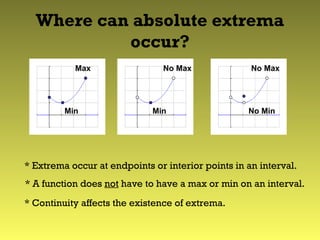
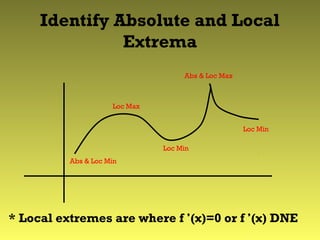
This document defines and discusses absolute and local extreme values of functions. It states that a continuous function on a closed interval will have both an absolute maximum and minimum value. Absolute extrema can occur at endpoints or interior points, while local extrema occur at interior points where the derivative is 0 or undefined. To find the absolute extrema on an interval, evaluate the function at the endpoints and critical points, and the greatest and least values will be the absolute max and min.

![Thm 1: Extreme Value Theorem
If f is continuous on a closed interval [a,b],
then f has both a maximum value and a
minimum value on the interval.
* What is the “worst case scenario,”
and what happens then?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture11relativeextrema-200523001236/85/Lecture-11-relative-extrema-4-320.jpg)



![Finding Absolute
Extrema on [a,b]…
To find the absolute extrema of a
continuous function f on [a,b]…
1. Evaluate f at the endpoints a and b.
2. Find the critical numbers of f on [a,b].
3. Evaluate f at each critical number.
4. Compare values. The greatest is the
absolute max and the least is the
absolute min.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture11relativeextrema-200523001236/85/Lecture-11-relative-extrema-9-320.jpg)
