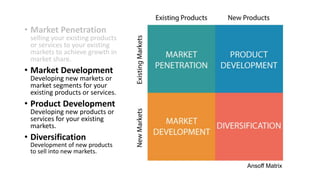
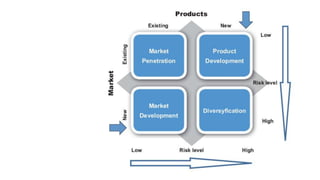
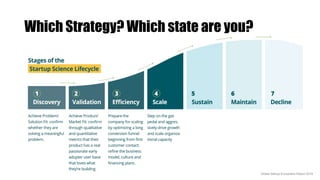
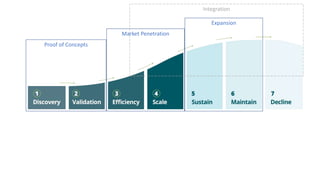
The document outlines various growth strategies for startups, emphasizing the importance of proofing concepts before scaling. Key strategies include market penetration, product development, and diversification, while also cautioning against premature scaling, which contributes to a high failure rate among startups. It highlights critical measures such as achieving product/market fit and understanding customer needs as essential for successful growth.