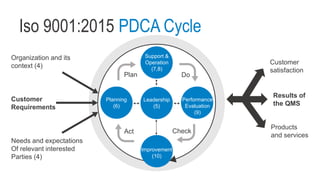
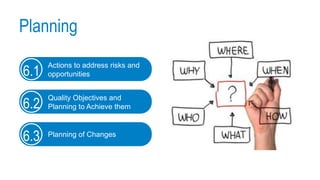
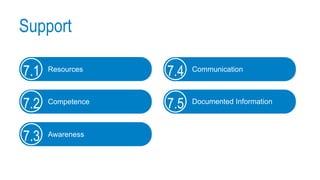
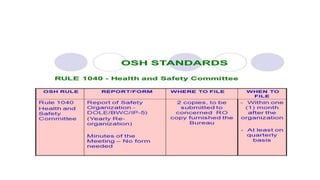
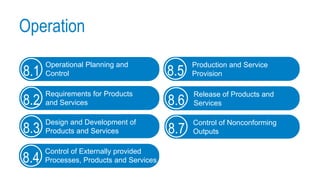
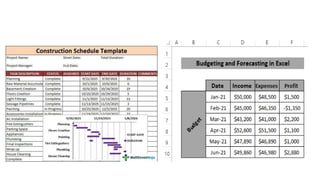
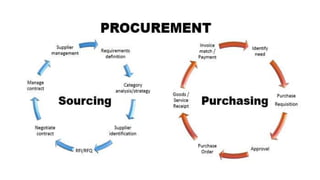
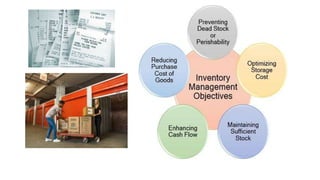
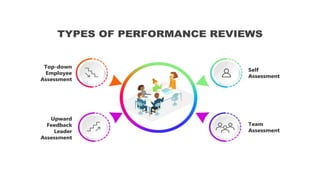
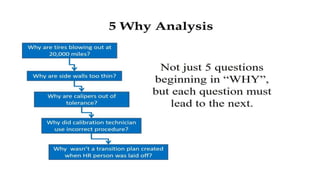
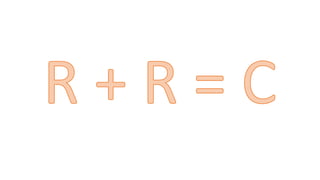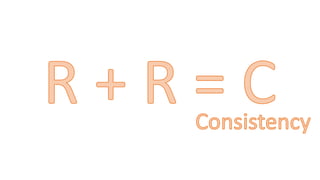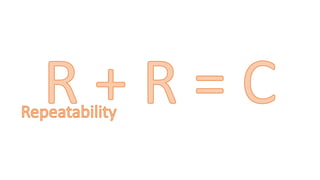This document provides an overview of ISO 9001:2015 requirements for process owners. It begins by defining key terms like quality management system and total customer satisfaction. It then discusses the history and purpose of ISO and some key changes between the 2008 and 2015 versions. The core content reviews each clause of ISO 9001:2015 including the context of the organization, leadership responsibilities, planning processes, the PDCA cycle, and requirements for support functions. Several worked examples are provided to demonstrate how to map business processes, identify key metrics, and plan for risk mitigation and continual improvement as required by the standard.