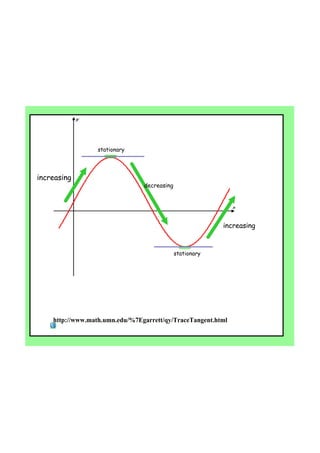
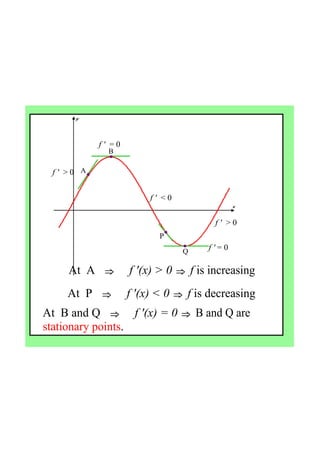
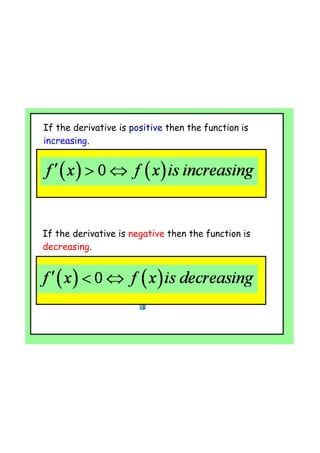
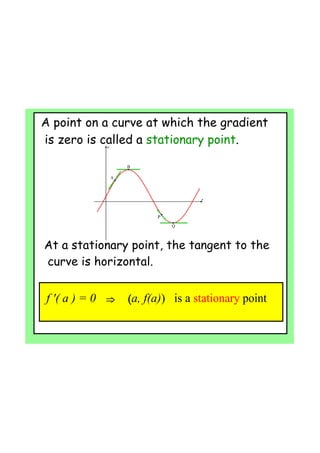
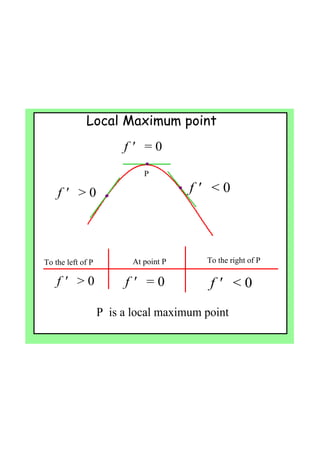
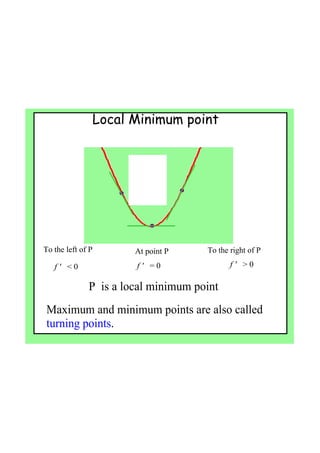
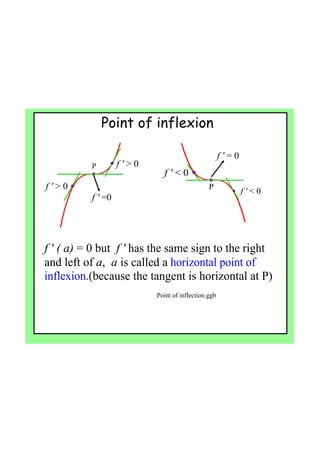
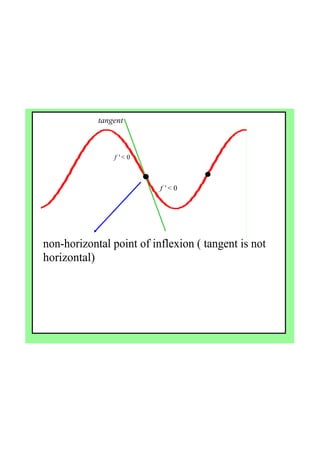
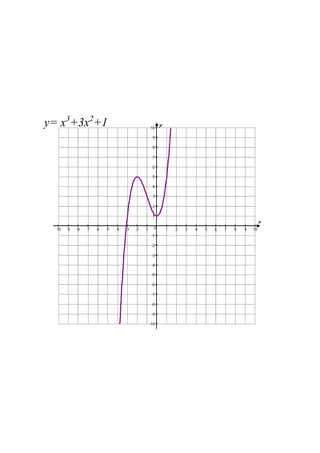
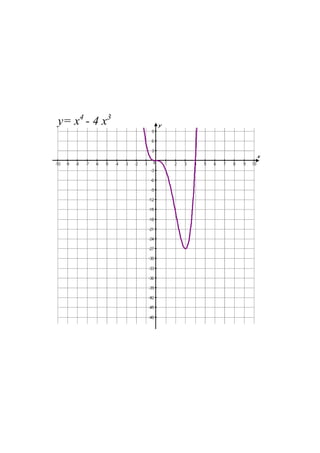
By the end of the lesson, students will be able to use derivatives to find maximum and minimum points of a function, and use second derivatives to determine the nature of stationary points and points of inflection. Specifically, they will learn that: (1) if the first derivative is zero at a point, it is a stationary point; (2) the second derivative test can determine if it is a local max, min or point of inflection; and (3) points of inflection occur when the curve changes concavity. Students will apply these concepts to find the stationary points of sample functions and classify their nature.