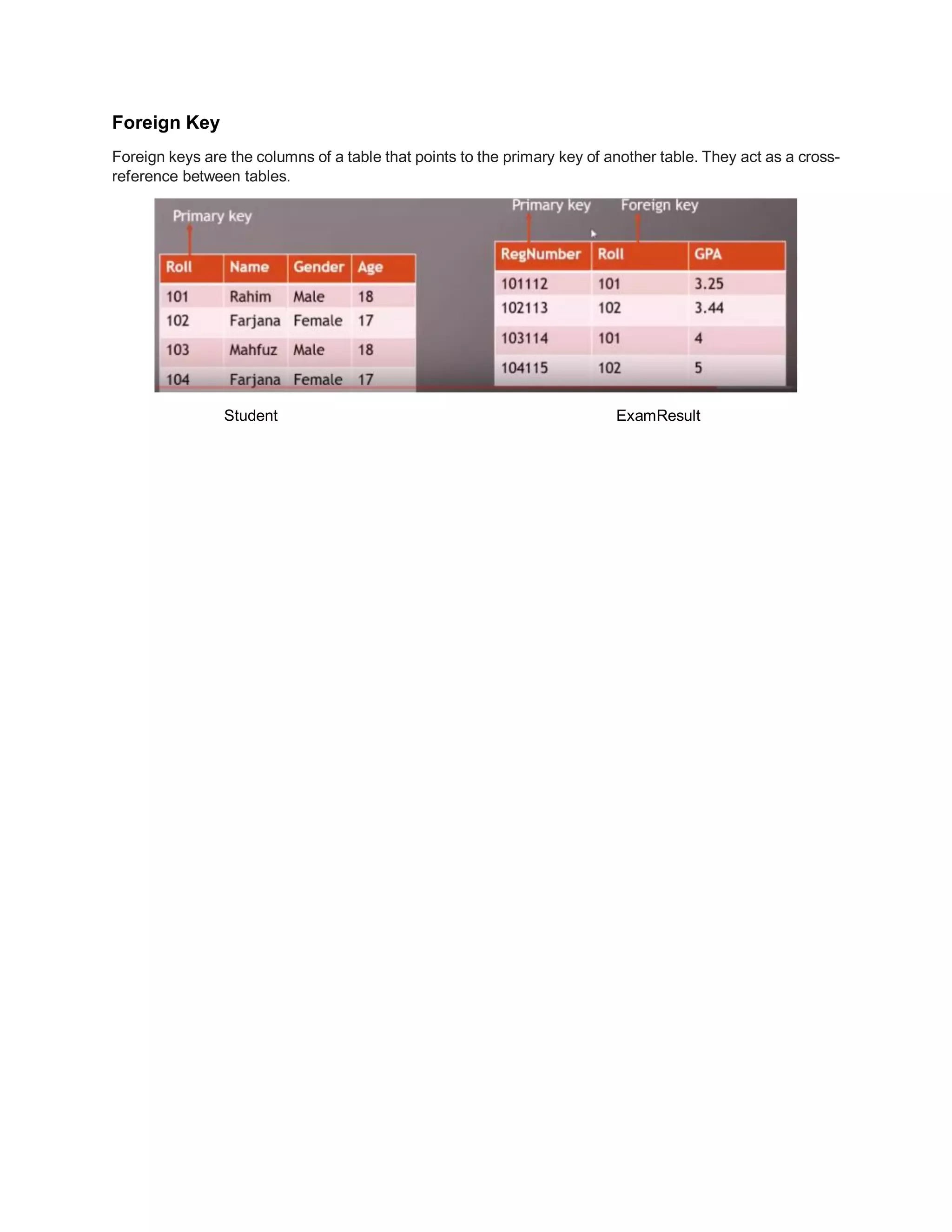
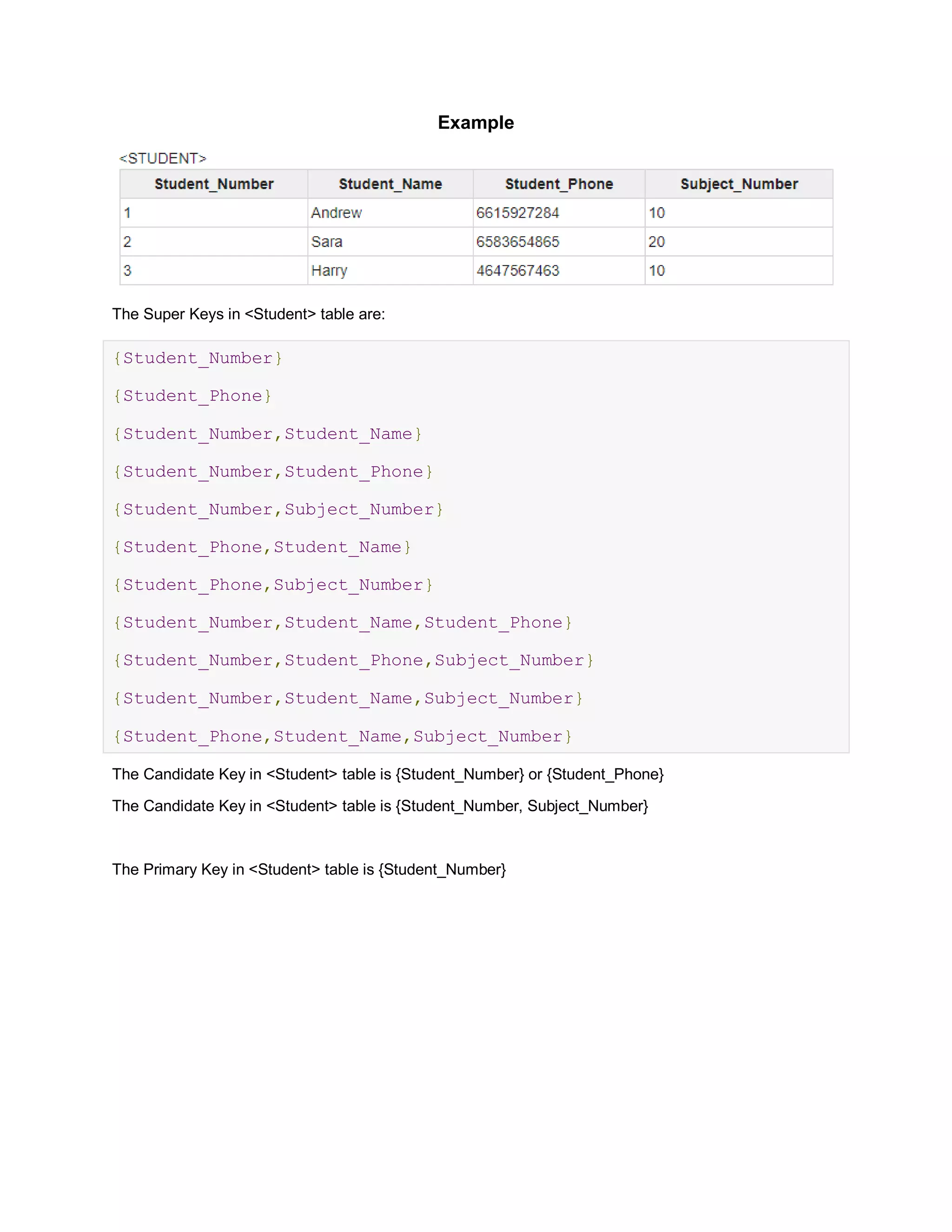
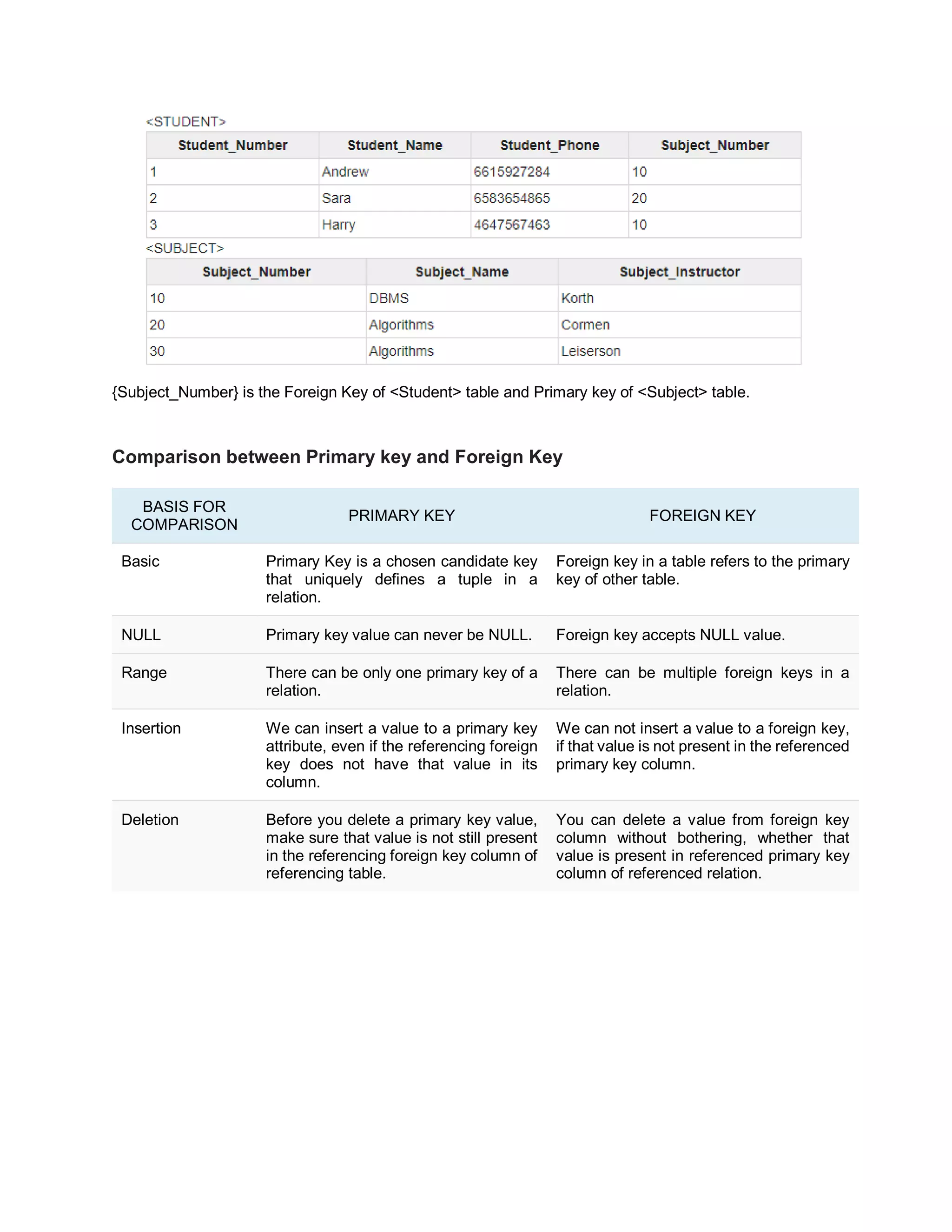
Keys in a database help uniquely identify rows. Super keys can identify rows but may contain redundant attributes, while candidate keys are minimal sets of attributes that uniquely identify rows. The primary key is the chosen candidate key that uniquely identifies each row; foreign keys in one table refer to the primary key of another table to link the tables.