Lecture 5 bio
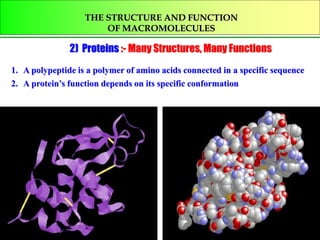
- 1. THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF MACROMOLECULES 2) Proteins :- Many Structures, Many Functions 1. A polypeptide is a polymer of amino acids connected in a specific sequence 2. A protein’s function depends on its specific conformation
- 2. Their functions include structural support, storage, transport of other substances, intercellular signaling اإلشاراتبينالخلوية , movement, defense against microbes and work as enzymes in the cell that regulate metabolism األيض. Humans have tens of thousands of different proteins, each with their own structure and function. All protein polymers are constructed from تتركبمن the same set of 20 monomers, called amino acids. Polymers of proteins are called polypeptides ببتيداتعديدة . A protein consists of one or more polypeptides folded and coiled into a specific conformation
- 3. - The physical and chemical characteristics صفاتof the R group determine تحددthe unique characteristics of a particular amino acid. Side chain Amino group Carboxyl group General Formula of the Amino Acid: C H R N H H C OH O - The side chain R links with ترتبطبـ different compounds *** - Monomer of amino acid includes a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a variable متغيرةR group (or side chain), all covalently bonded to C atom. - Differences in R groups produce the 20 different amino acids.
- 4. 1. Hydrophobic: the amino acids that have hydrophobic R groups (non-polar).
- 5. 2- Hydrophilic: the amino acids that have polar R groups, making them hydrophilic. 3- Ionized: the amino acids with functional groups that are charged (ionized) at cellular pH (7). So, some R groups are bases, others are acids.
- 6. The Peptide Bond الرابطةالبيبتيدية Peptide bond formed between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of the other by dehydration. OH C C H R N H H O H C H R N H C OH O Peptide bond Polypeptide (Protein) Dehydration نزعالماء Amino acids Peptide
- 7. Amino acids are joined together when a dehydration reaction removes a hydroxyl group from the carboxyl end of one amino acid and a hydrogen from the amino group of another. The resulting covalent bond is called a peptide bond. • Repeating the process over and over عدةمرات creates a long polypeptide chain. – At one end is an amino acid with a free amino group the (the N-terminus) and at the other is an amino acid with a free carboxyl group the (the C- terminus). • The repeated sequence (N-C-C) is the polypeptide backbone. • Attached to the backbone are the various R groups. • Polypeptides range in size from a few monomers to thousands.
- 8. The folding إلتفافof a protein from a chain of amino acids occurs spontaneously ذاتيا. There are three levels of structure: primary أولى, secondary ثانوى, and tertiary ثالثىstructure, are used to organize the folding within a single peptide chain. Quaternary باعىُرstructure arises when two or more polypeptides (proteins) join to form another kind of protein.
- 9. 1. Primary structure: It is a single peptide chain of amino acids. Lysozyme, an enzyme that attacks bacteria, consists of a polypeptide chain of 129 amino acids. A slight change تغييرطفيف in the primary structure can affect a protein’s conformation and ability to function.
- 10. Sickle cell disease المنجليةخالياالدم : an abnormal hemoglobin because of a single amino acid substitution تغيير. These abnormal hemoglobin crystallize, deforming كسرُيthe red blood cells and leading to clogs إنسدادin tiny blood vessels .أوعية
- 11. 2. The secondary structure: Results from hydrogen bonds at regular intervals علىأبعادمتساوية along the polypeptide backbone. A. Coils الحلزونى(α-helix) are typical shapes that develop from secondary structure B. Folds (β-pleated sheets) الشيتجعـدُمال . Composed of several parallel α-helix coils attached by H bonds
- 12. An example for folds (β-pleated sheets) الشيتجعدُمال : Is the structural properties of silk الحريرbecause of the presence of so many hydrogen bonds makes each silk fiber stronger than steel.
- 13. 3. Tertiary structure: is determined by a variety of interactions among خاللR groups and between R groups and the polypeptide backbone. These interactions include weak bonds like hydrogen bonds among polar areas, ionic bonds between charged R groups, and hydrophobic interactions and Van der Waals interactions among hydrophobic R groups. - Also include disulfide bridges, strong covalent bonds that form between the sulfhydryl groups (SH) of cysteine monomers, stabilize the structure.
- 14. 4- The quaternary structure: Results from the aggregation تجمعof two or more polypeptide chains. Collagen is a fibrous protein of three polypeptides that are supercoiled, and function in connective tissues. Hemoglobin is a globular protein with two copies of two kinds of polypeptides (2α and 2β). Collagen Hemoglobi n
- 15. The 4 forms of protein
- 16. It is the change of protein’s conformation in response to إستجابةلـ the physical and chemical conditions. For example, alterations تغييرin pH, salt concentration, temperature, or other factors can denature يفردa protein. These forces break the hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and disulfide bridges that maintain the protein’s complicated shape. Some proteins can return to their original shape again after denaturation, but others cannot.
- 18. Amino acids Primary structure Secondary structure Tertiary structure Quaternary structure 1- Hydrophobic Interaction (Van der Waals interaction); 2- H bonds; 3- Ionic bonds; 4- Di-sulfide bridges; Single chain of amino acids e.g. Lysozyme Coils & Folds H bonds e.g. silk e.g. Collagen & Hemoglobin two or more polypeptide chains Peptides Hydrophobic (non-polar R group) *** Hydrophilic (polar R group) Ionized (charged functional groups) ProteinsPolypeptides
- 19. Lipids; The Hydrophobic Molecules 1. Fats store large amounts of energy 2. Phospholipids are major components of cell membranes 3. Steroids include cholesterol and certain hormones
- 20. Lipids are an exception among macromolecules because they do not have polymers. The unifying feature الصفةزةٍـيَمُمال of lipids is that they all have little or no affinity for water المتزجَـتبالماء . This is because their structures are dominated by non-polar covalent bonds. Lipids are the components كوناتُمof fats, and are highly diverse in form and function. Although fats are not polymers, they are large molecules assembled from تتكونمن smaller molecules by dehydration reactions. A fat is constructed from two kinds of smaller molecules, glycerol and fatty acids أحماضُهنيةد .
- 21. A fat is composed of three fatty acids linked with one glycerol molecule. Fats are classified into Saturated مشبعand Un-saturated غيرمشبع fats OH H H C C CC C C H HH H H H H H H O OC C C H H H H OH OH H H Dehydration Fatty AcidGlycerol Glycerol consists of a three C skeleton with an OH group attached to each C. A fatty acid consists of a carboxyl group (COOH) attached to a long carbon skeleton, often 16 to 18 carbons long. Ester link
- 22. The many non-polar C-H bonds in the long hydrocarbon skeleton make fats hydrophobic. In a fat, three fatty acids are joined to glycerol by an ester linkage, رابطة إستيريةcreating a triacylglycerol( = triglyceride) .
- 23. Fatty acids may vary تختلفin length (number of carbons) and in the number and locations of double bonds. If there are no carbon-carbon double bonds, then the molecule is a saturated fatty acid (مشبعhas H at every possible position). •If there are one or more carbon-carbon double bonds, then the molecule is an unsaturated fatty acid حامضدهنىغيرمشبع - formed by the removal of H atoms from the carbon skeleton.
- 24. The Fatty acid components are saturated (there is no double bonds between the carbons. All C are linked with H. Thus, it is saturated with H. Most animal fats are saturated. They are solid at room temperature. Saturated fats-rich diet results in Atherosclerosis التصلبالشريانى . These double bonds are formed by the removal of H atoms. Most vegetable fats (oils) and fish fats are unsaturated. They are liquid at room temperature. They can be synthetically converted to saturated (solid) by adding H (Hydrogenation ََْردَهةﭽالَـ). B)- Un-saturated Fats الغيرمشبعةالدهون
- 25. The major function of fats is energy storage. A gram of fat stores more than twice as much energy as a gram of a polysaccharide. Humans and other mammals store fats as long-term energy reserves كمخزونطاقةطويلالمدى in adipose cells خاليادهنية .
- 26. Phospholipids have two fatty acids attached to glycerol and a phosphate group at the third position. The phosphate group carries a negative charge. • The interaction of phospholipids with water is complex. • The fatty acid tails are hydrophobic, but the phosphate group and its attachments form a hydrophilic head.
- 27. When phospholipids are added to water, they self-assemble تتشكلذاتيا into aggregates تجمعاتwith the hydrophobic tails pointing toward the center and the hydrophilic heads on the outside. This type of structure is called a micelle .الزهرة • At the surface of a cell phospholipids are arranged as a bilayer طبقةمزدوجة . – Again, the hydrophilic heads are on the outside in contact with the aqueous solution المحلولالمائى and the hydrophobic tails in the core .المركز – The phospholipid bilayer طبقةمزدوجة forms a barrier حاجزbetween the cell and the external environment البيئة .الخارجية • They are the major component of cell membranes.
- 28. Steroids are lipids with a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused ملتحمةcarbon rings. Different steroids are created by varying functional groups attached to the rings. • Cholesterol, an important steroid, is a component in animal cell membranes. • Cholesterol is also the precursor المادةالخام from which all other steroids are synthesized. • Many of these other steroids are hormones, including the sex hormones. • While cholesterol is clearly an essential molecule, high levels of cholesterol in the blood may contribute to Atherosclerosis تصلبالشرايين
- 29. F a t s (Composed of Lipids) Saturated Unsaturated Phospholipids Animal Fats Vegetable Fats Bi-layer of cell membrane Hydrogenation ََْردـَهــــــــةﭽَـ Steroids Sex Hormones & Cholesterol ***
- 30. CHAPTER 5 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF MACROMOLECULES THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF MACROMOLECULES 4- Nucleic Acids: The Informational Polymers 1. Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary information المعلوماتالوراثية 2. A nucleic acid strand is a polymer of nucleotides 3. Inheritance is based on replication of the DNA double helix