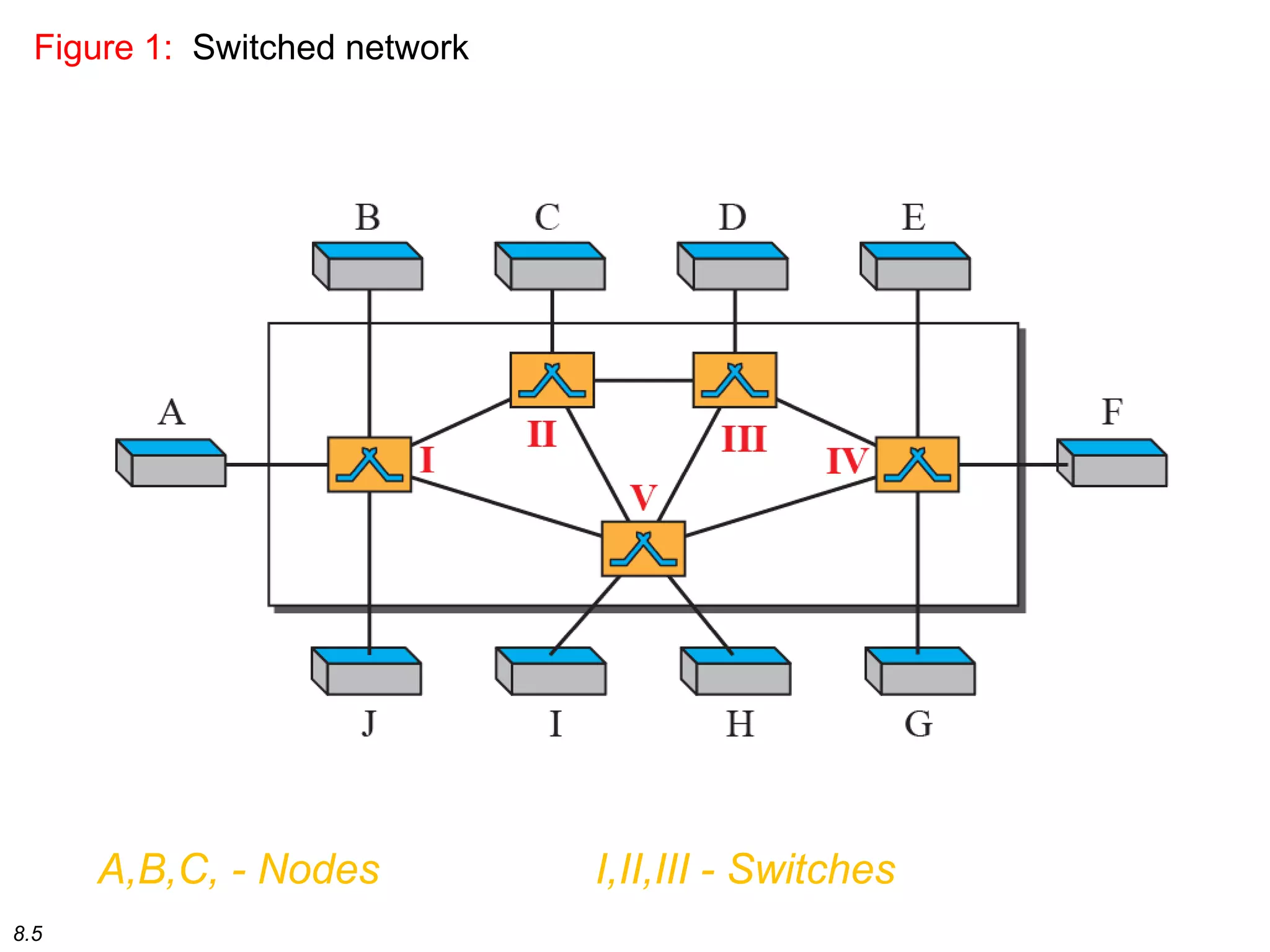
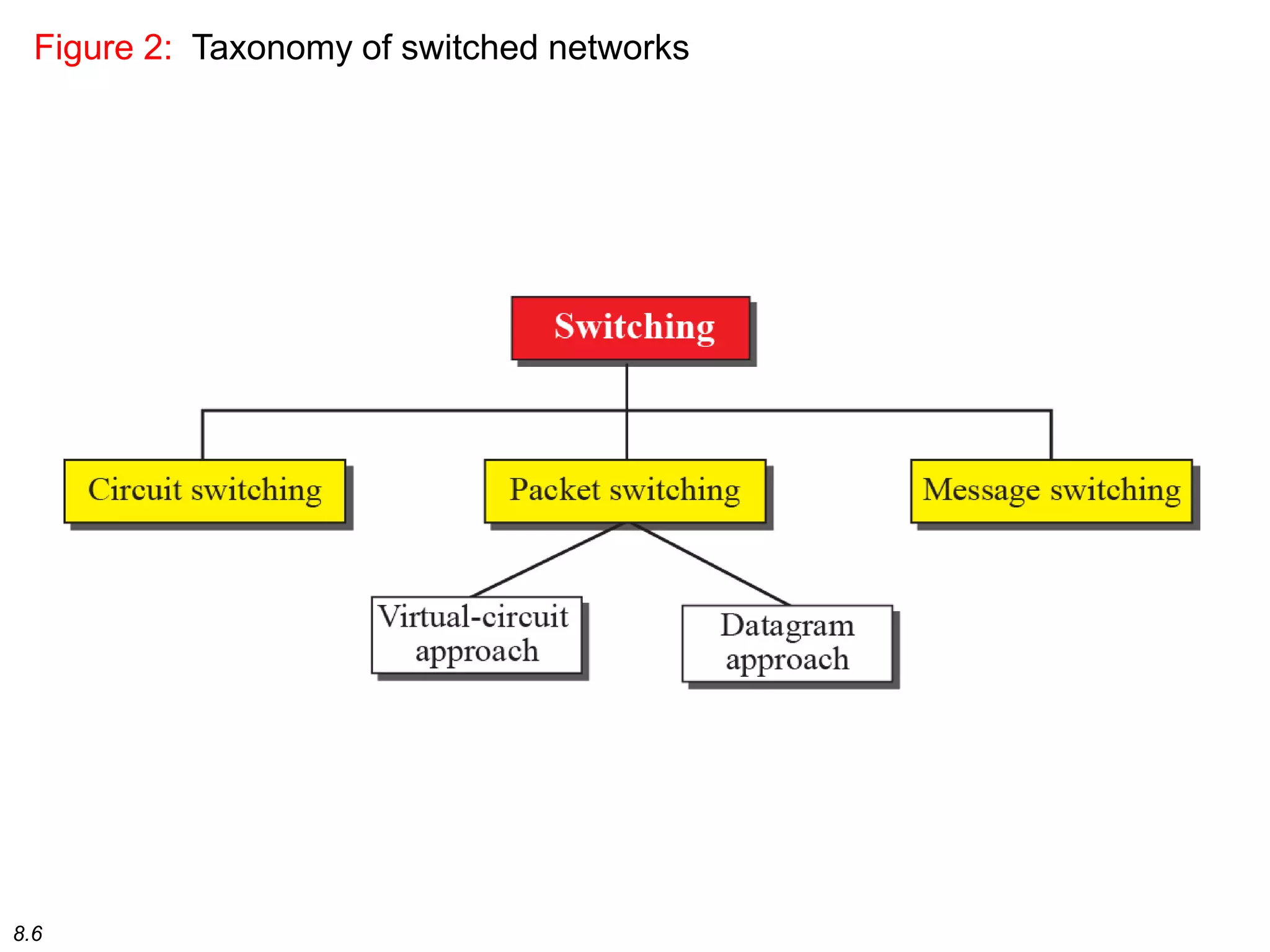
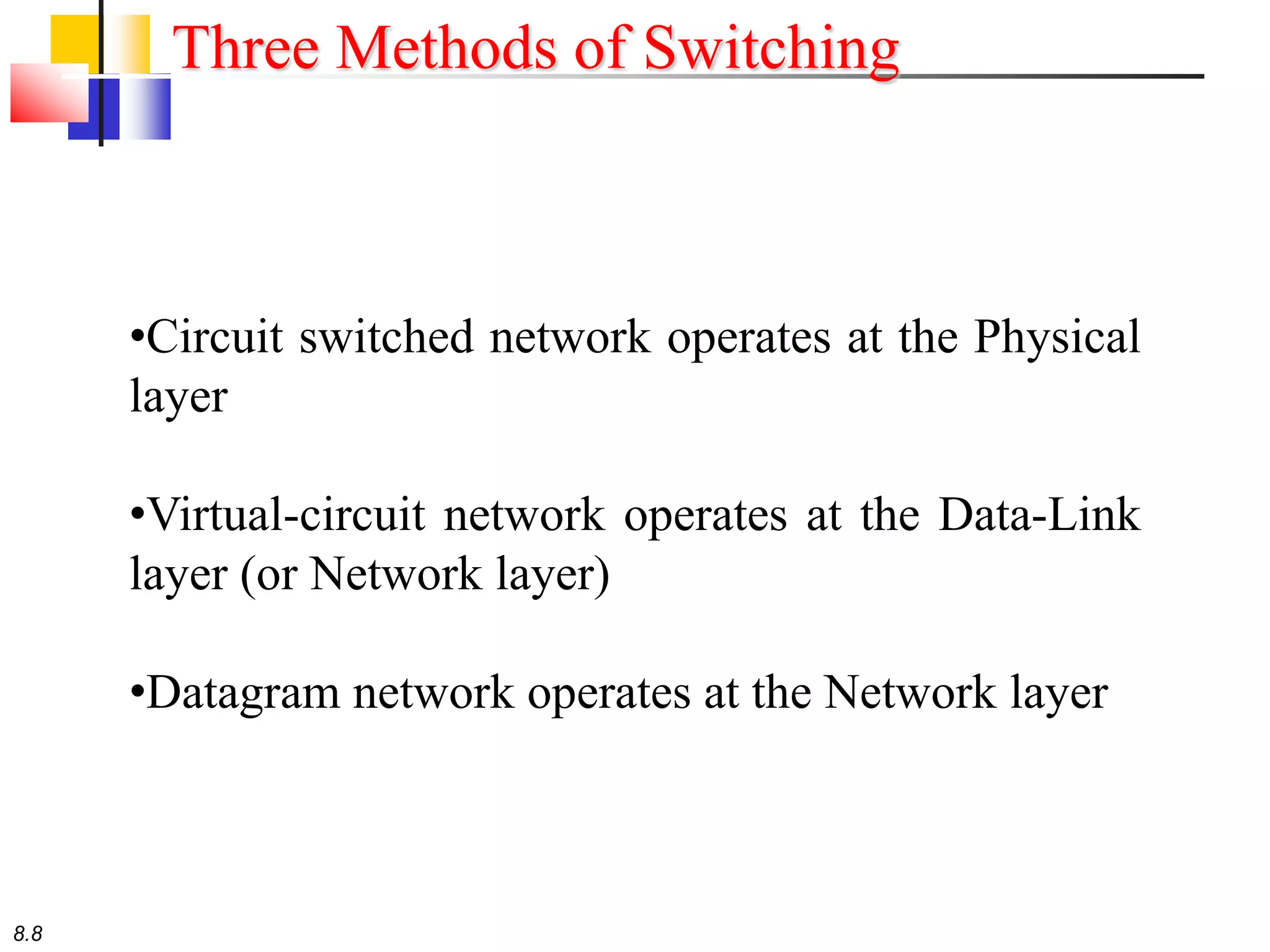
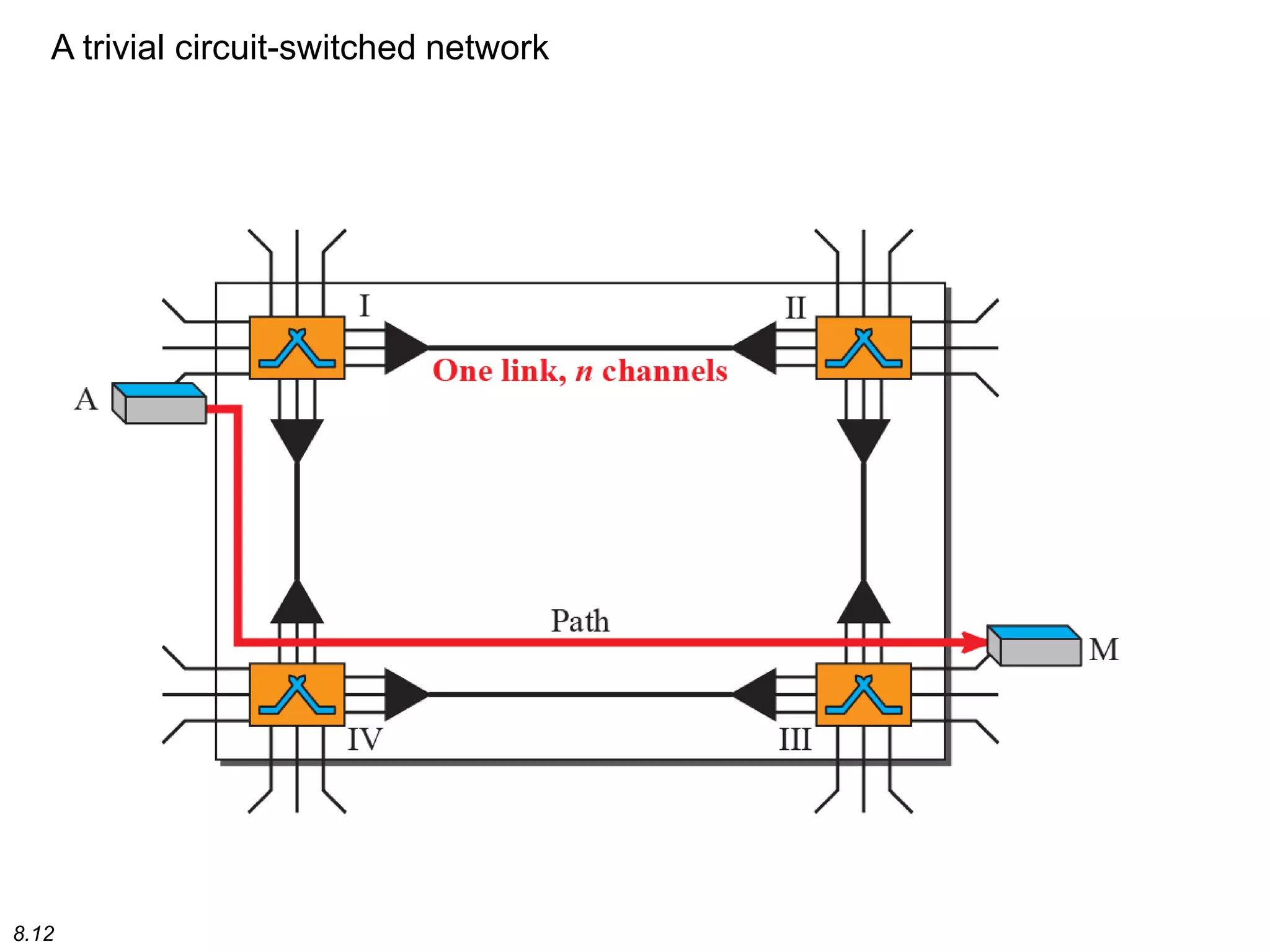
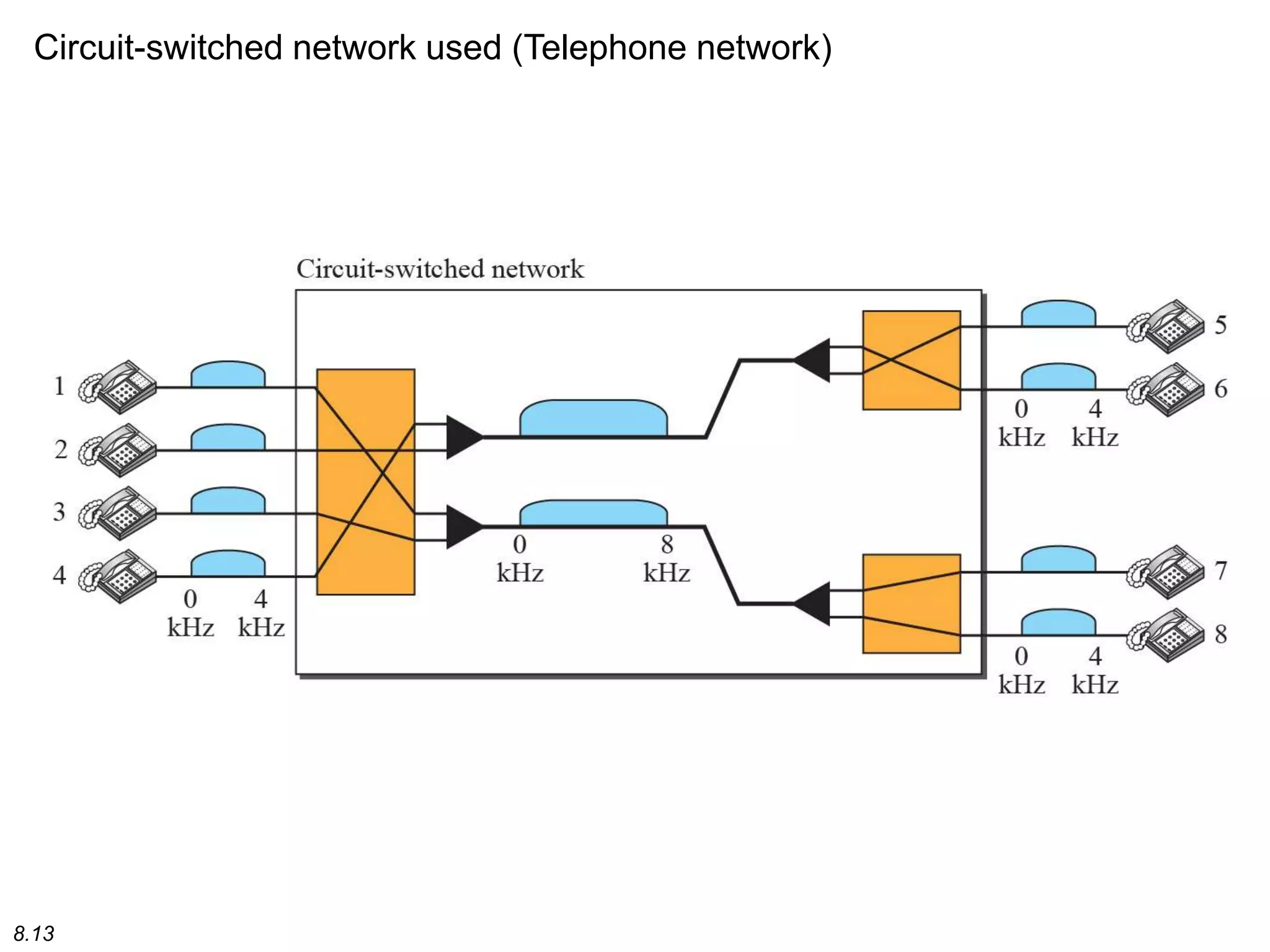
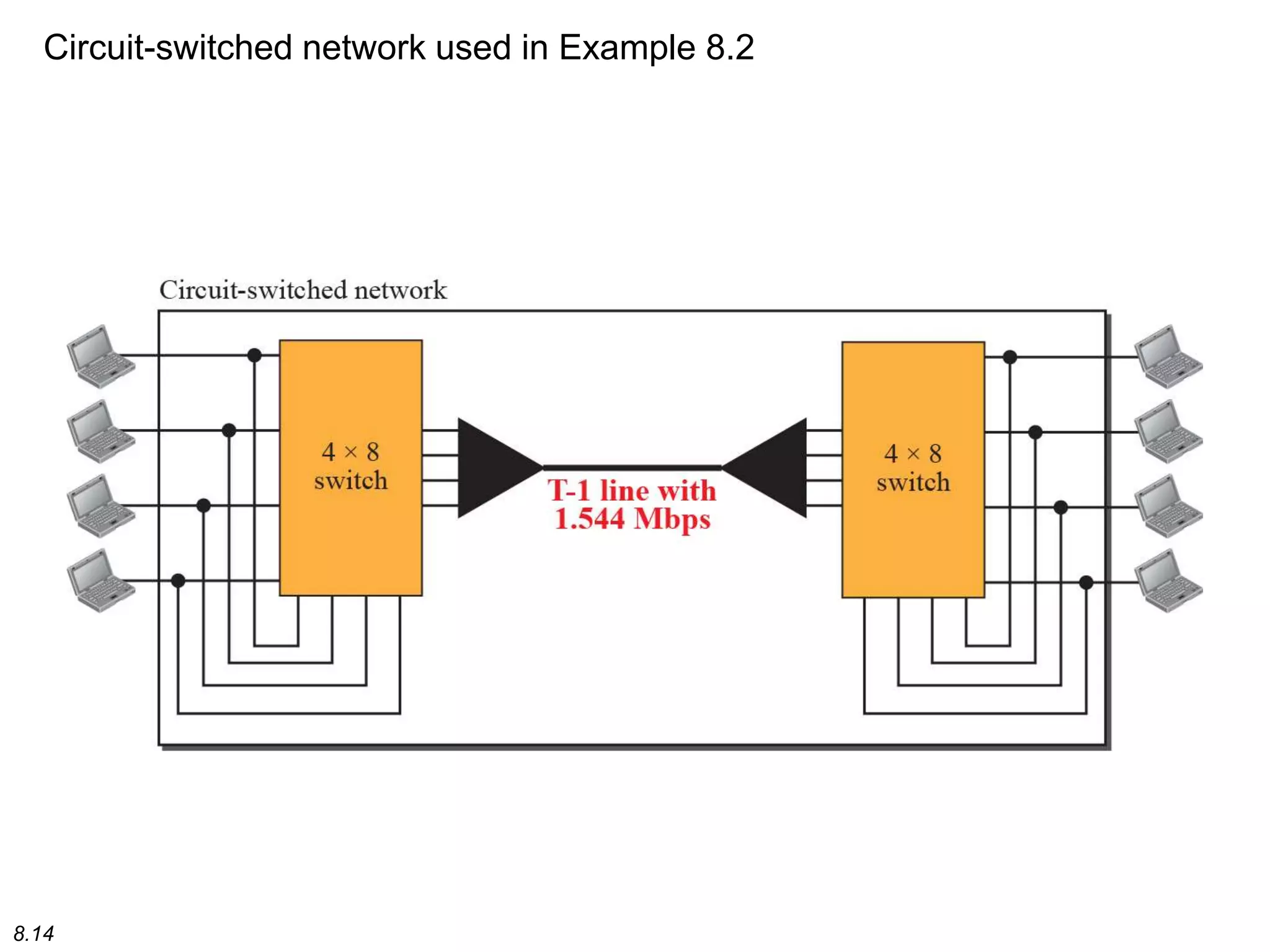
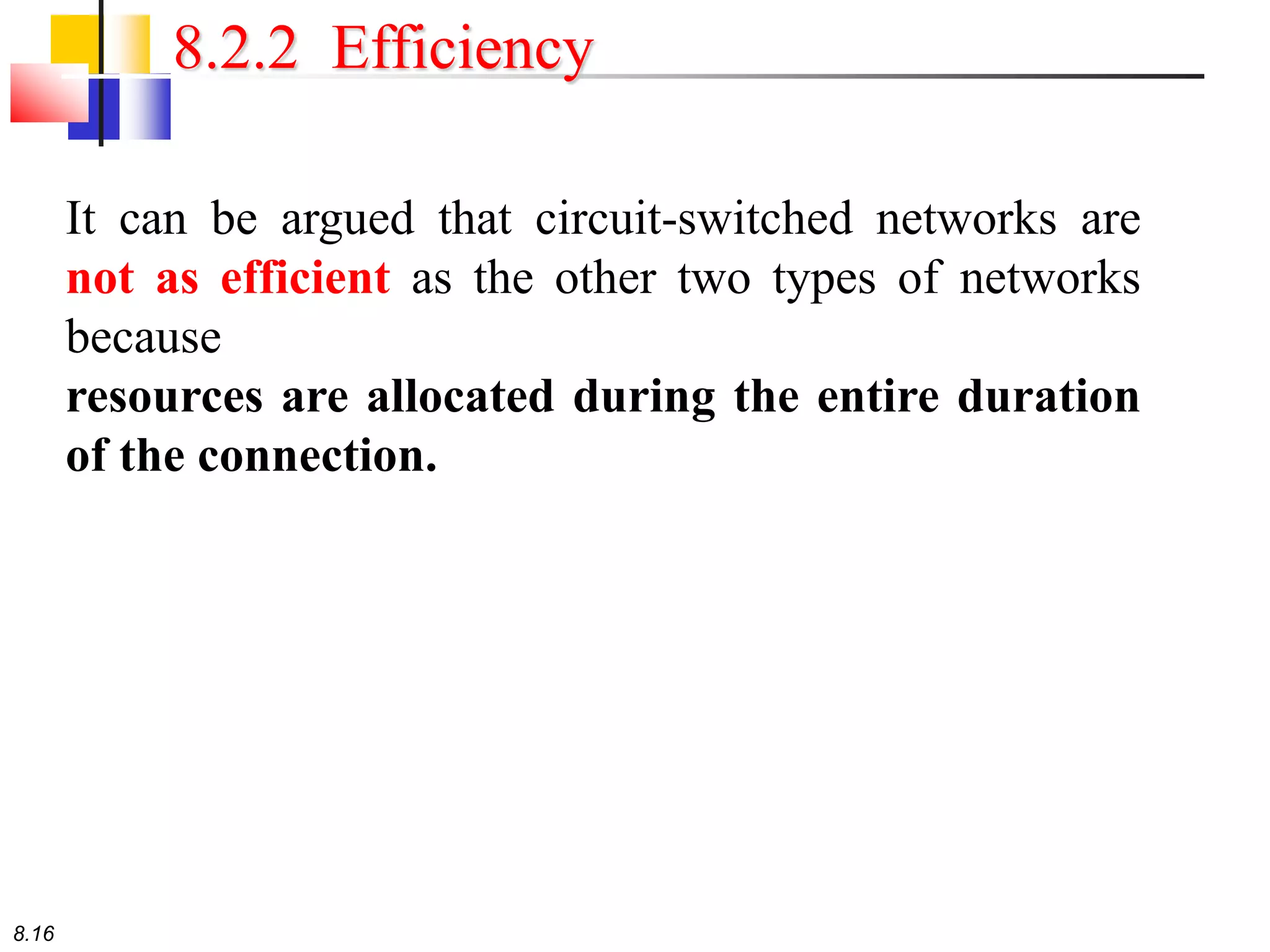
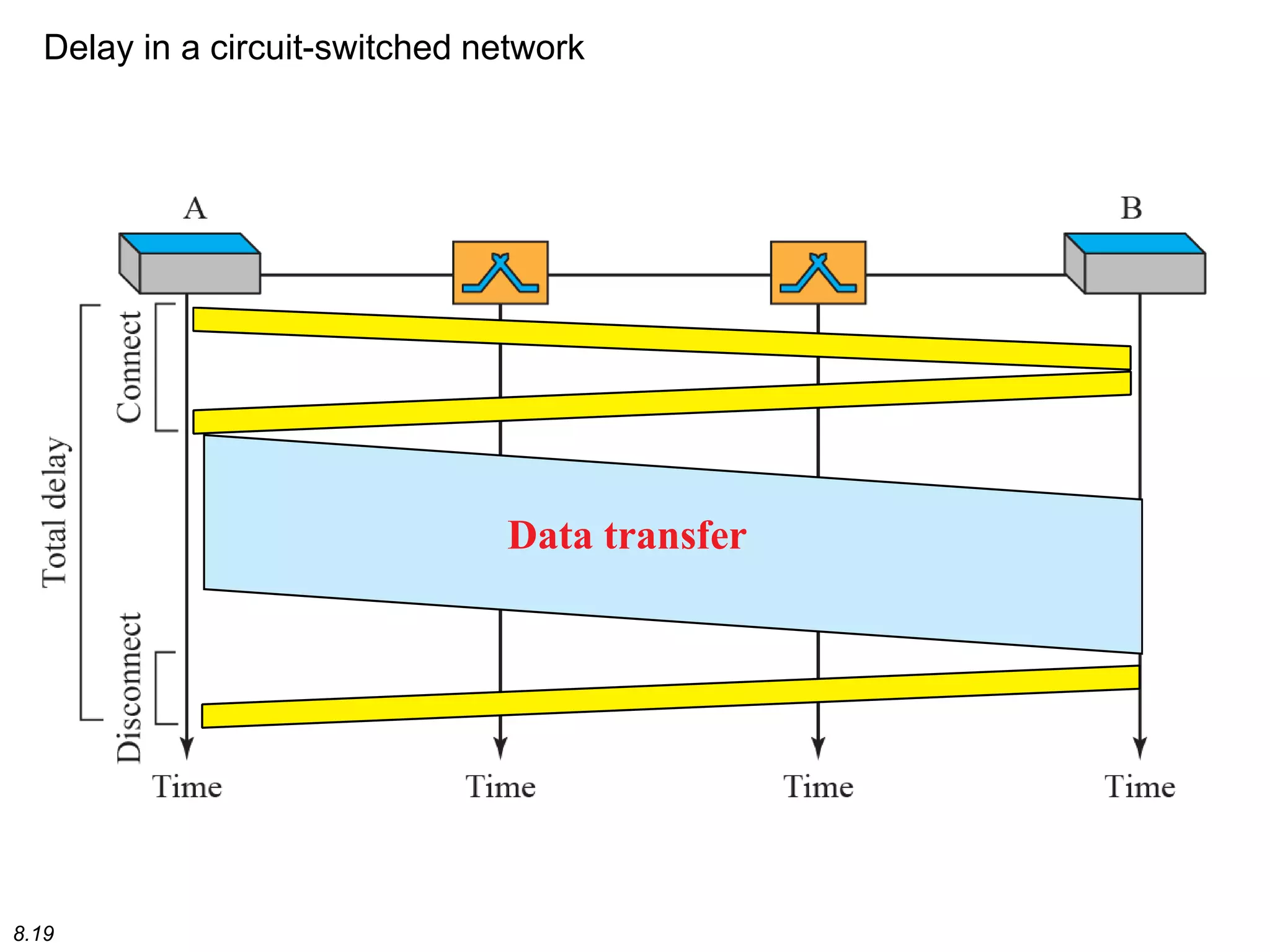
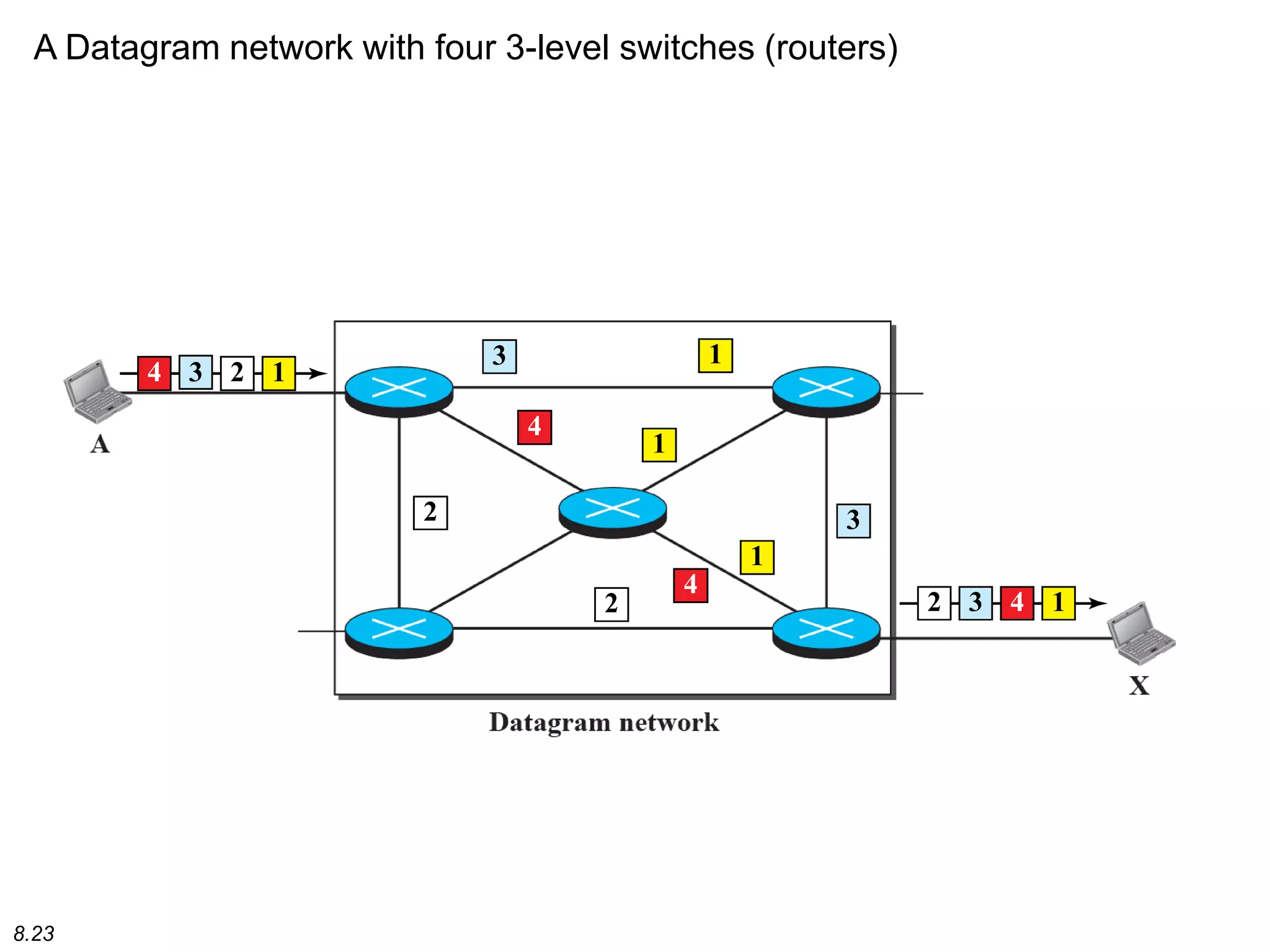
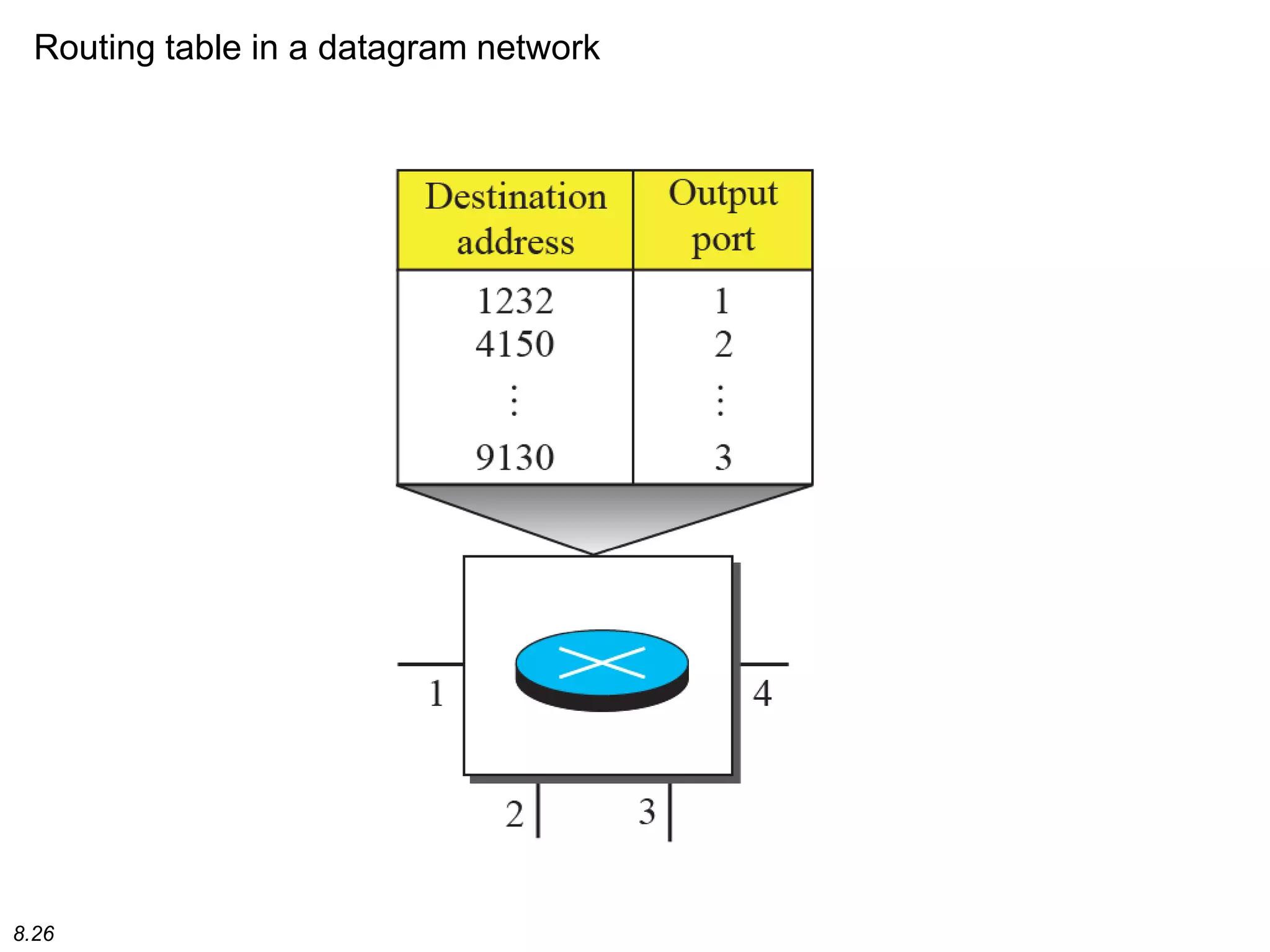
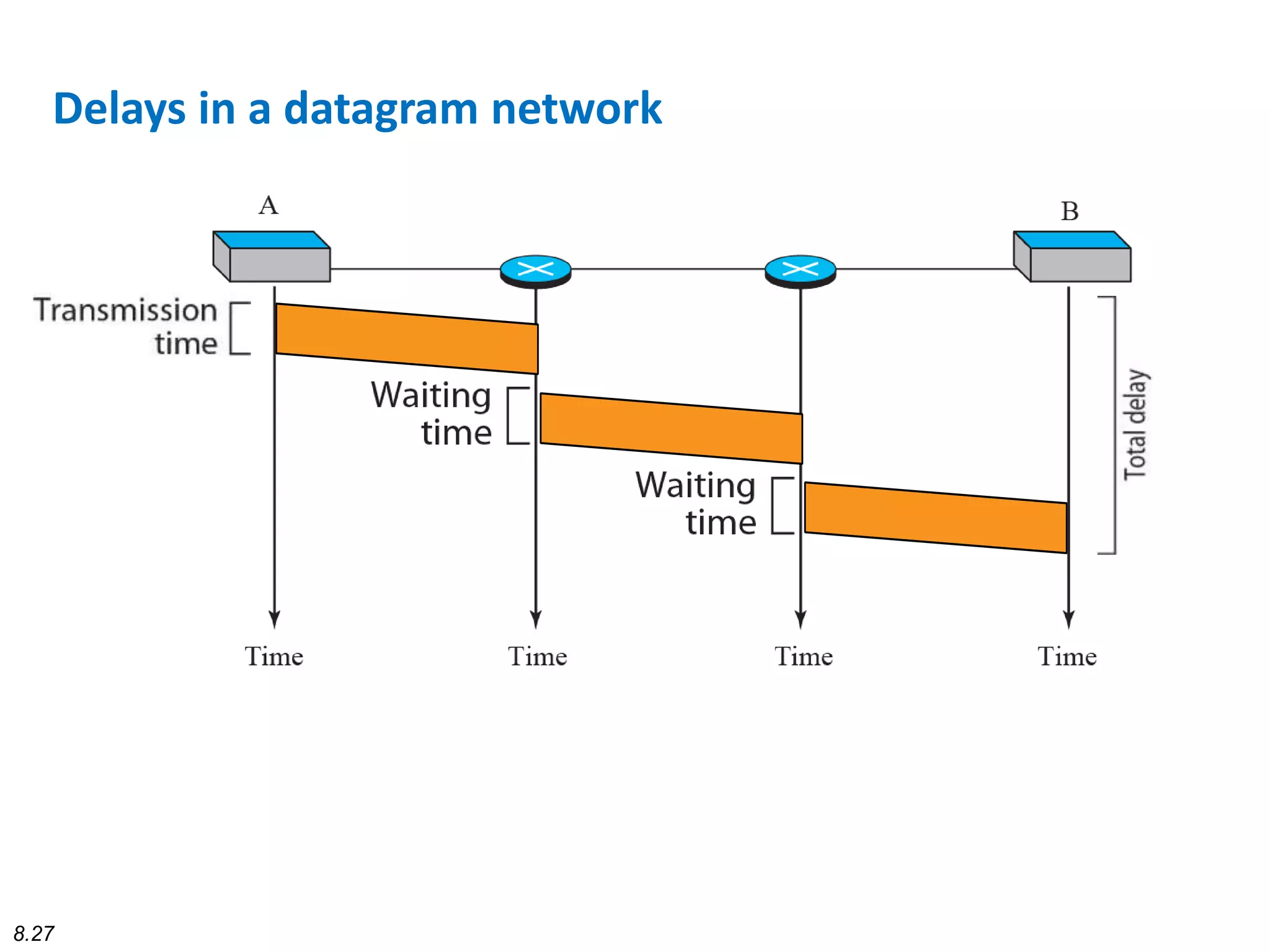
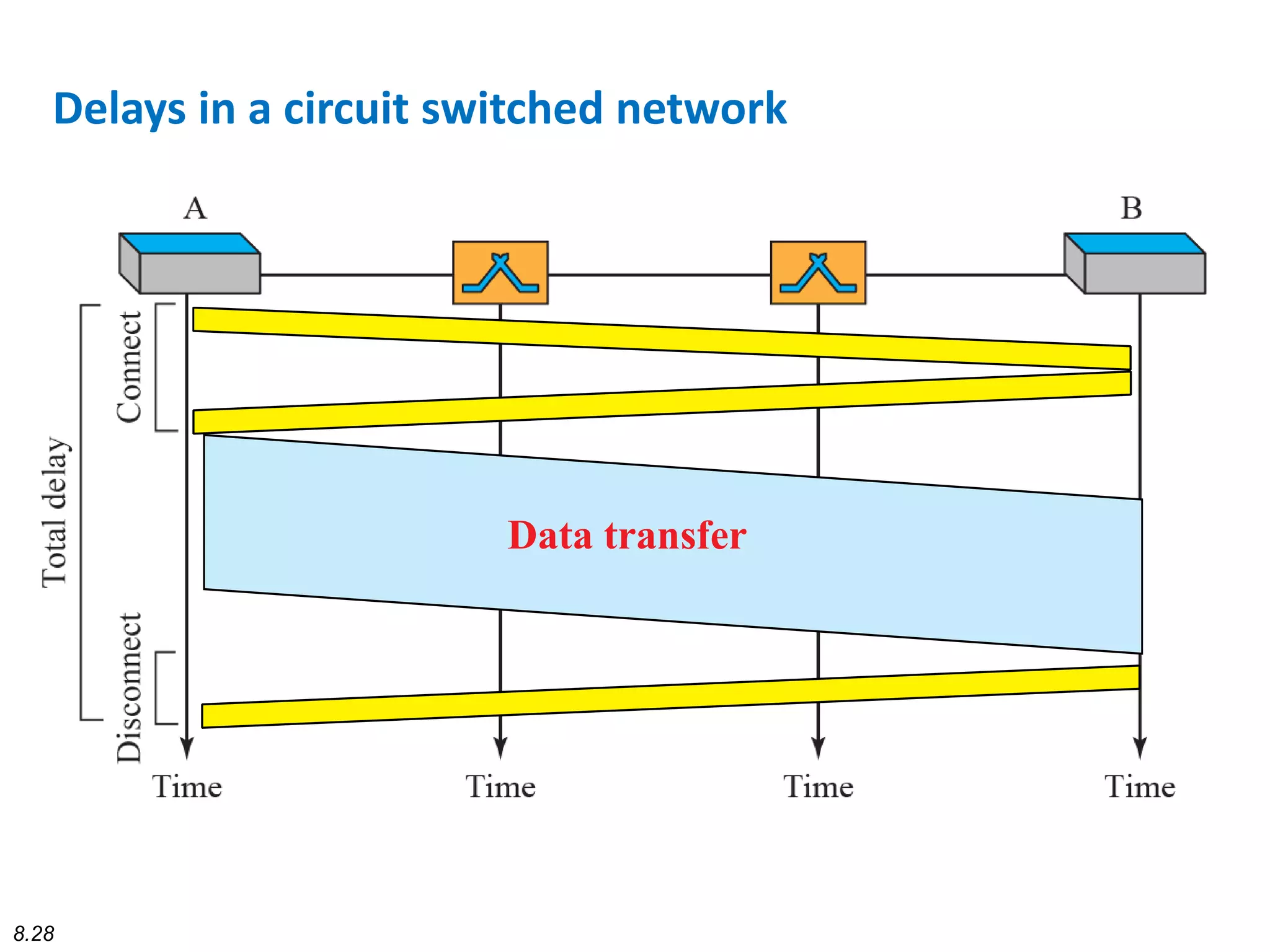
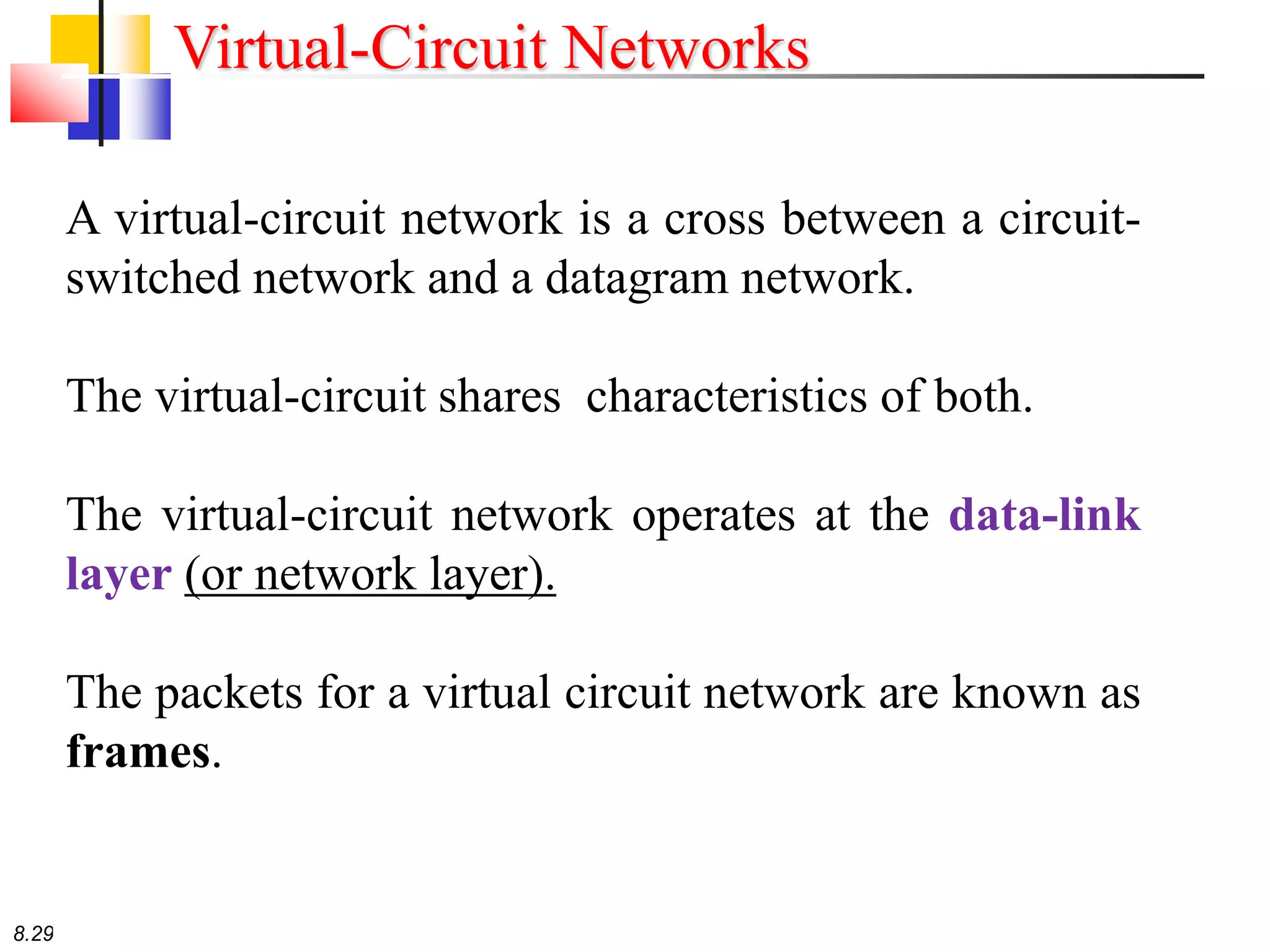
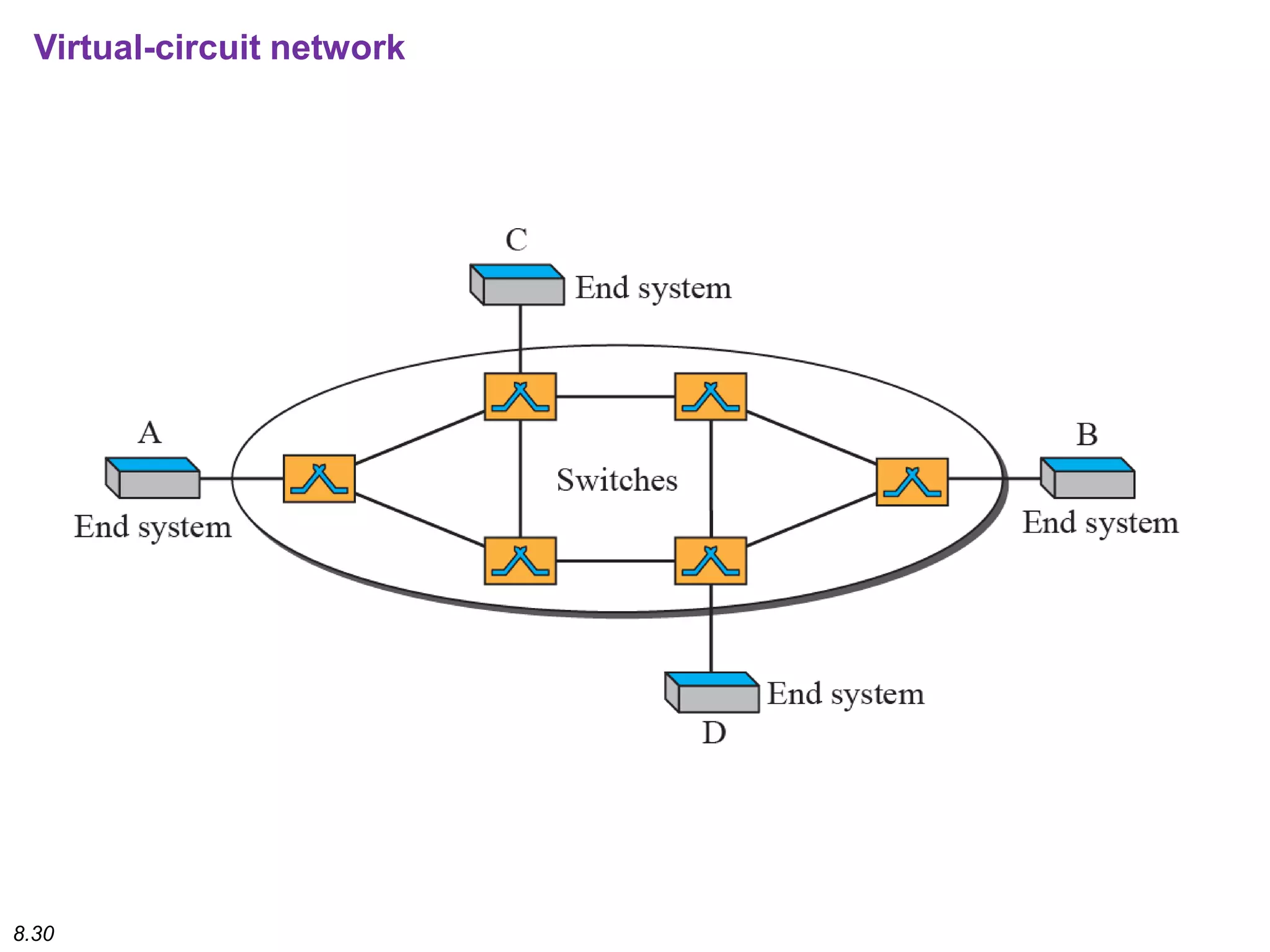
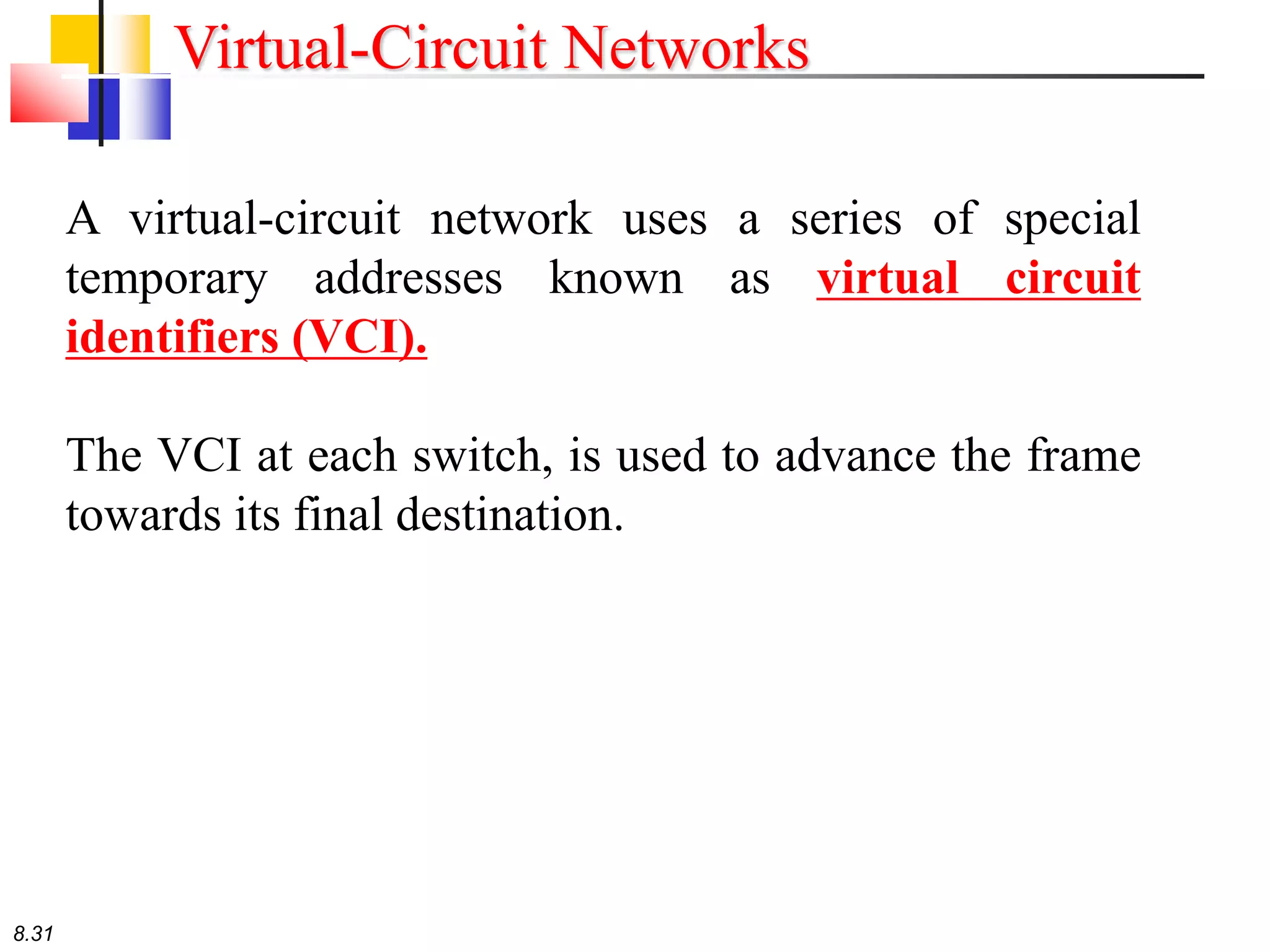
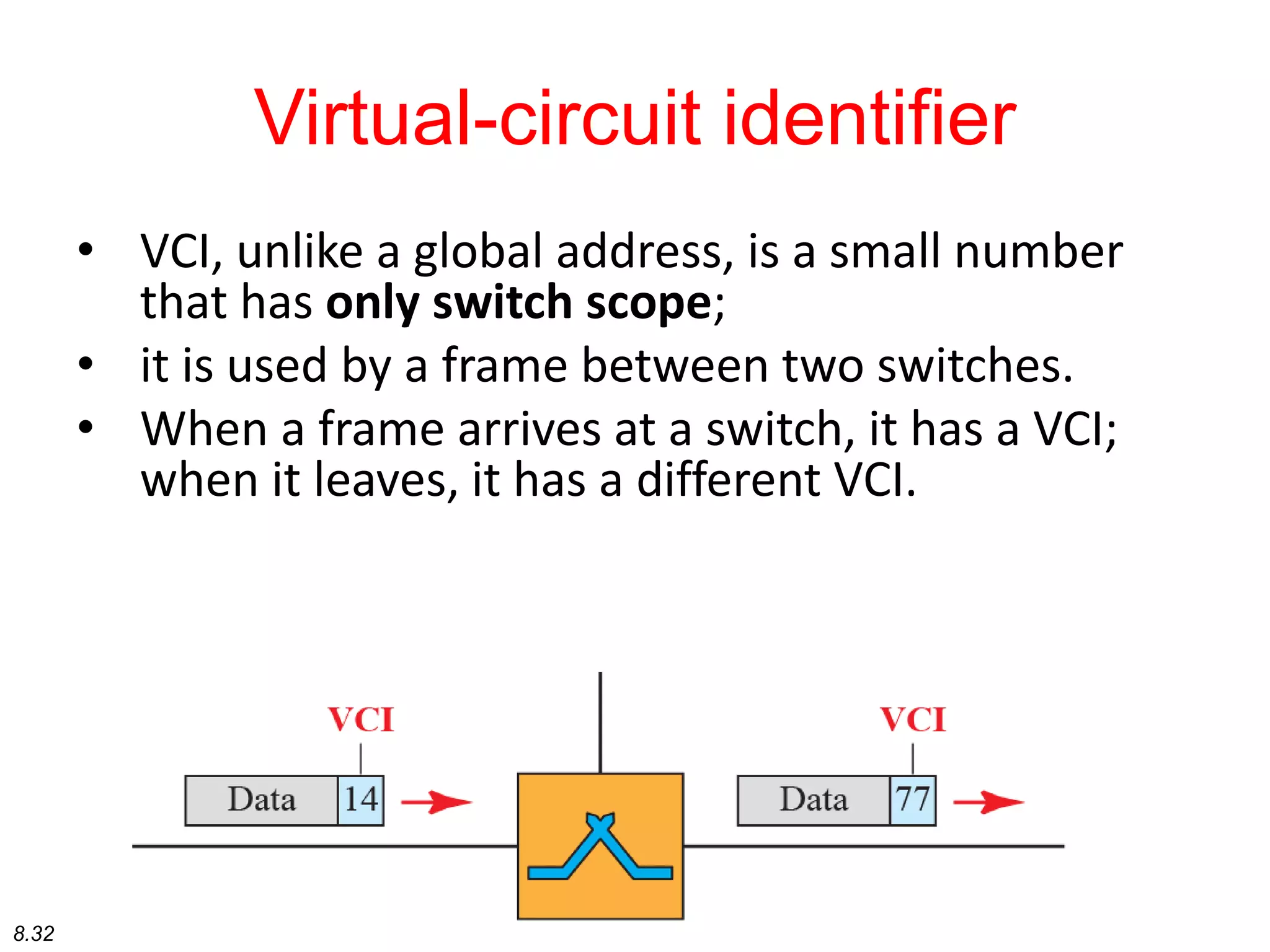
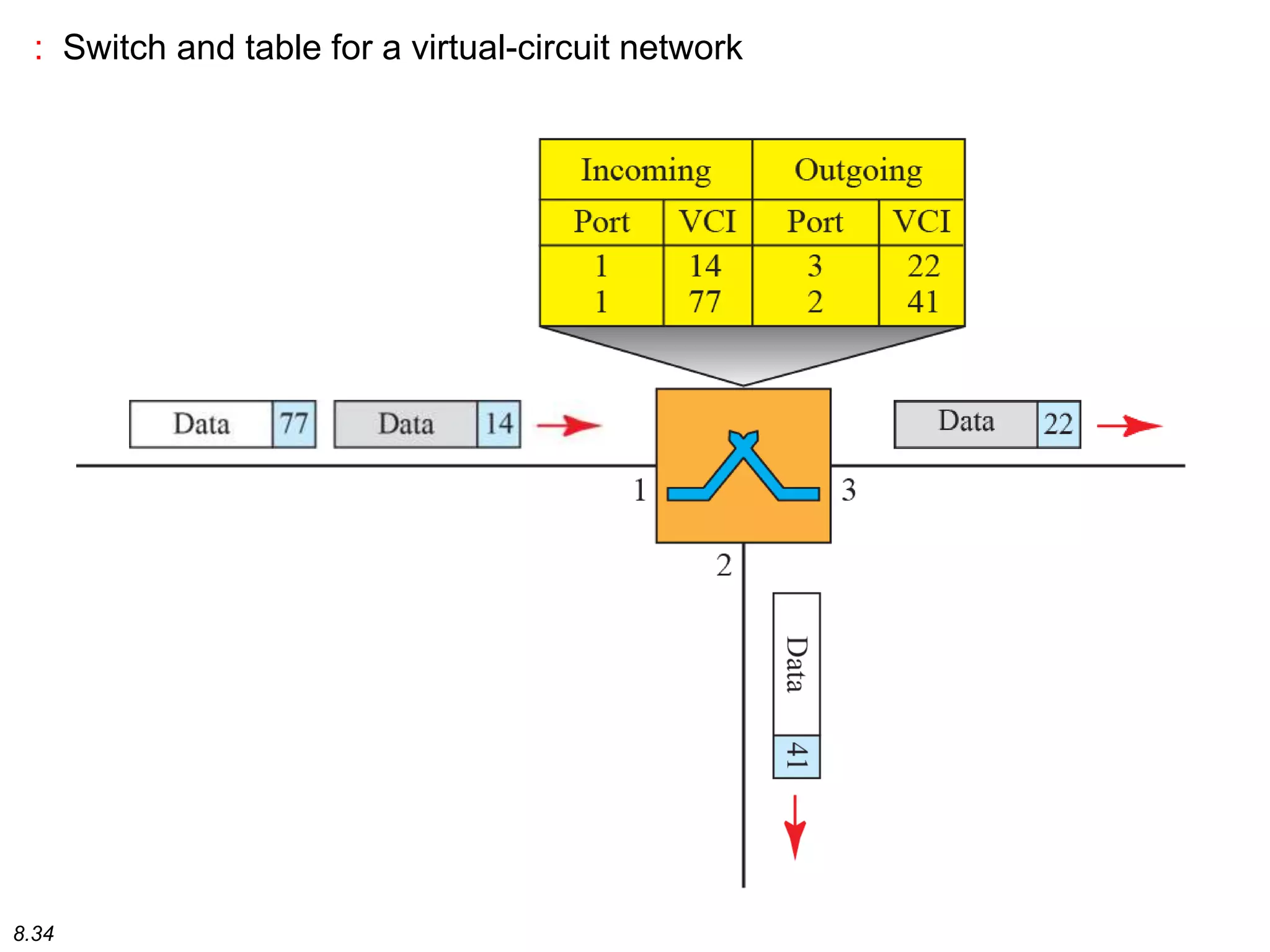
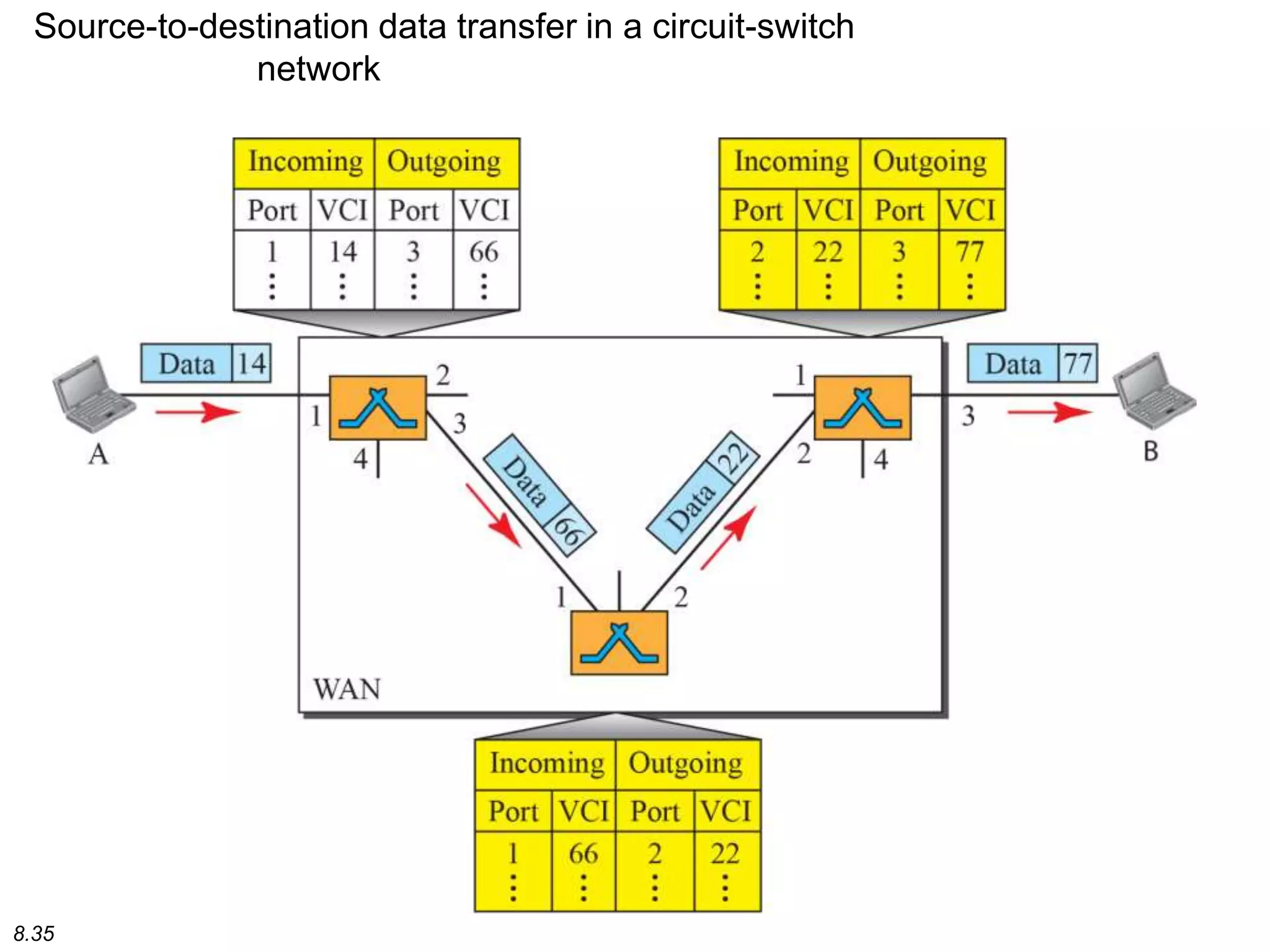
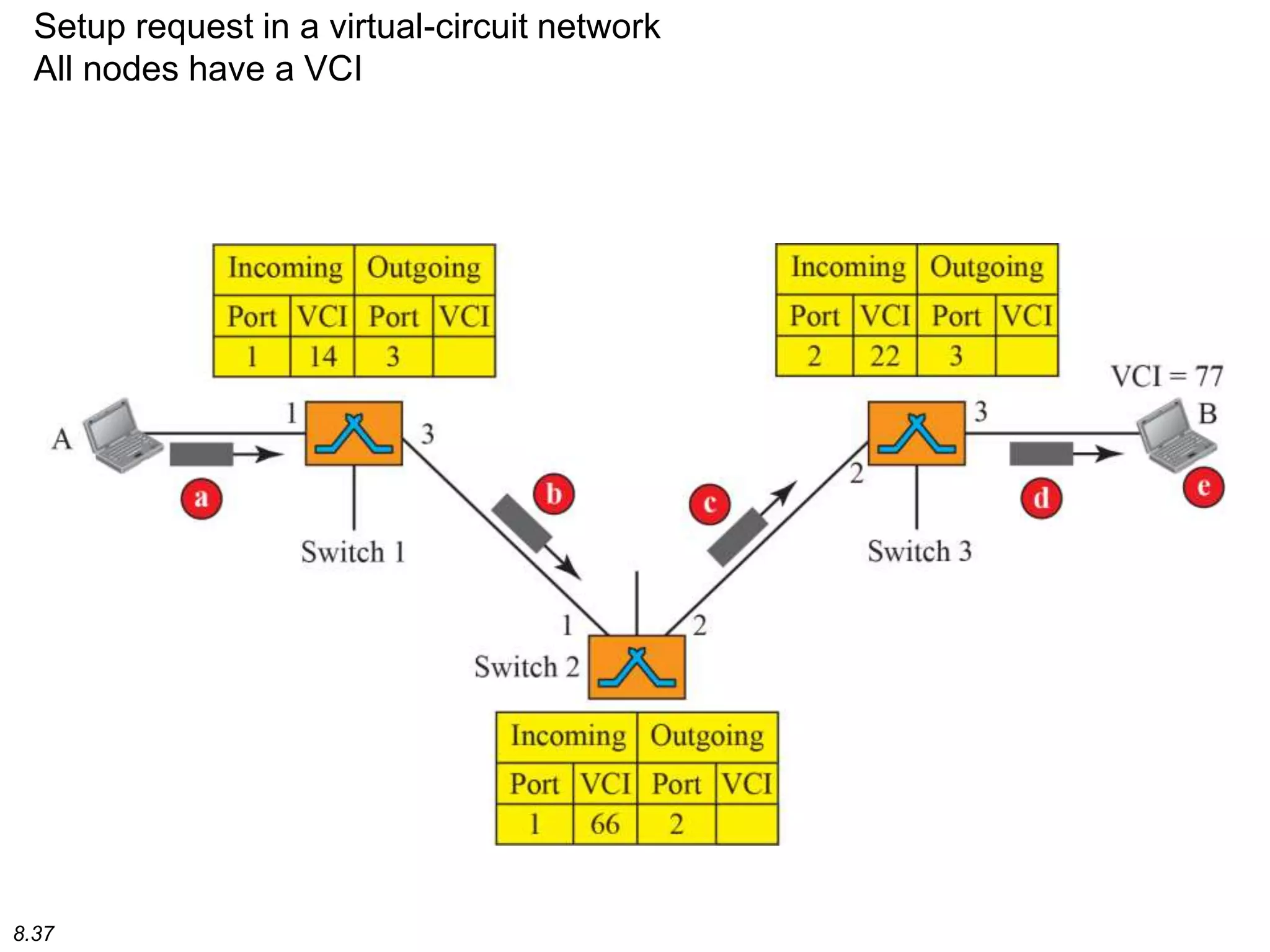
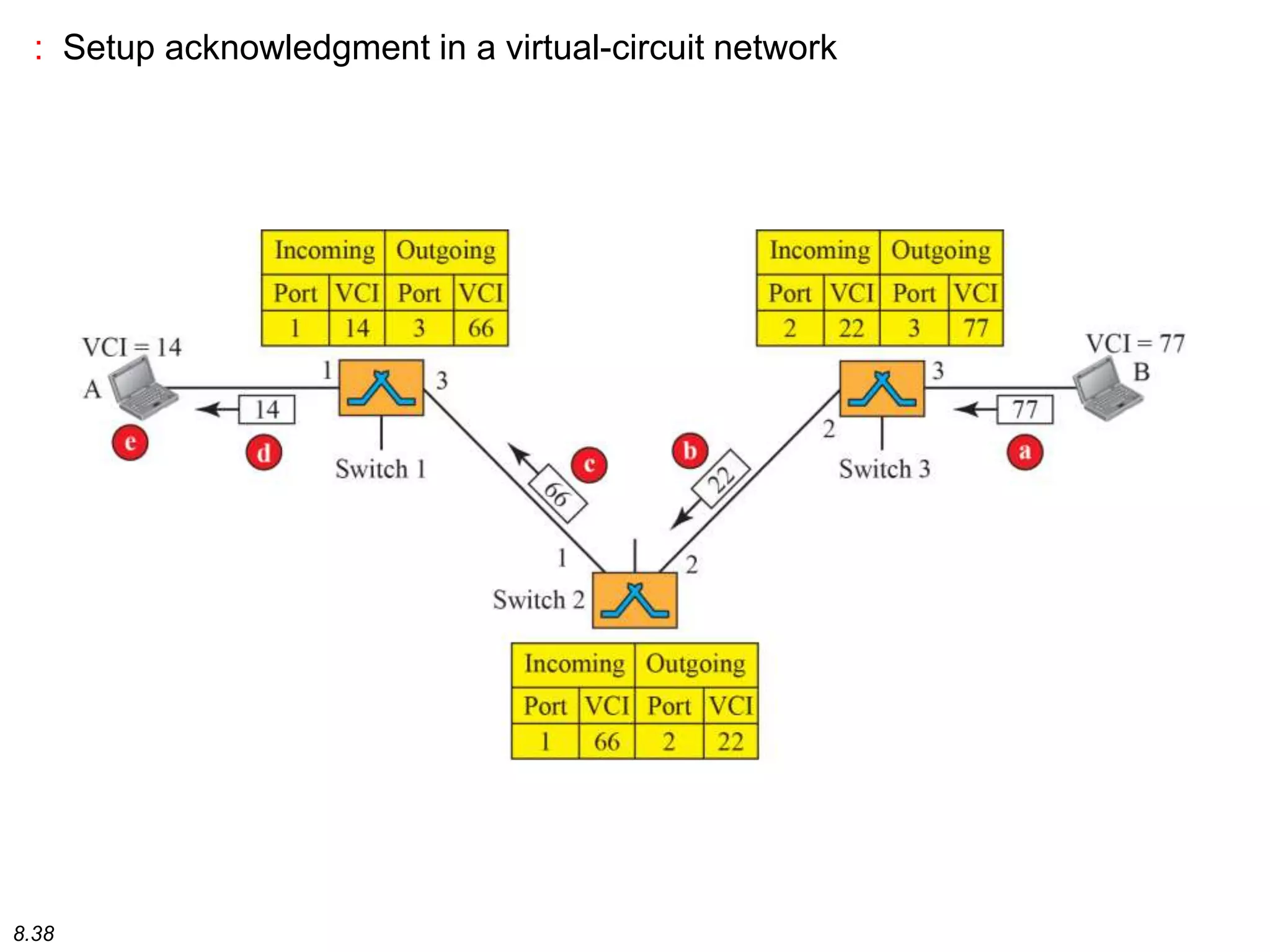
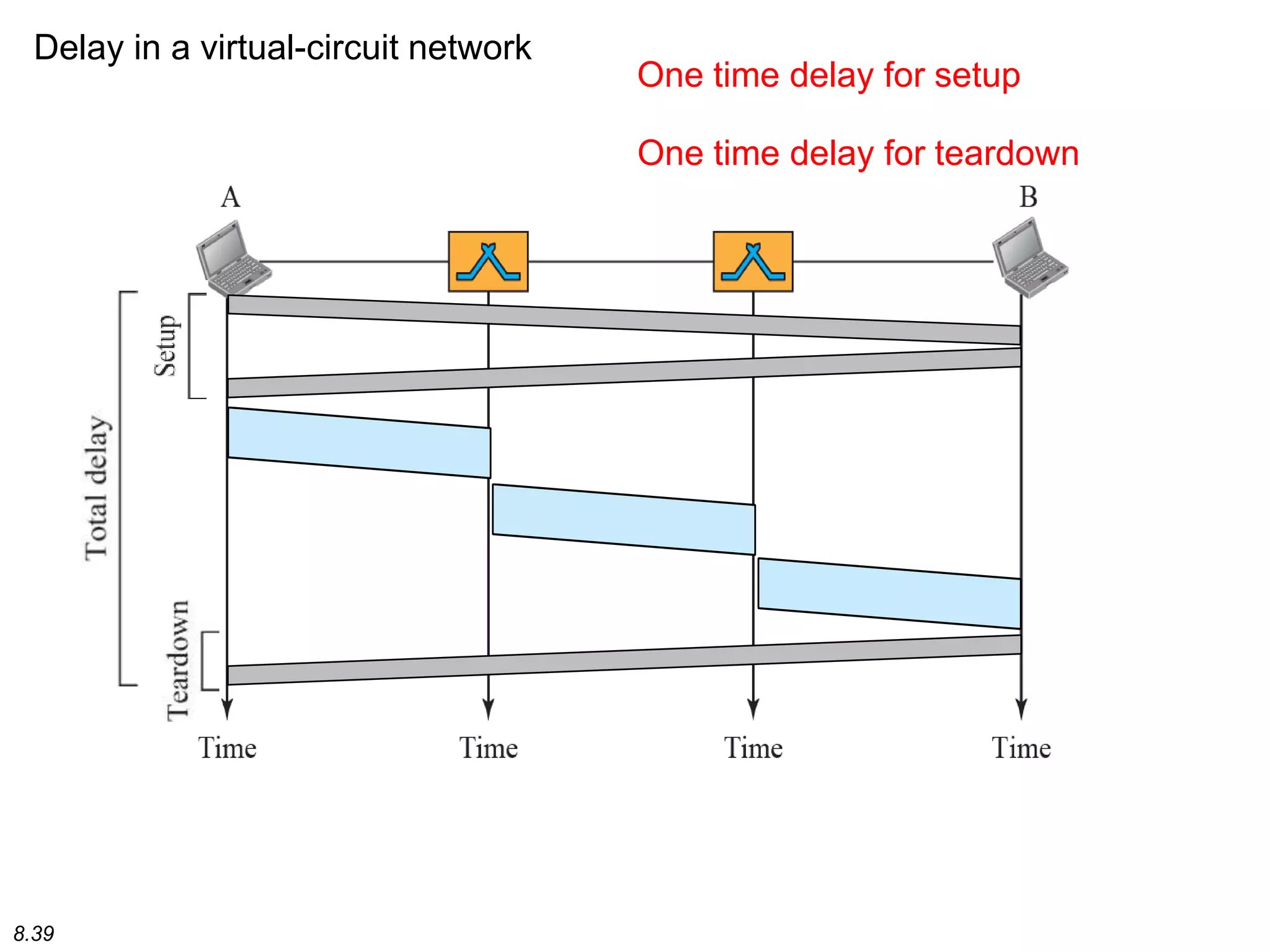
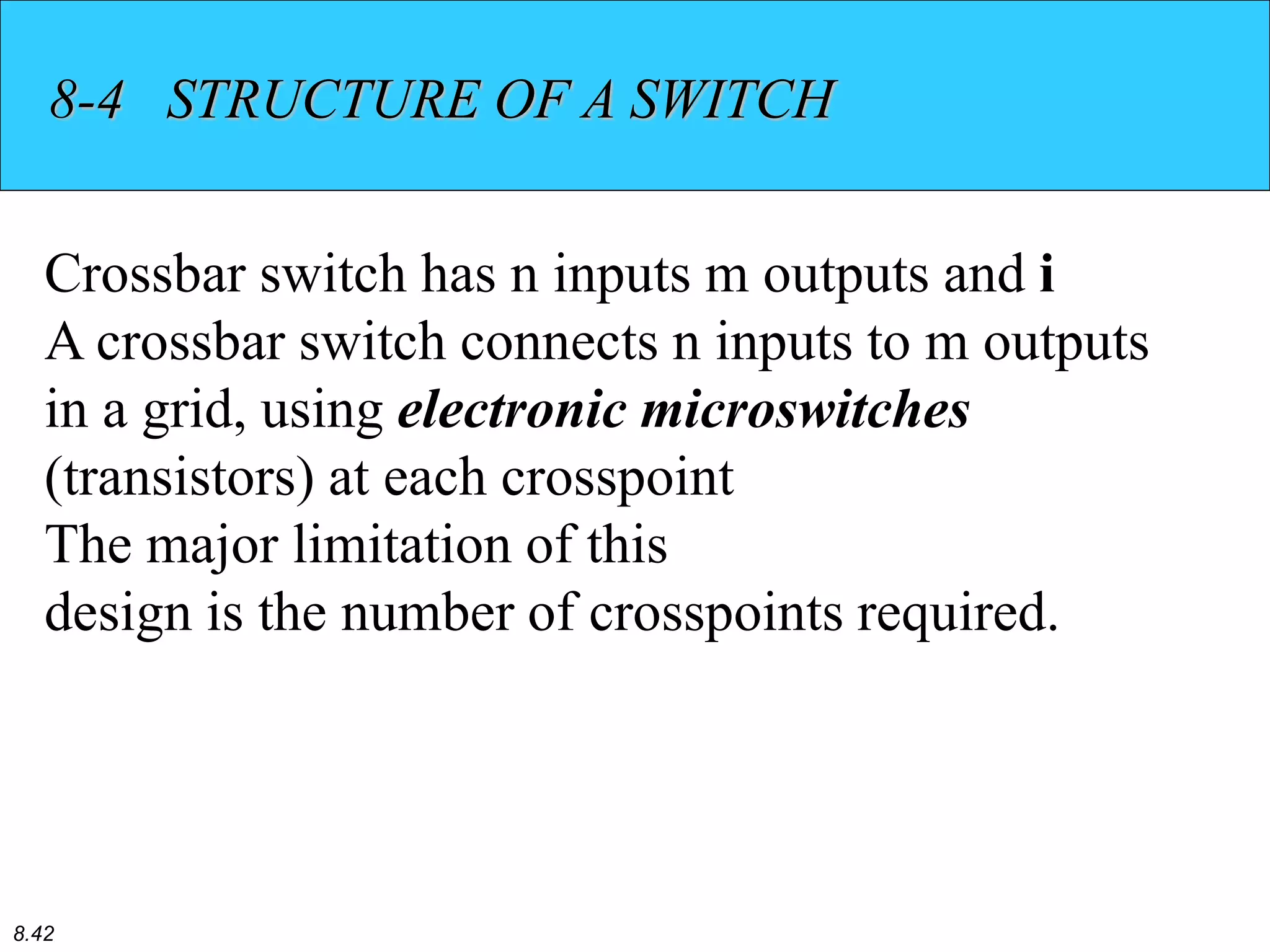
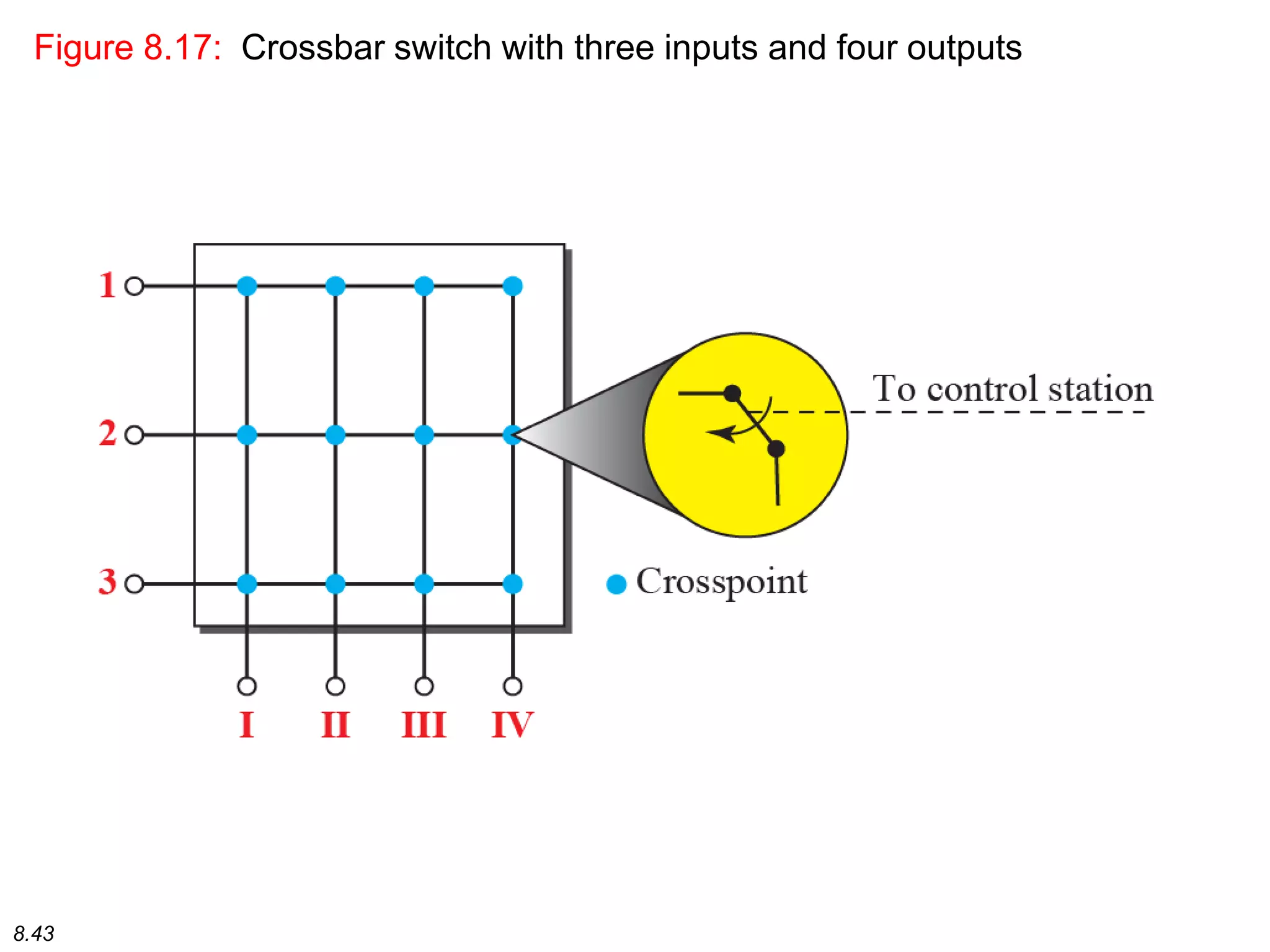
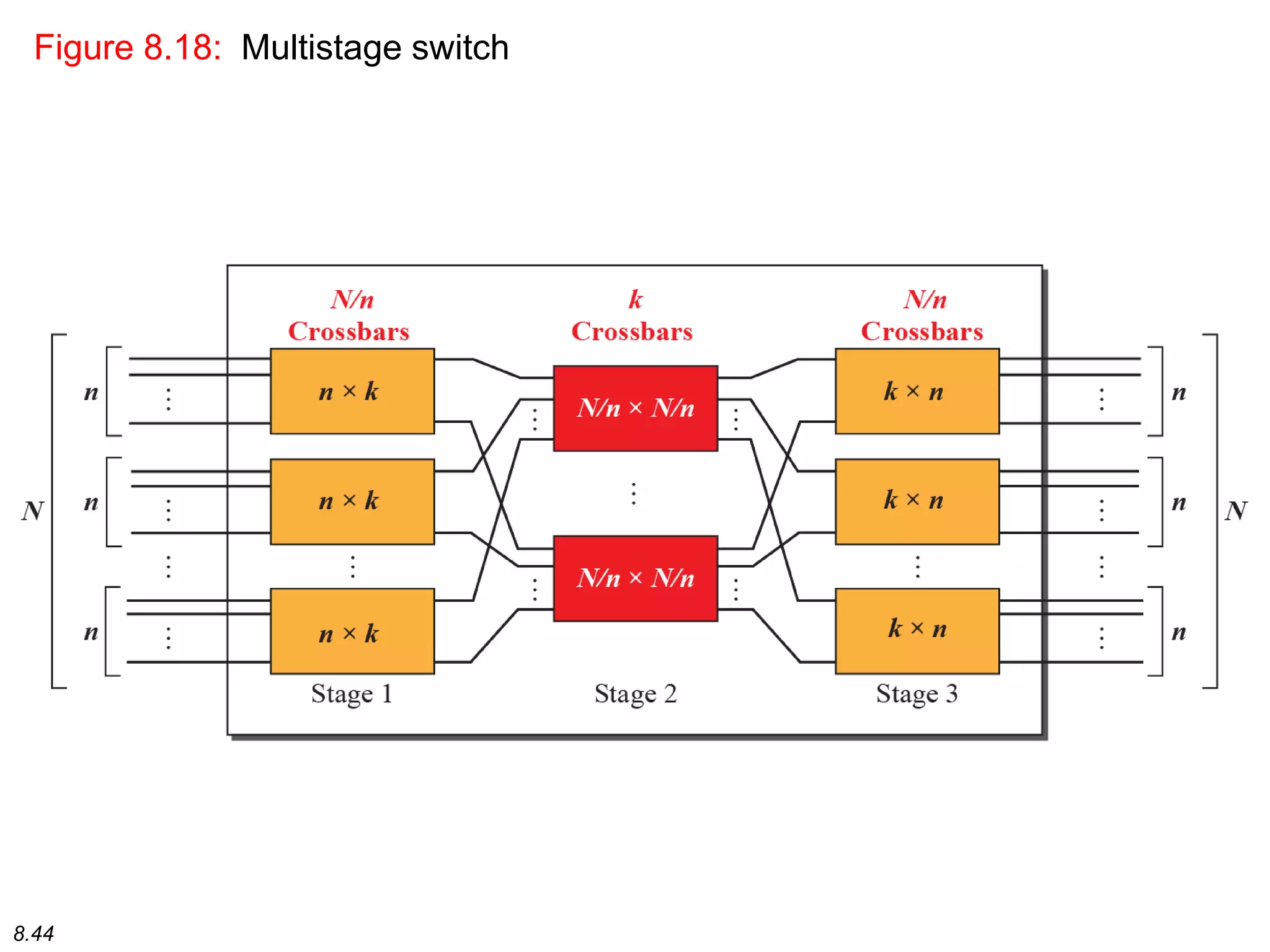
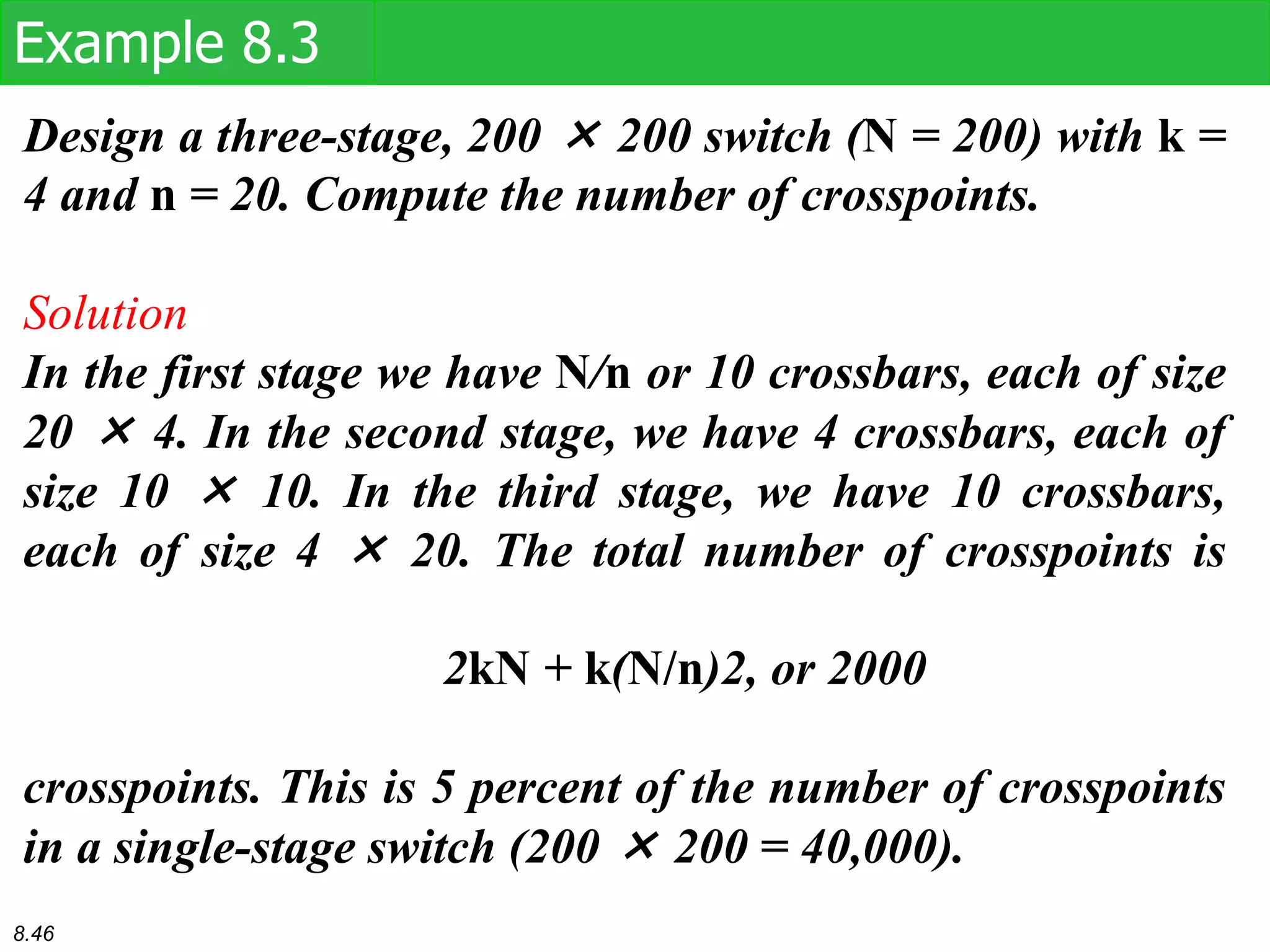
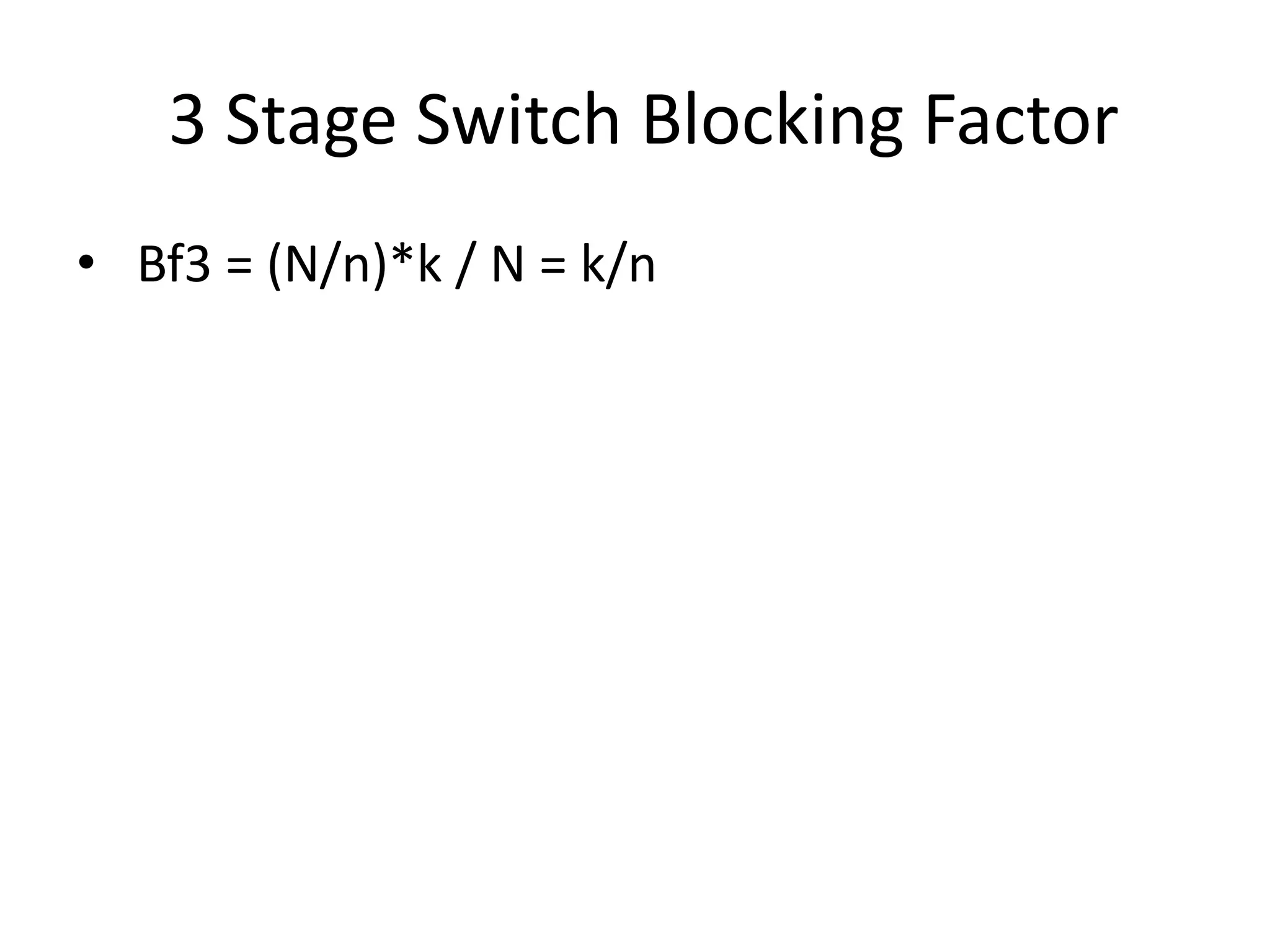
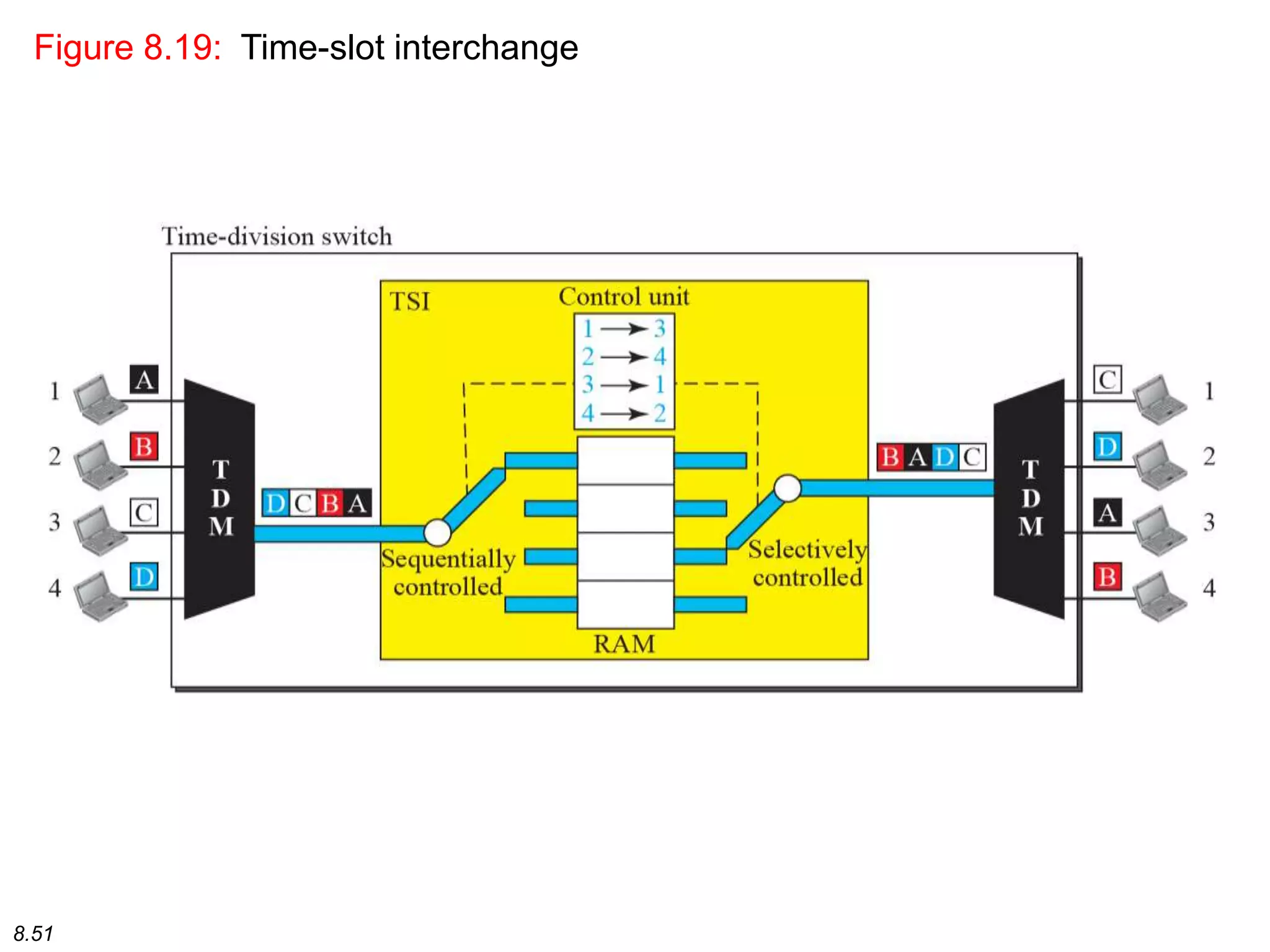
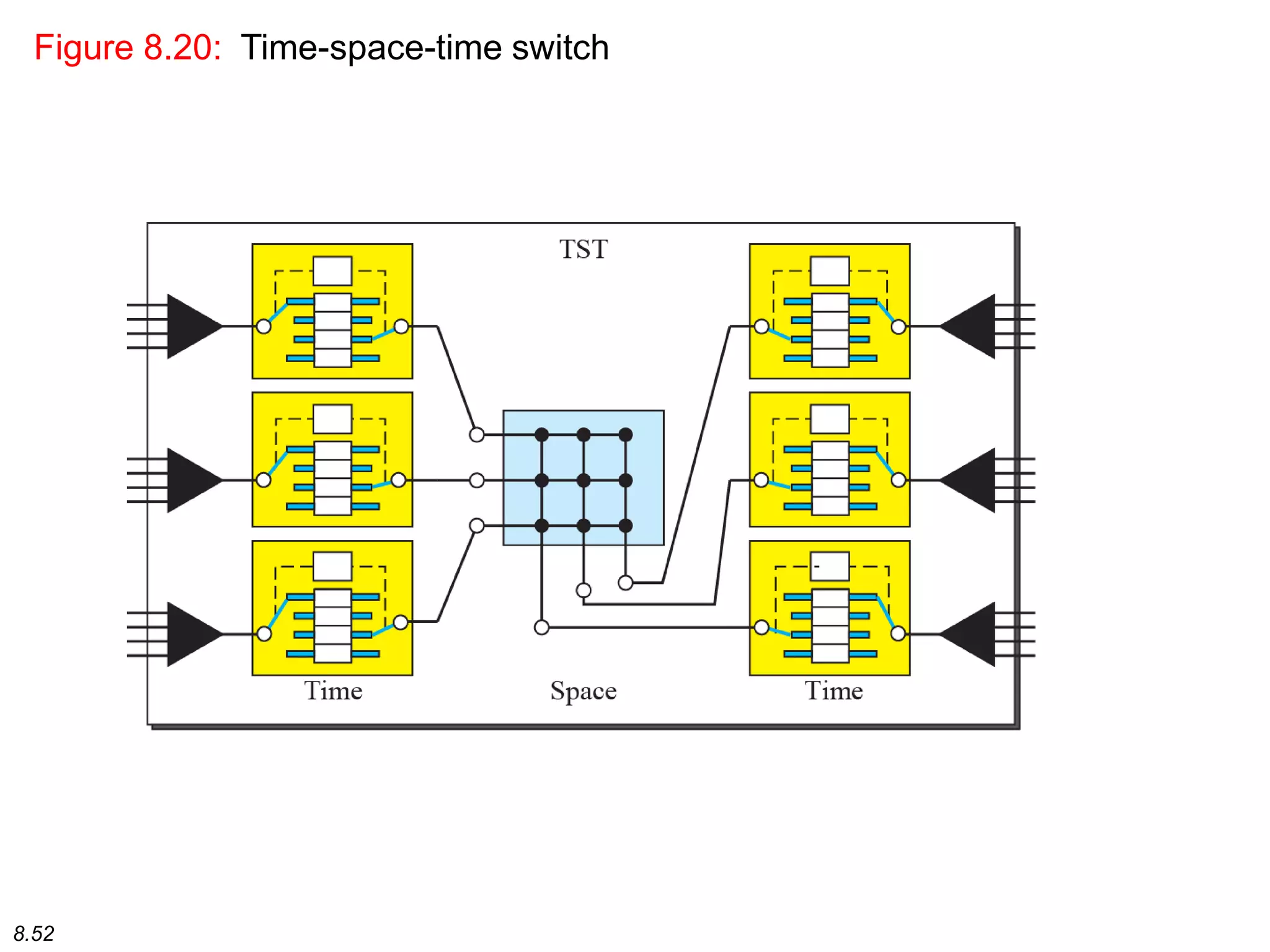
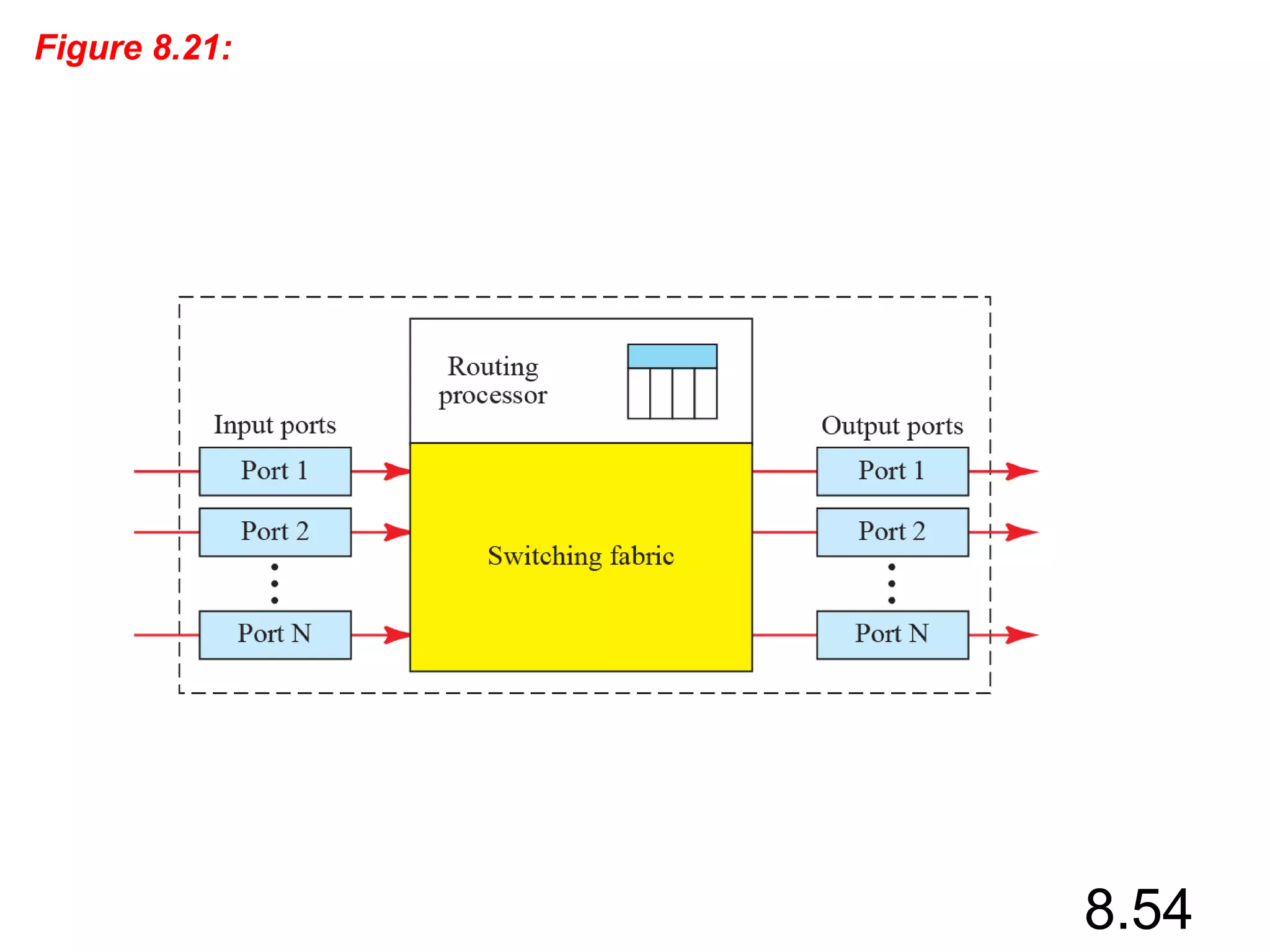
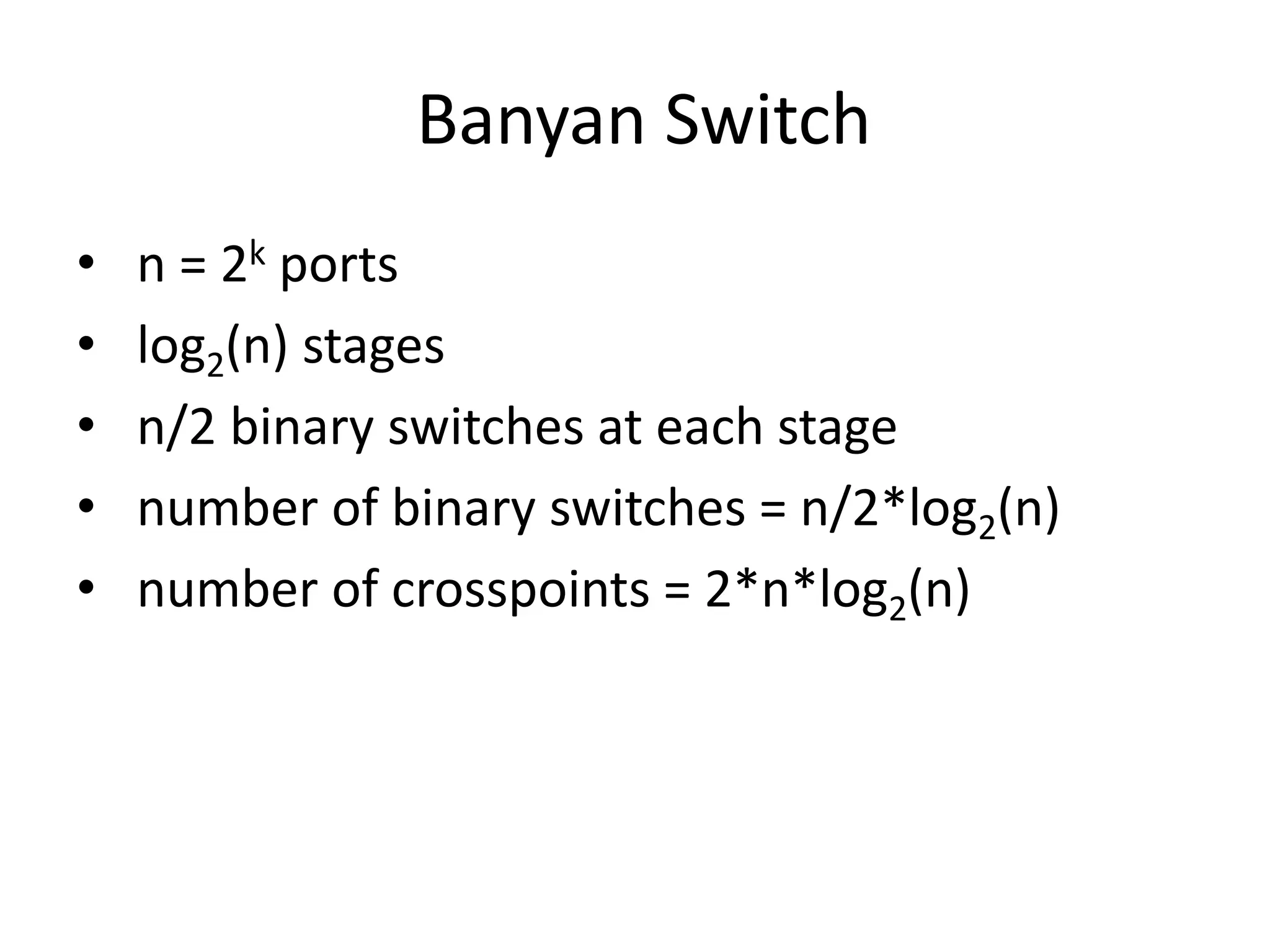
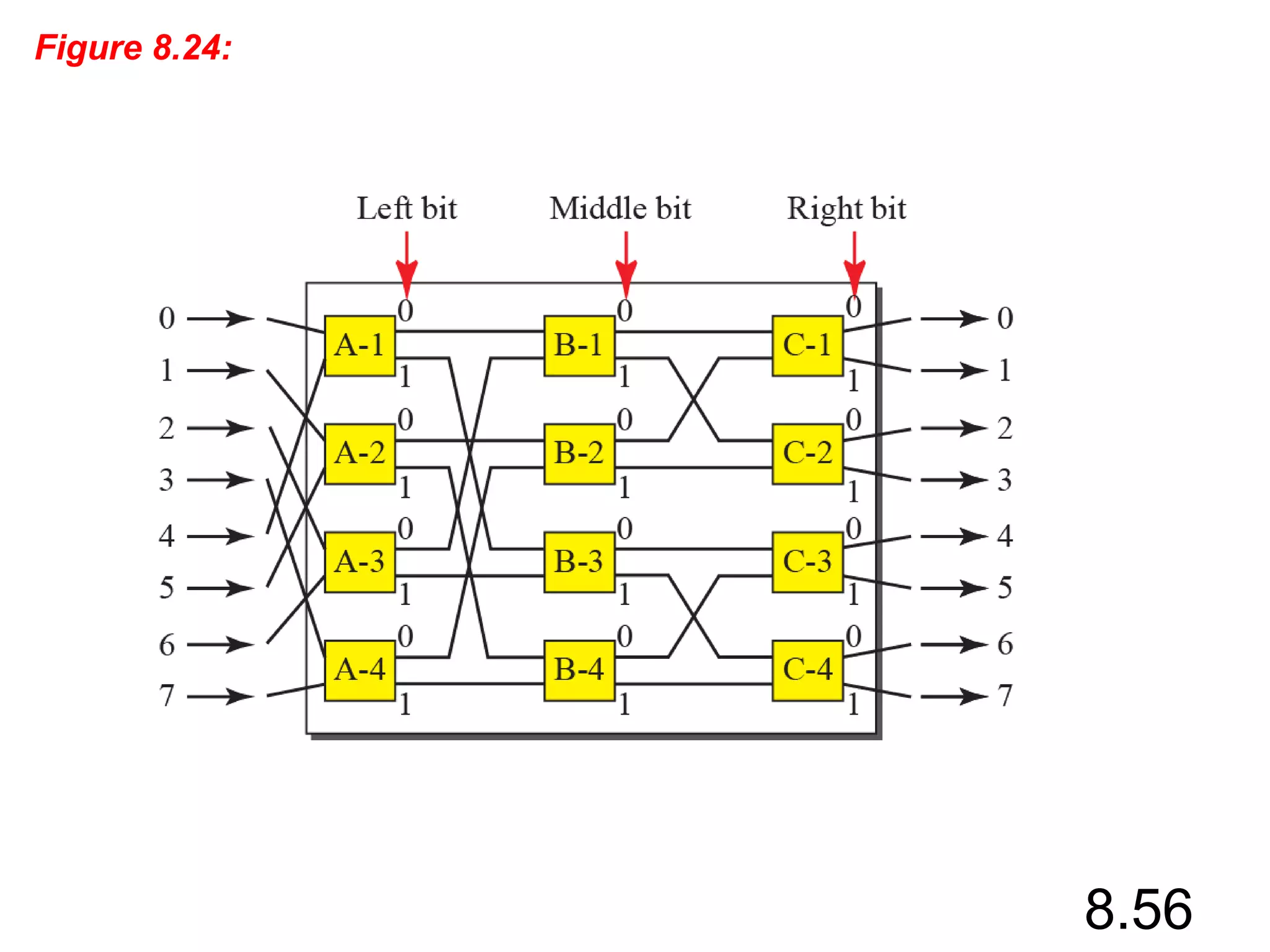
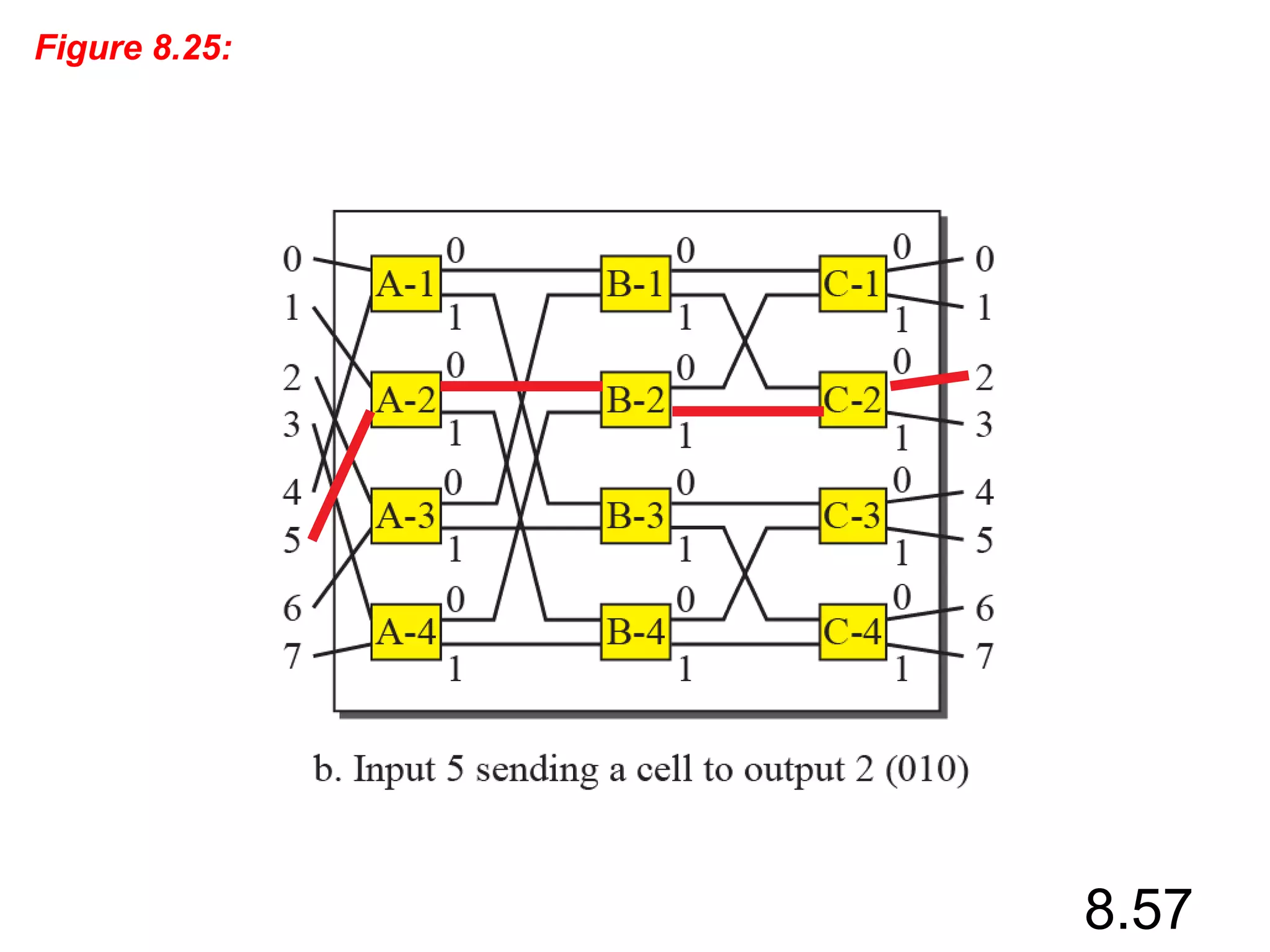
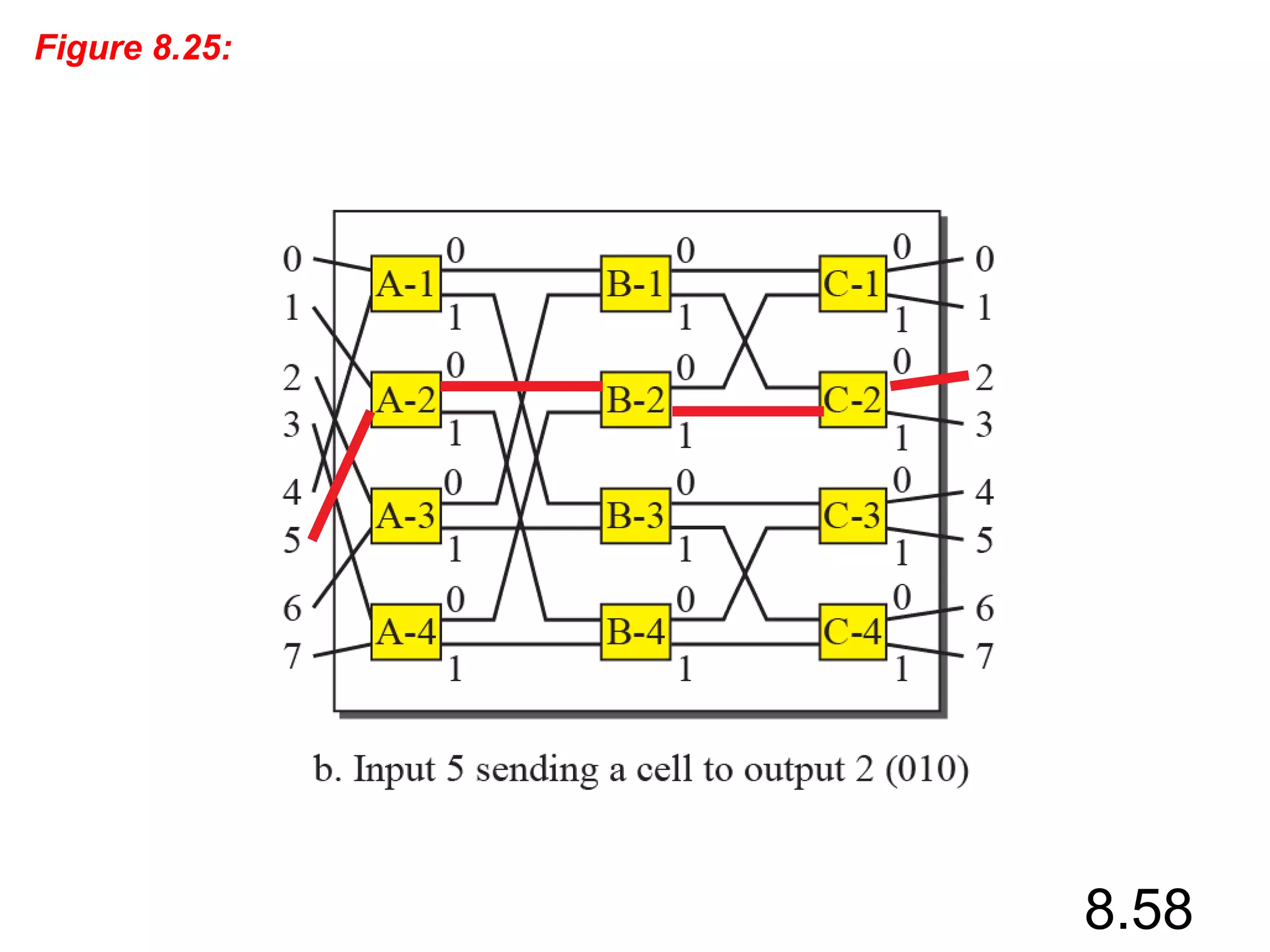
This document discusses different types of switching used in computer networks. It begins by introducing circuit switching, which operates at the physical layer and establishes a dedicated connection between sender and receiver. Packet switching is then covered, including datagram networks that operate at the network layer and treat each packet independently, and virtual circuit networks that operate at the data link layer using temporary virtual circuit identifiers to route frames. The document also discusses different types of switches including space division switches like crossbar switches and time division switches. Key aspects like setup, data transfer, and teardown phases are compared for different switching techniques.