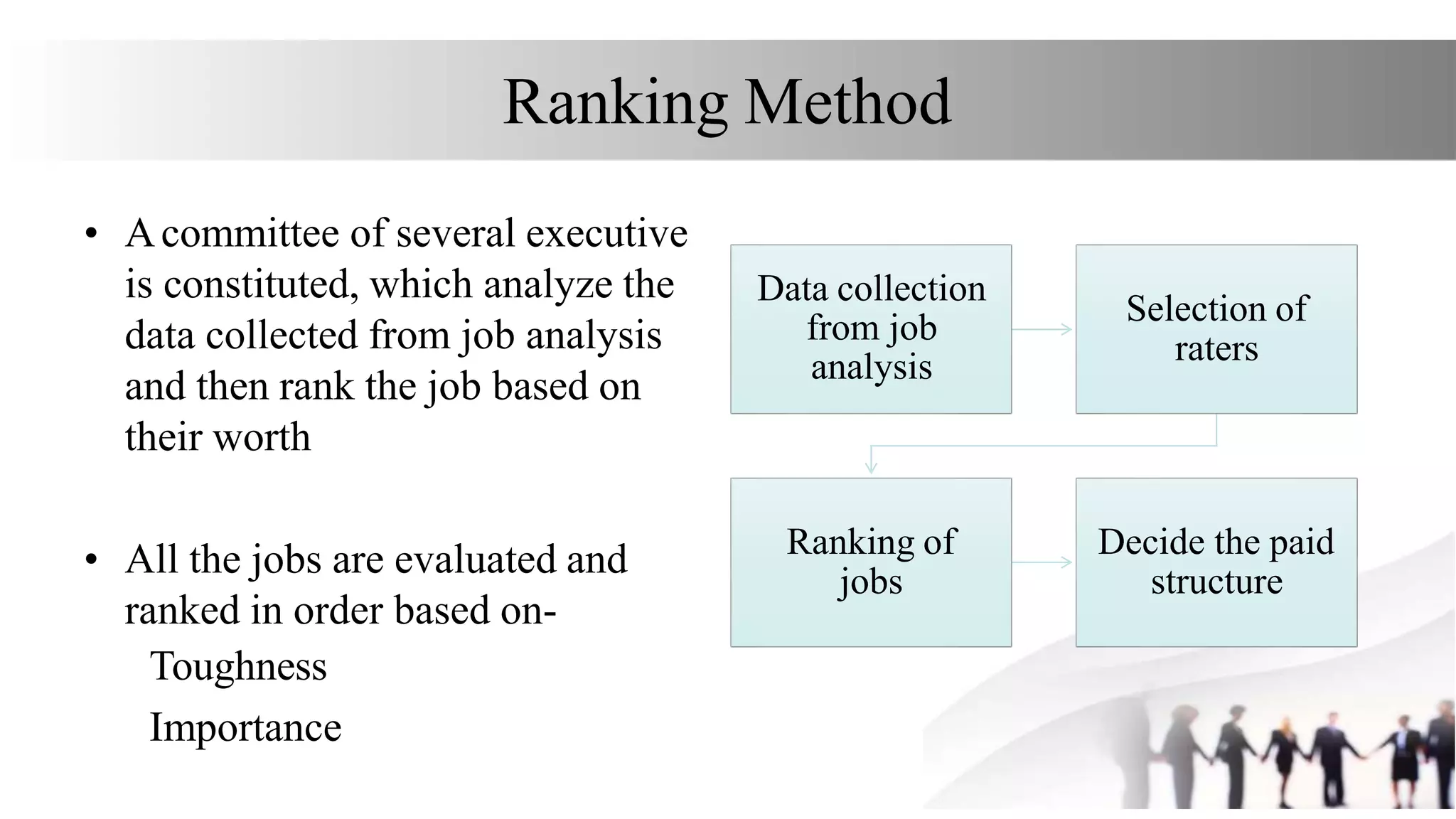
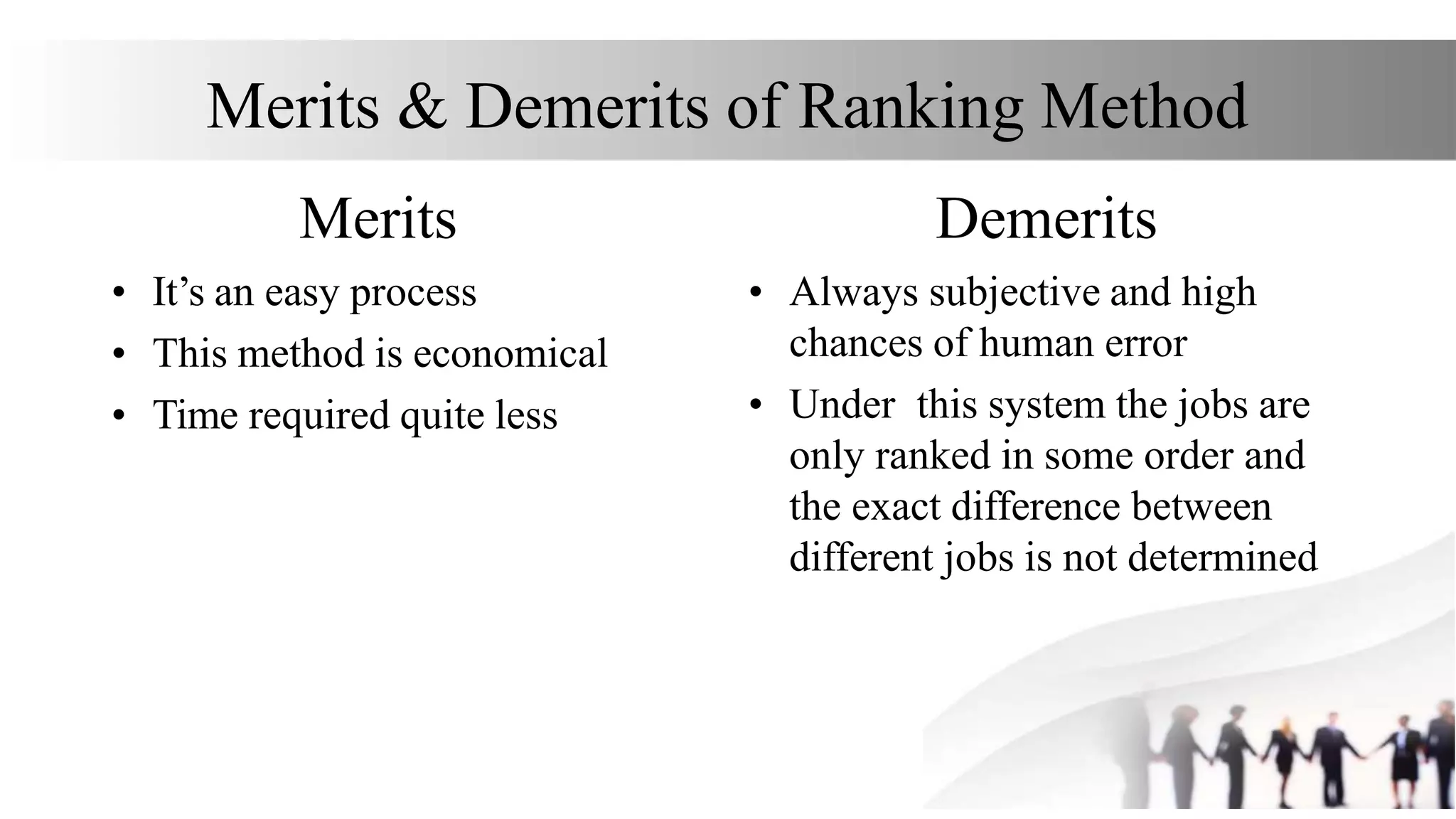
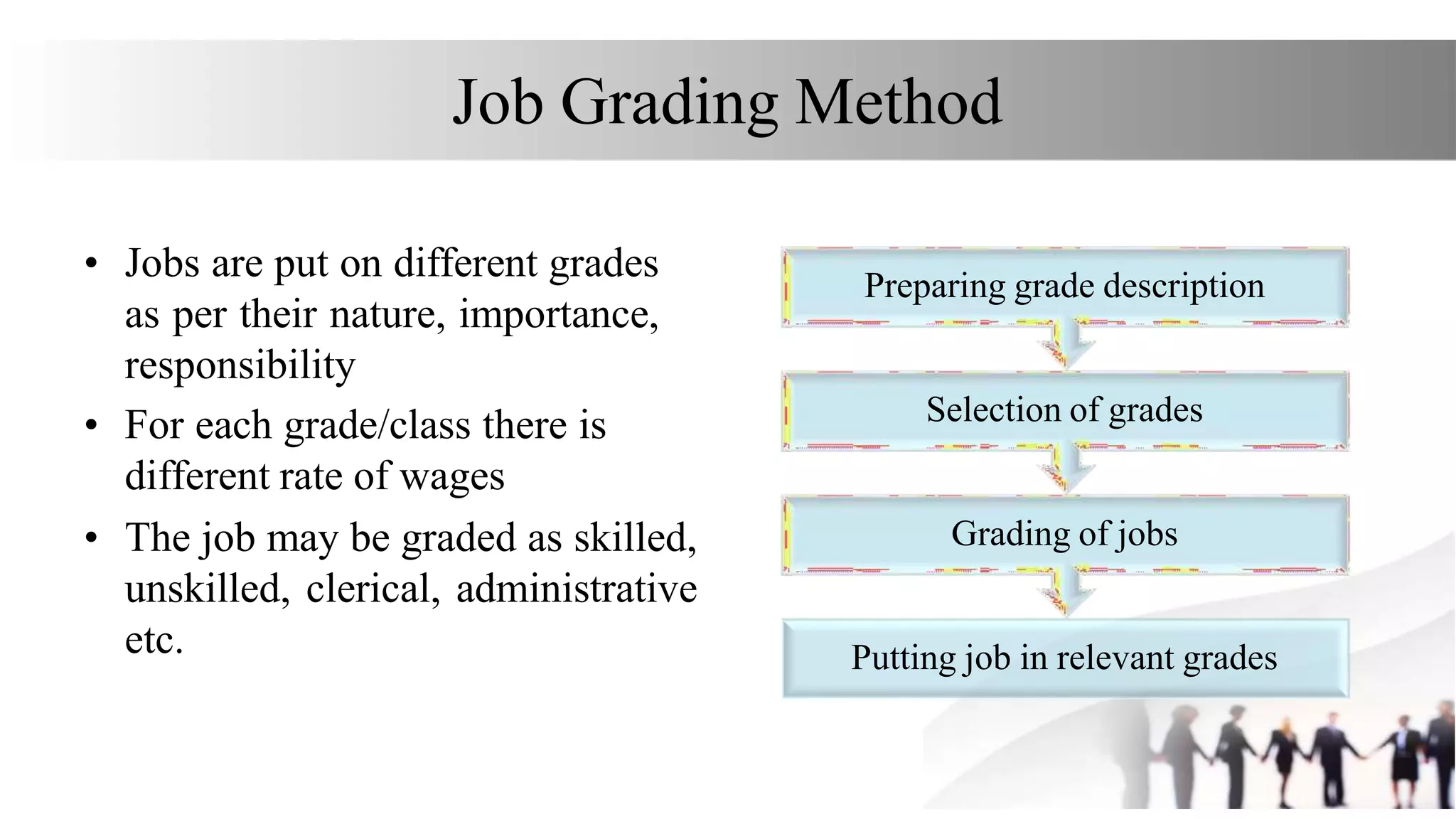
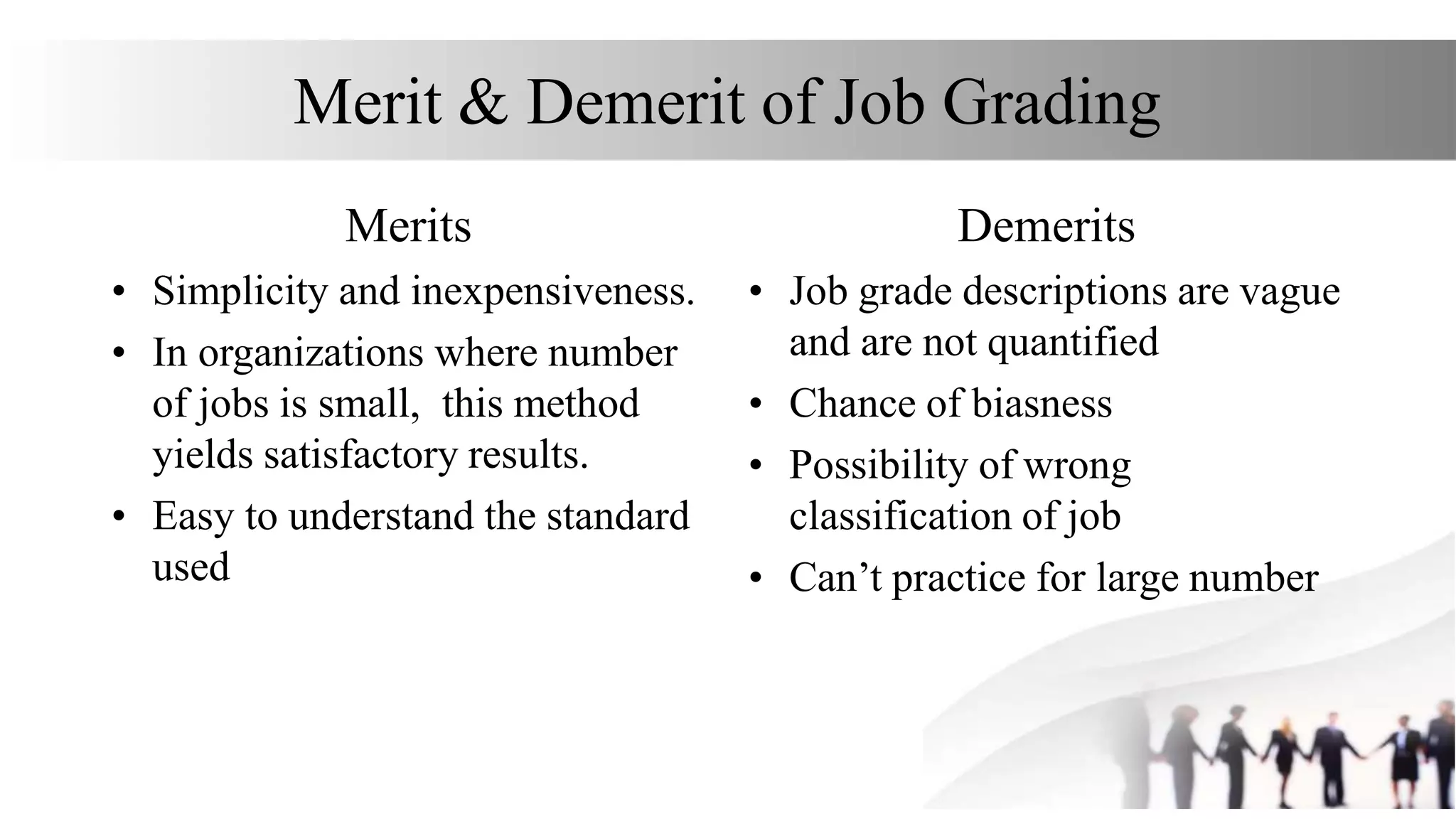
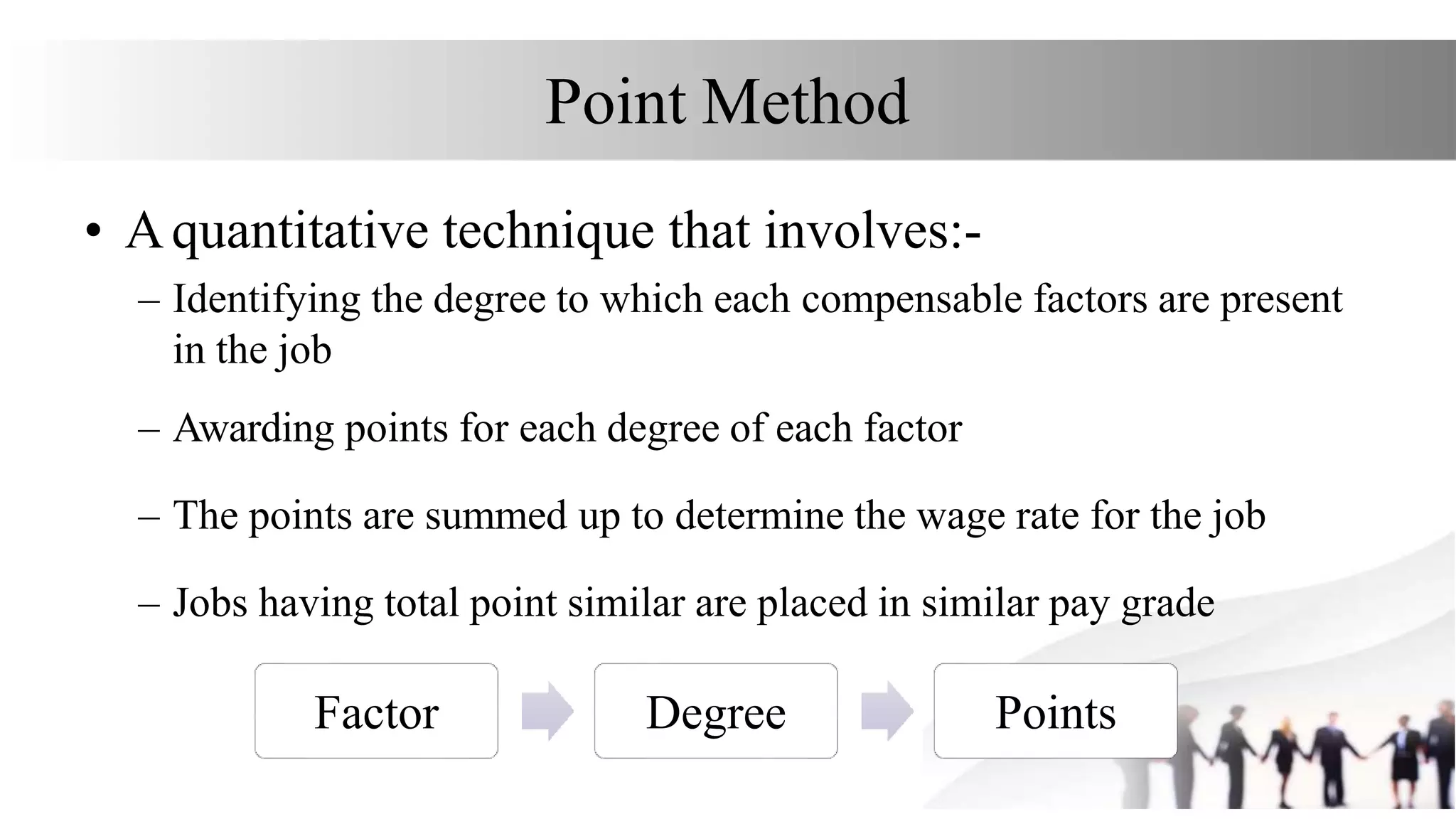
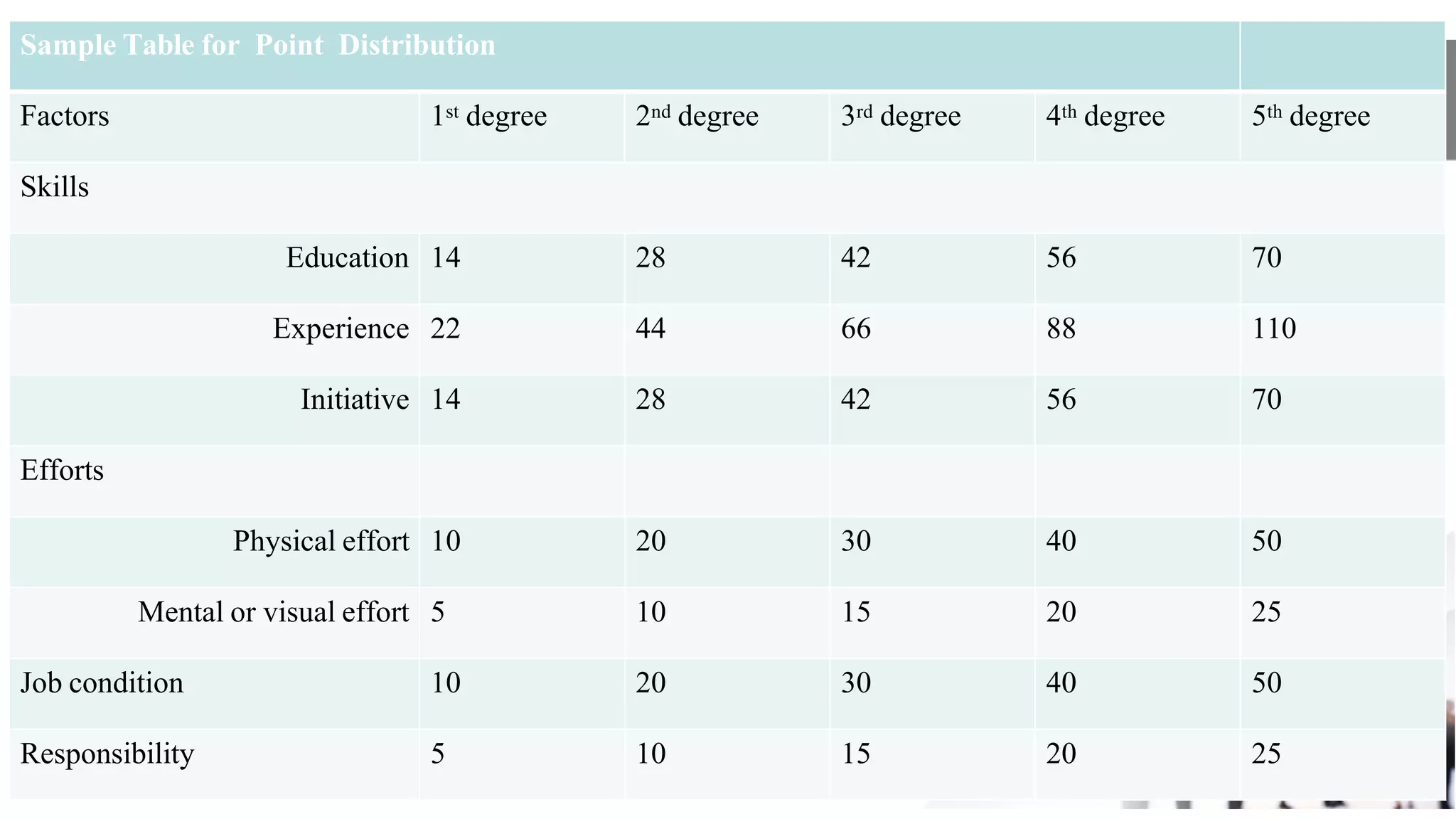
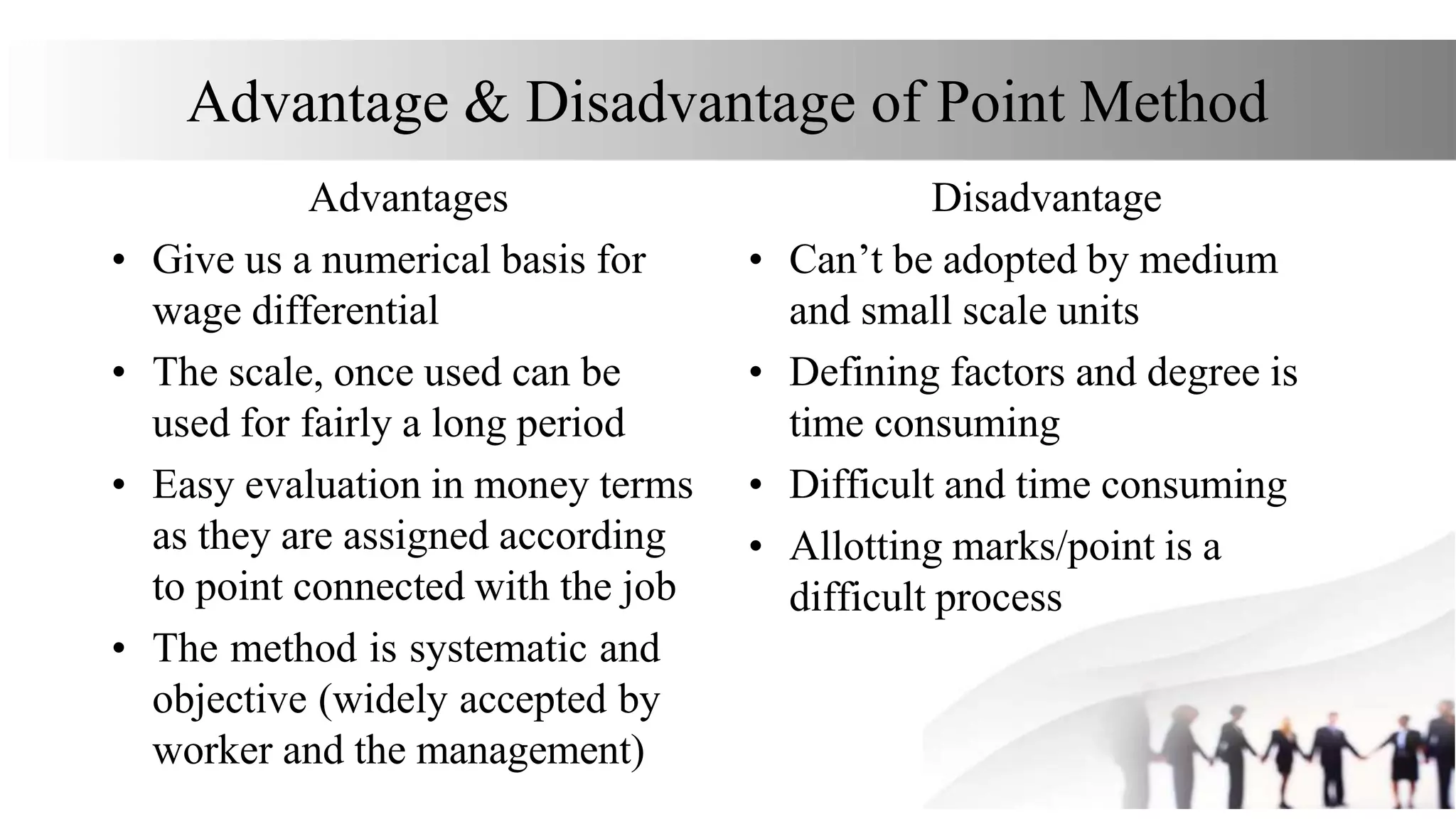
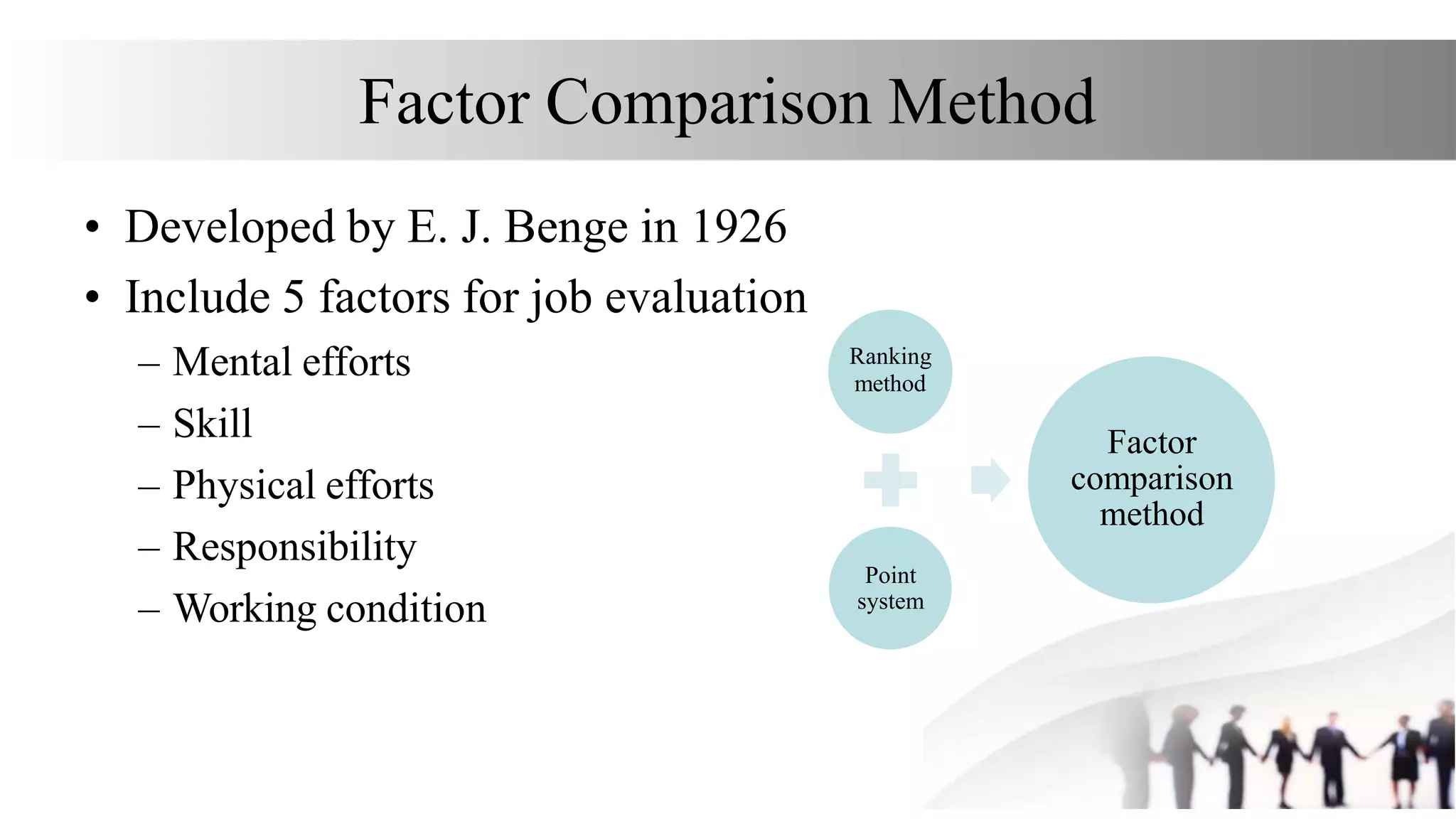
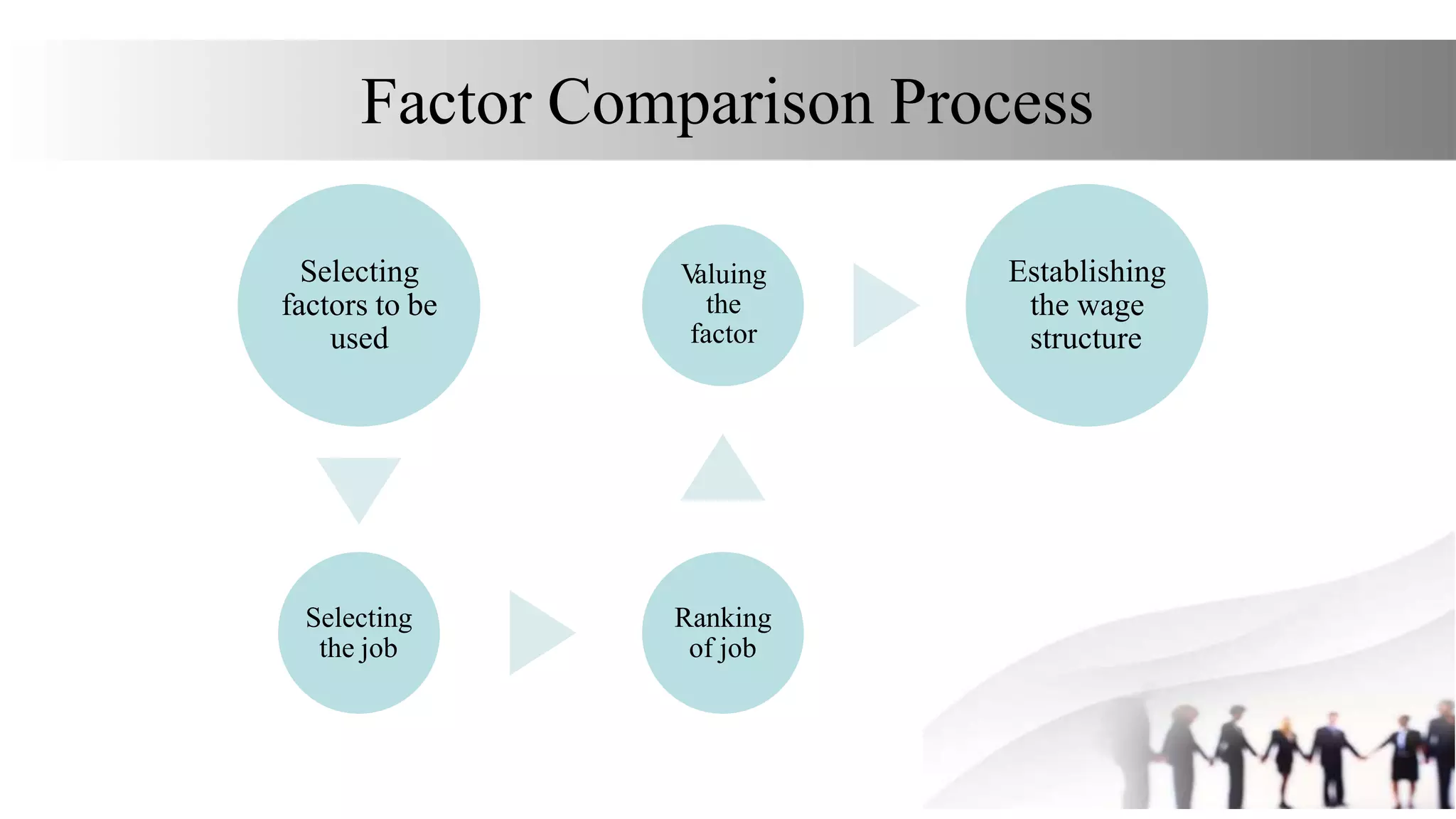
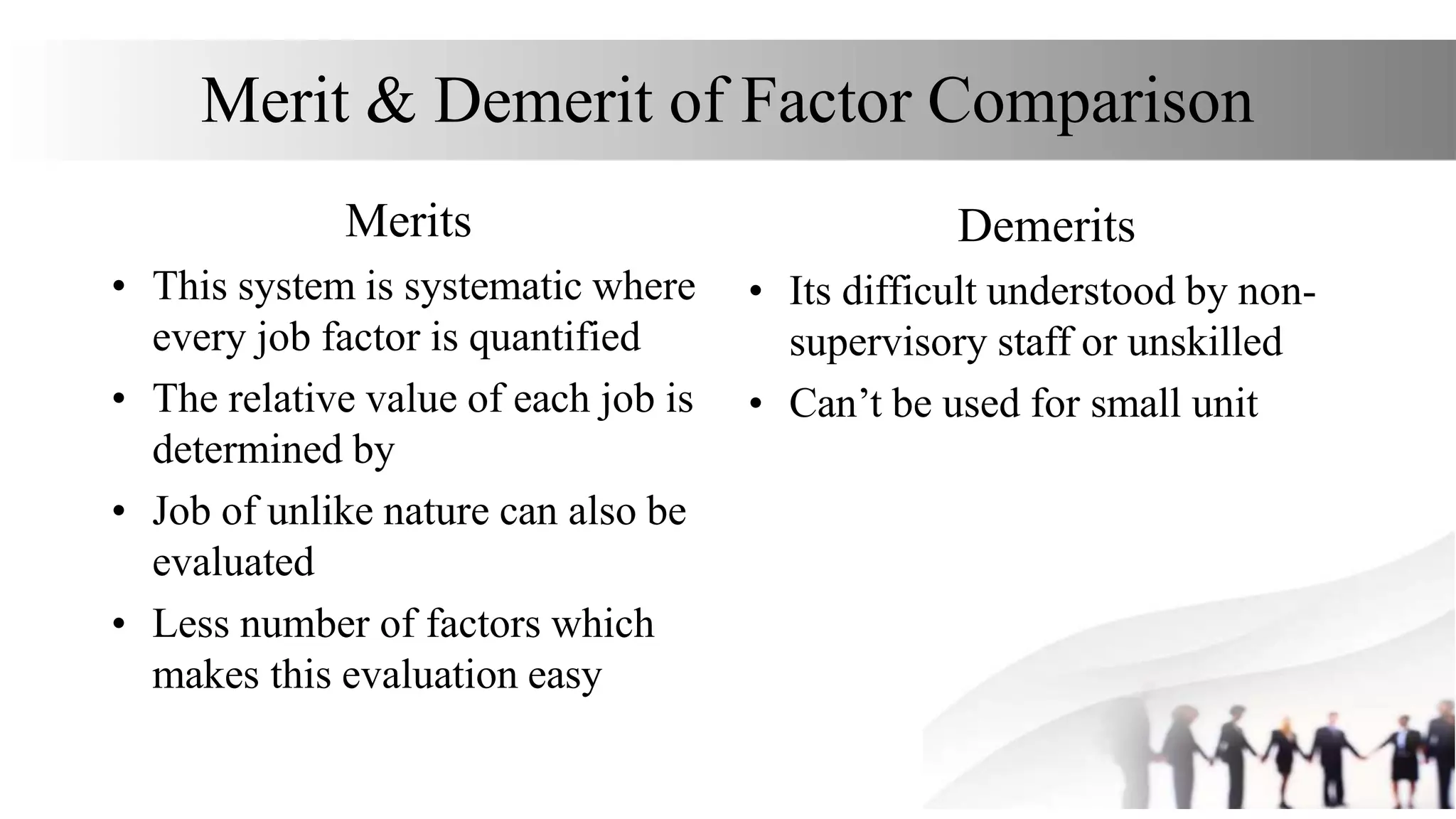
This document discusses various methods for job evaluation, including analytical and non-analytical approaches. It describes the ranking method and job grading method as non-analytical approaches and the point method and factor comparison method as analytical approaches. For each method, it provides details on the process and highlights merits and demerits. The point method assigns numerical points to factors like skills, education, experience, and responsibilities to determine pay grades. The factor comparison method ranks and values factors like mental effort, skill, and working conditions to establish wage structure.