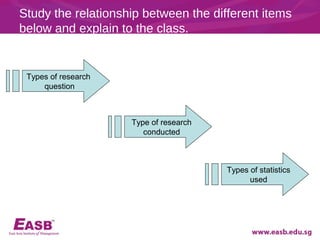
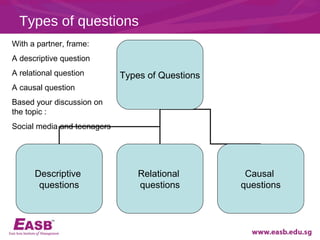
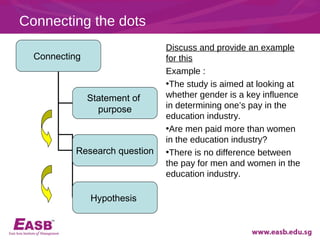
This document discusses key aspects of developing a research study such as determining research questions, purpose statements, hypotheses, and types of research questions. It provides guidance on formulating feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, and relevant research topics using the FINER criteria. Descriptive, relational, and causal questions are defined. Steps for constructing a research question and hypothesis are outlined. Finally, tips for structuring a research report are provided.