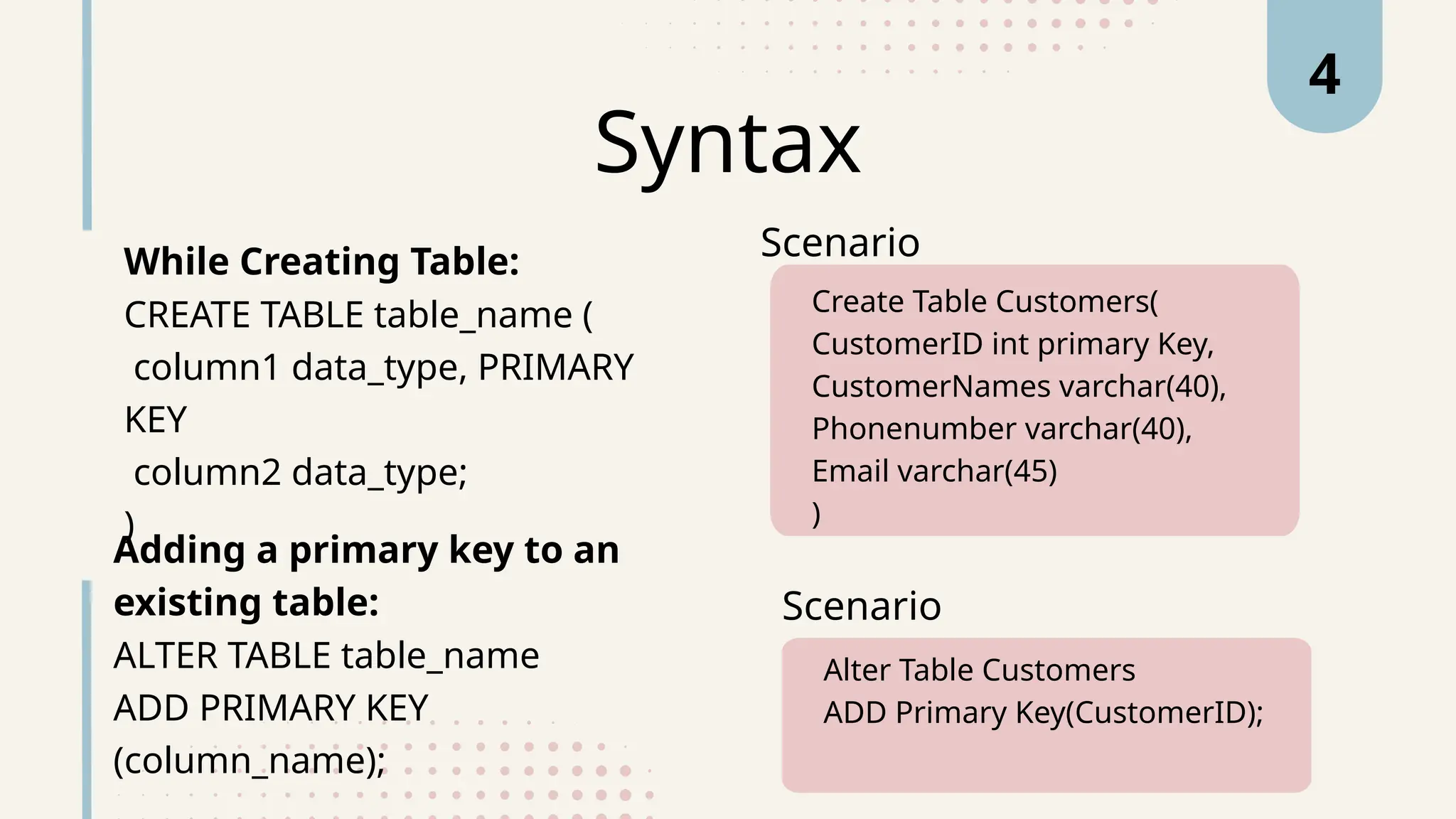
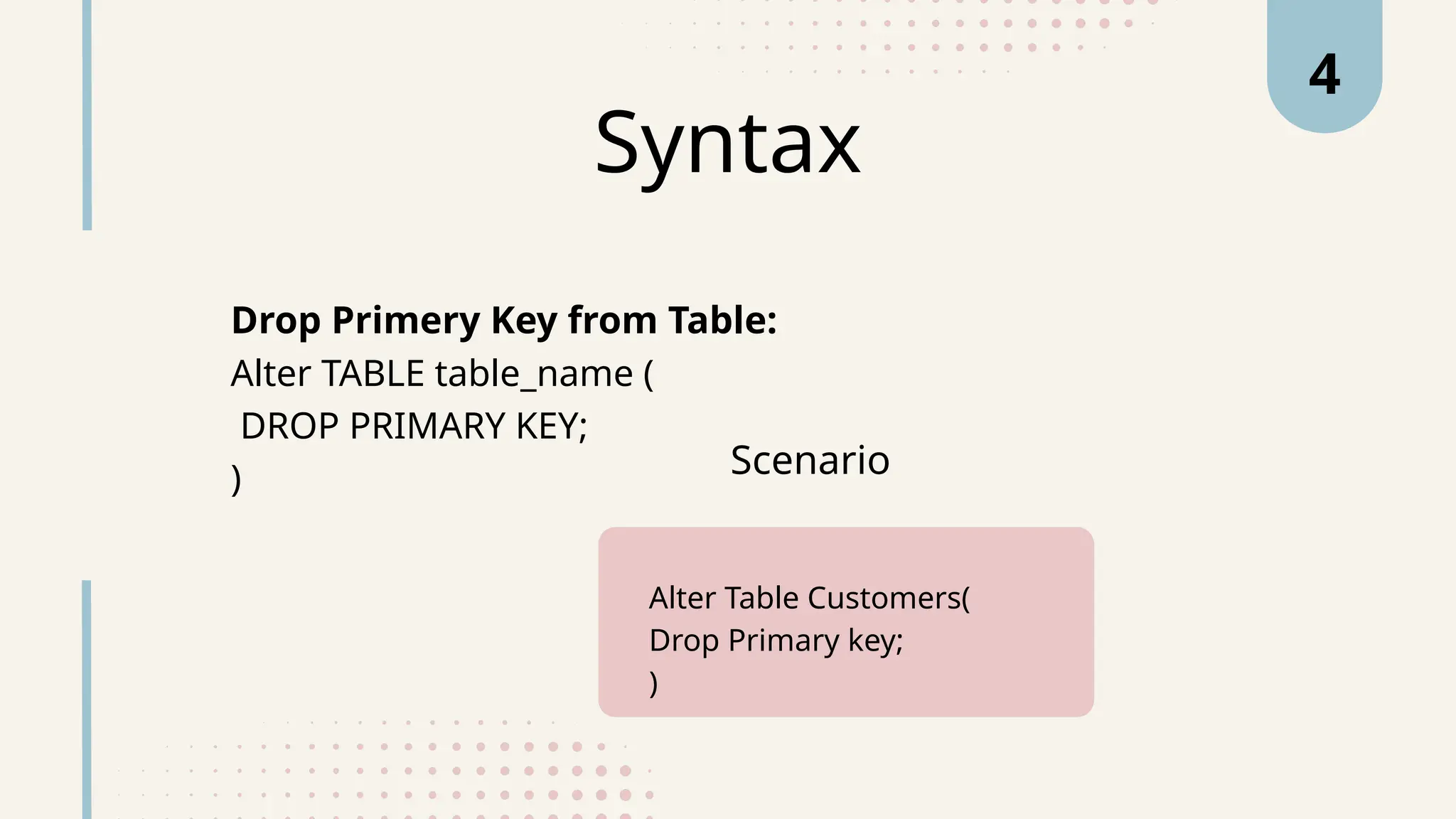
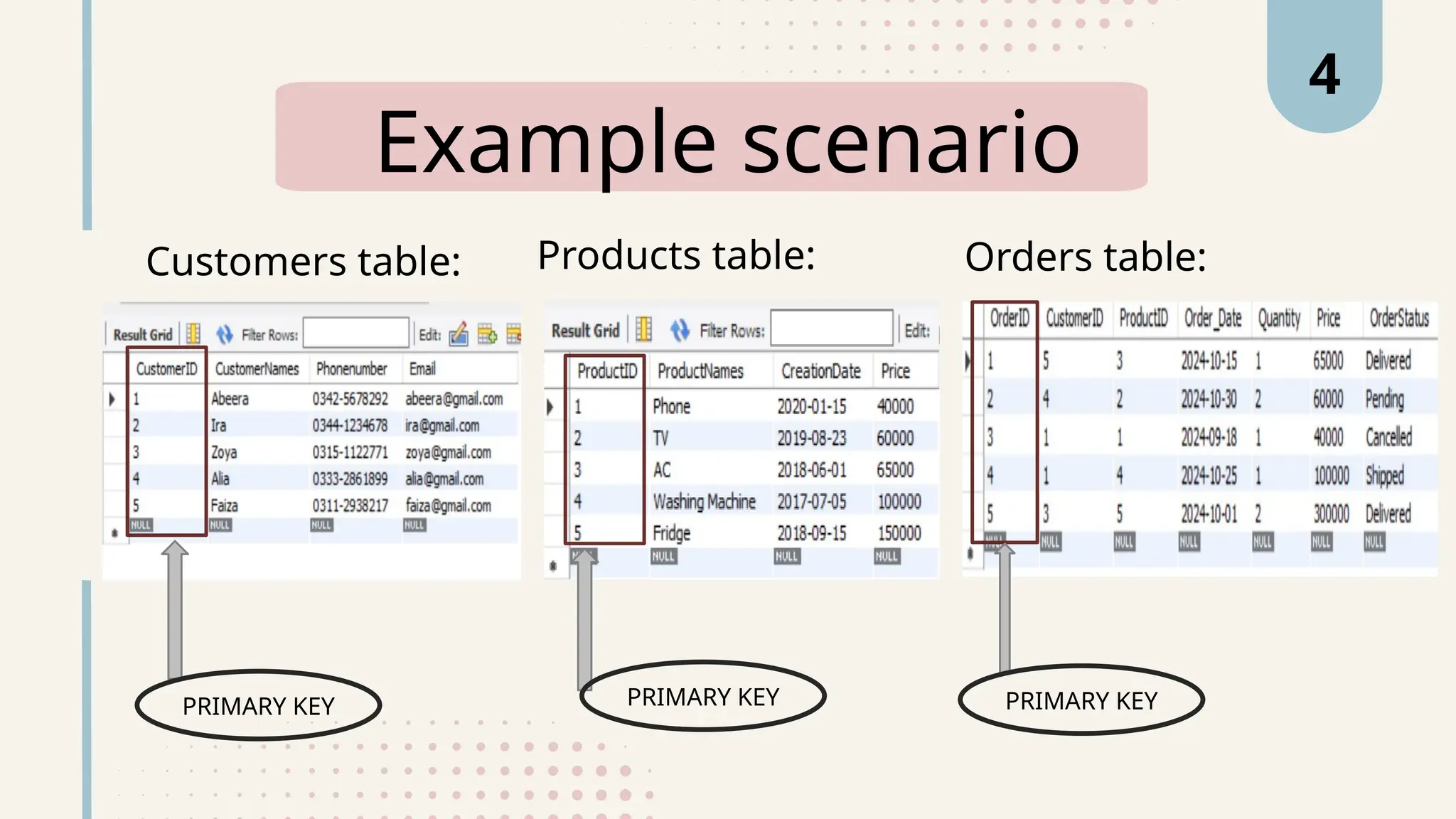
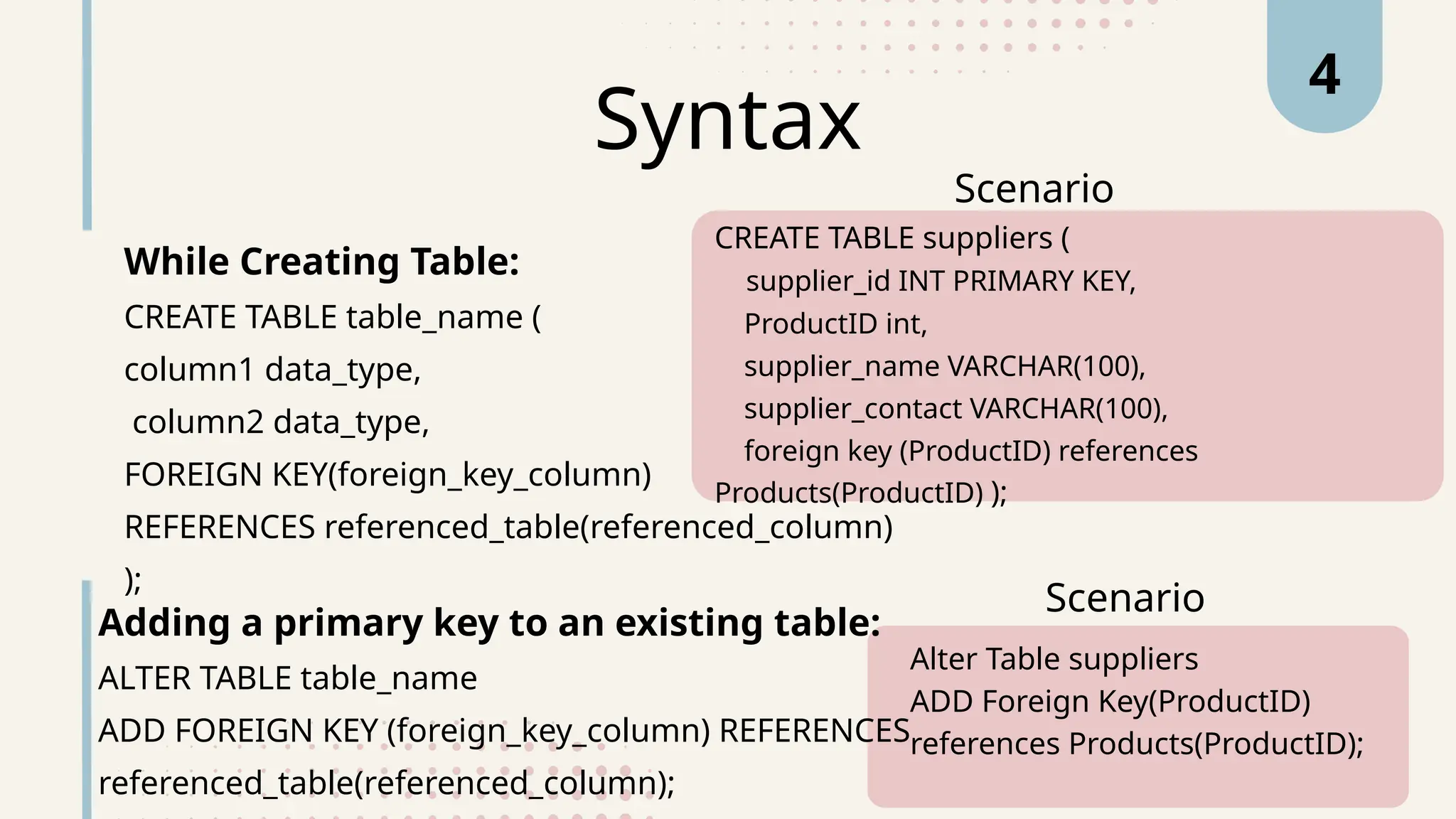
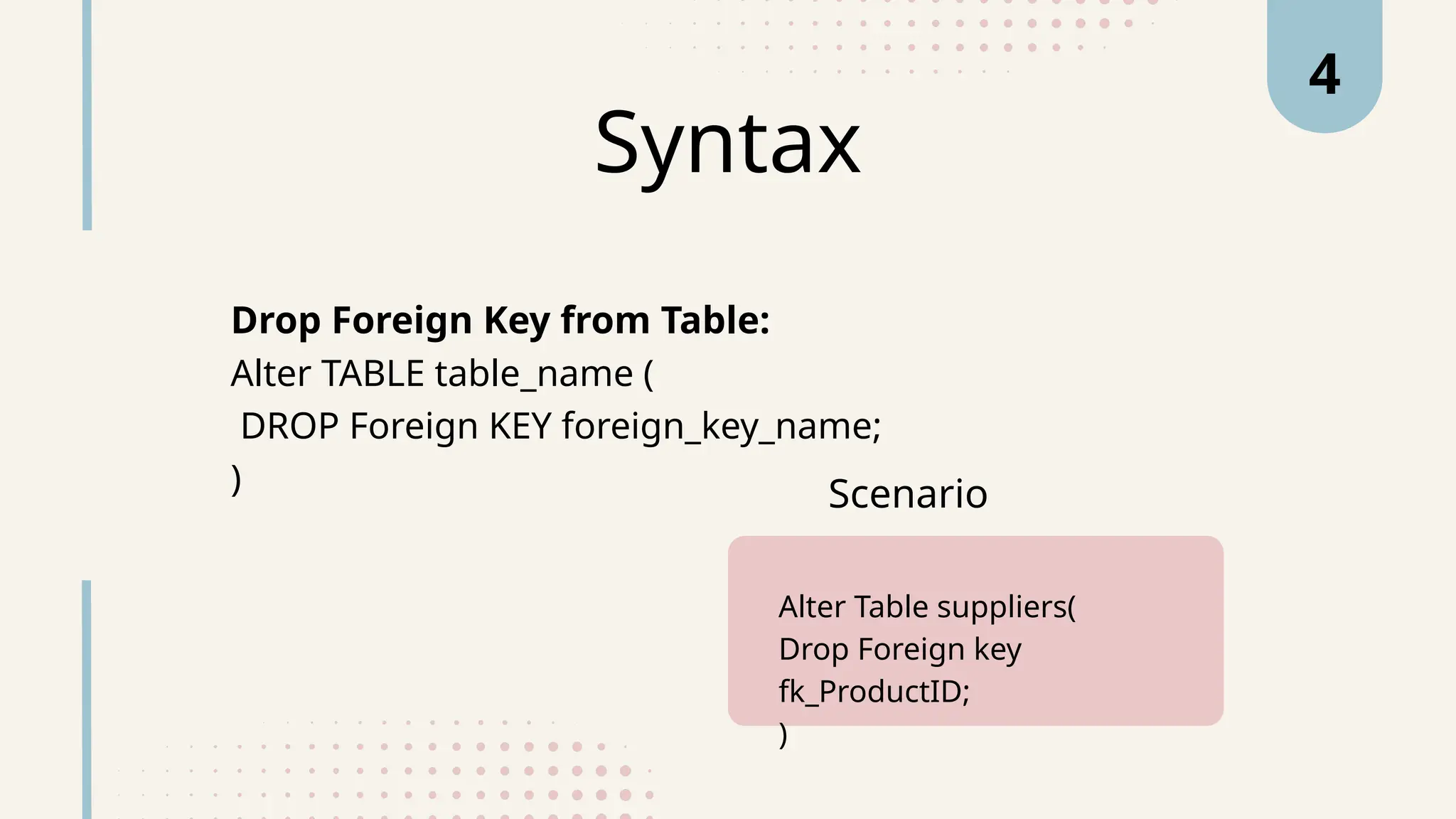
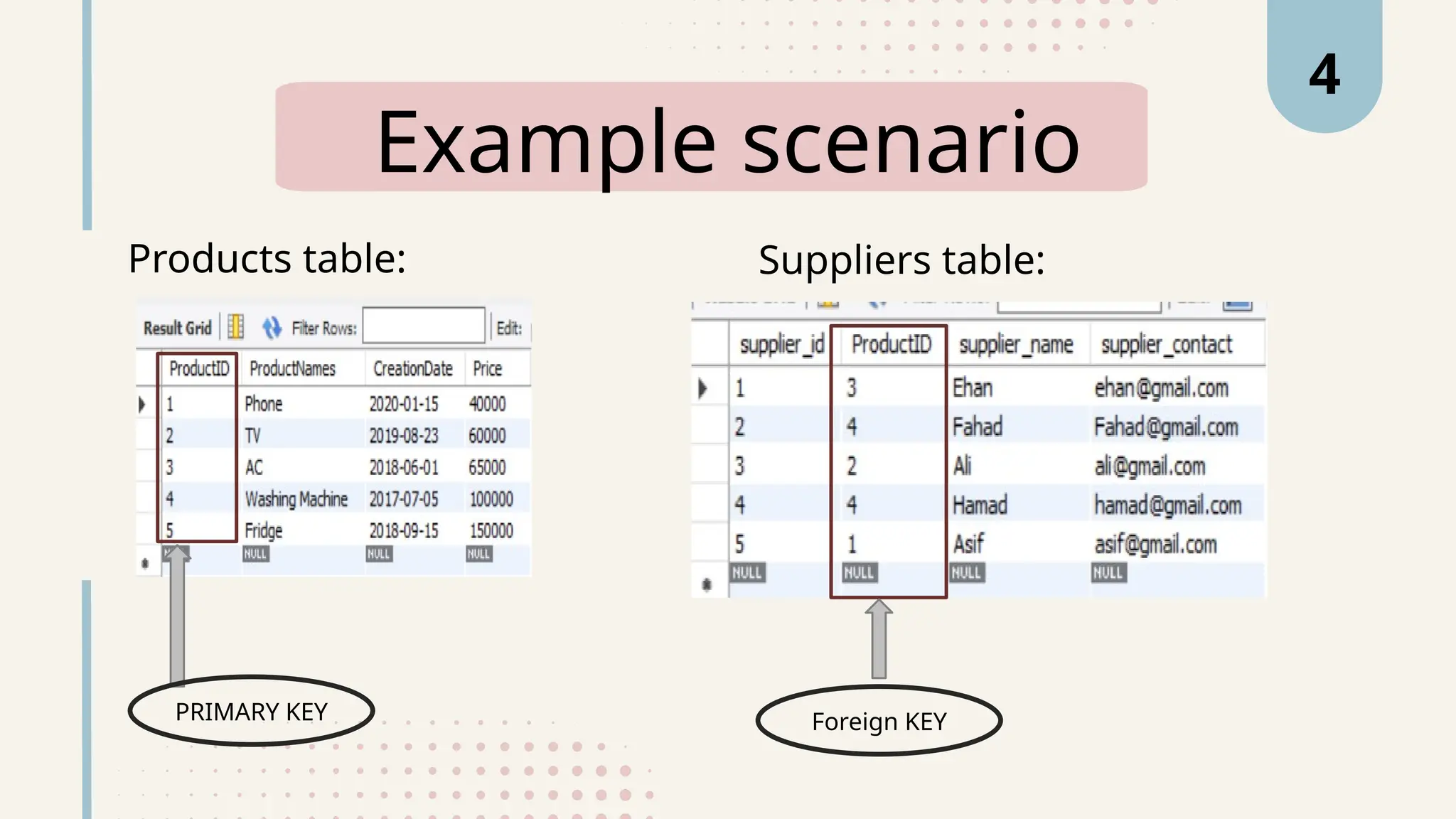
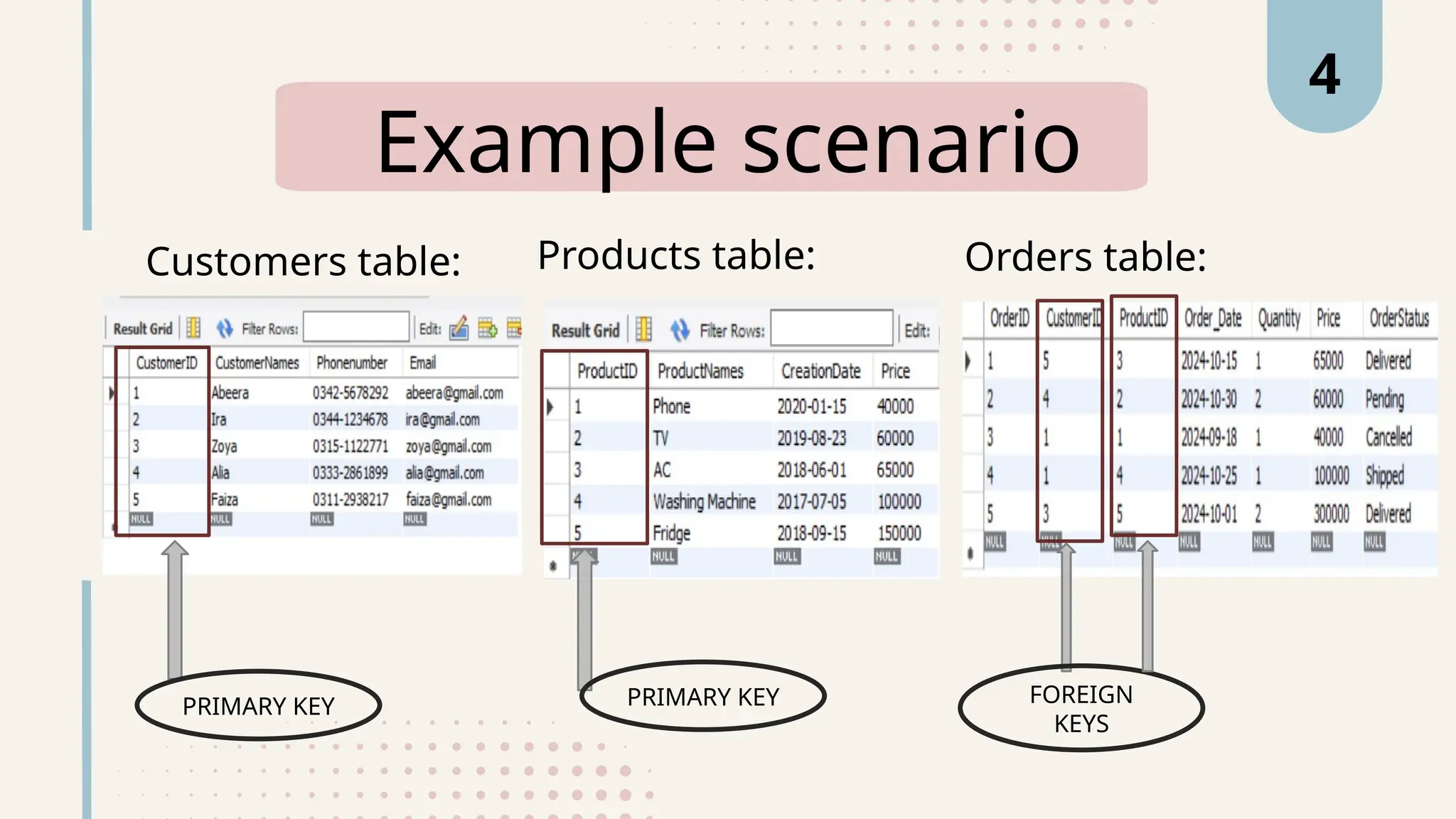
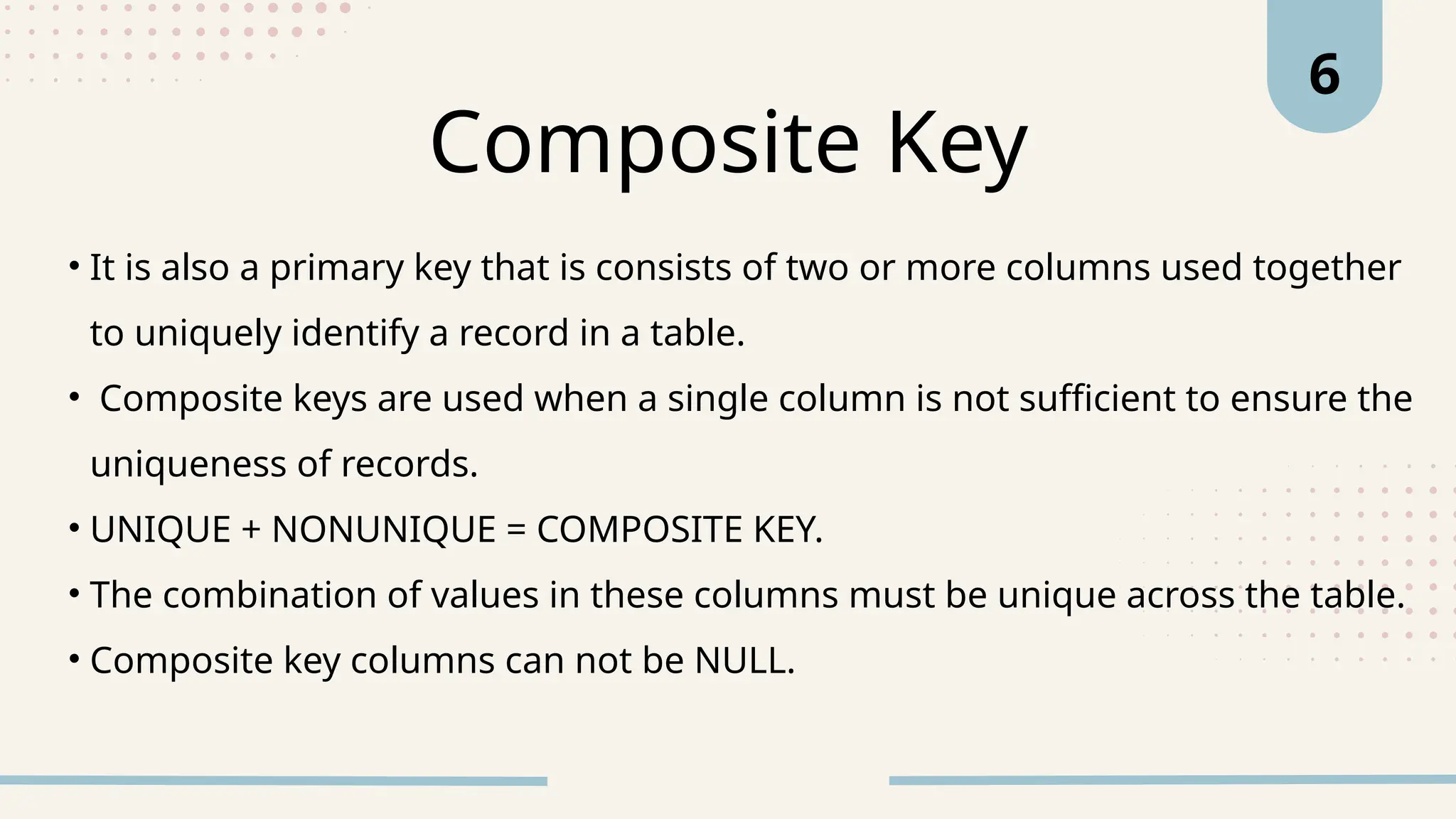
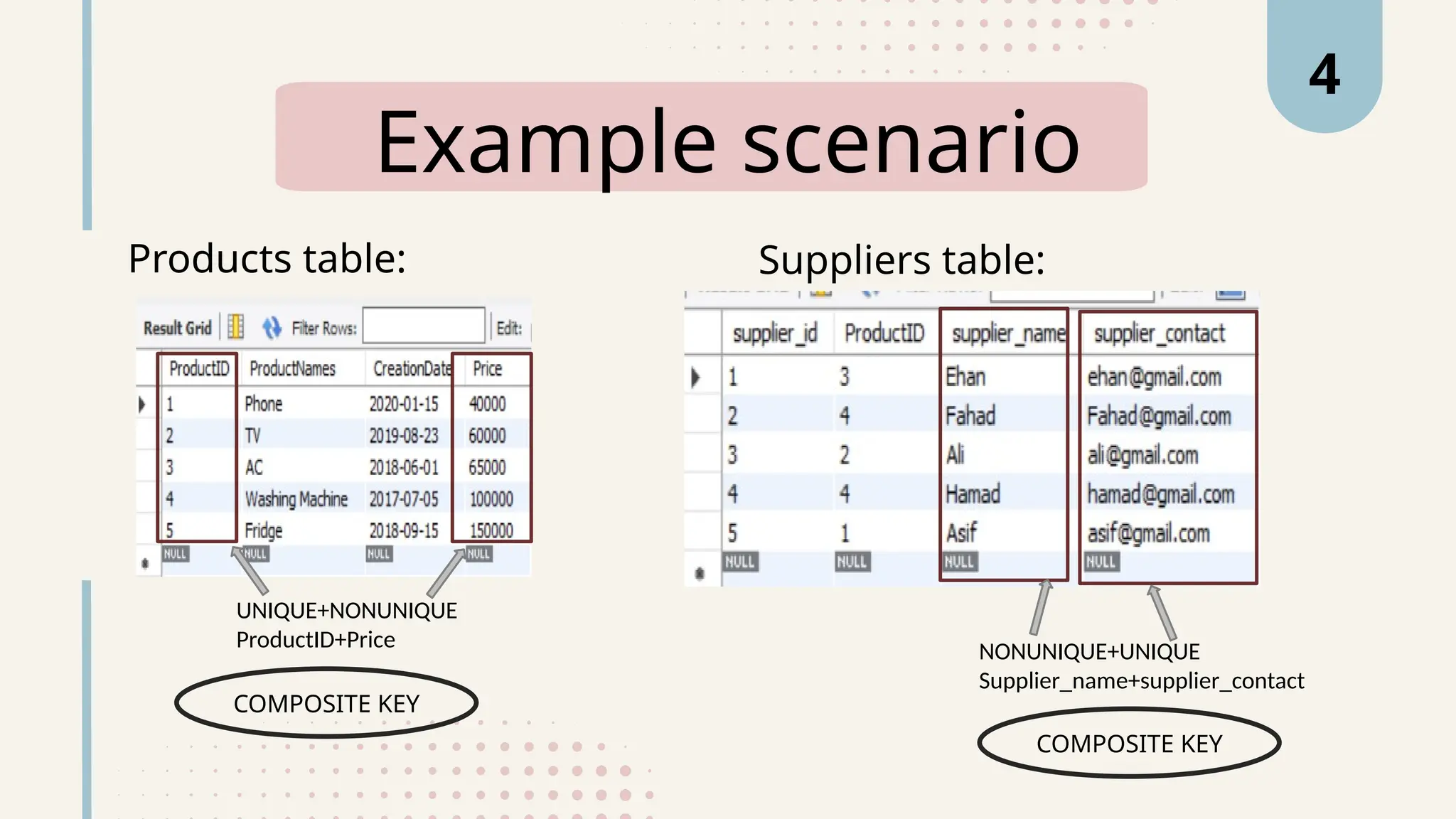
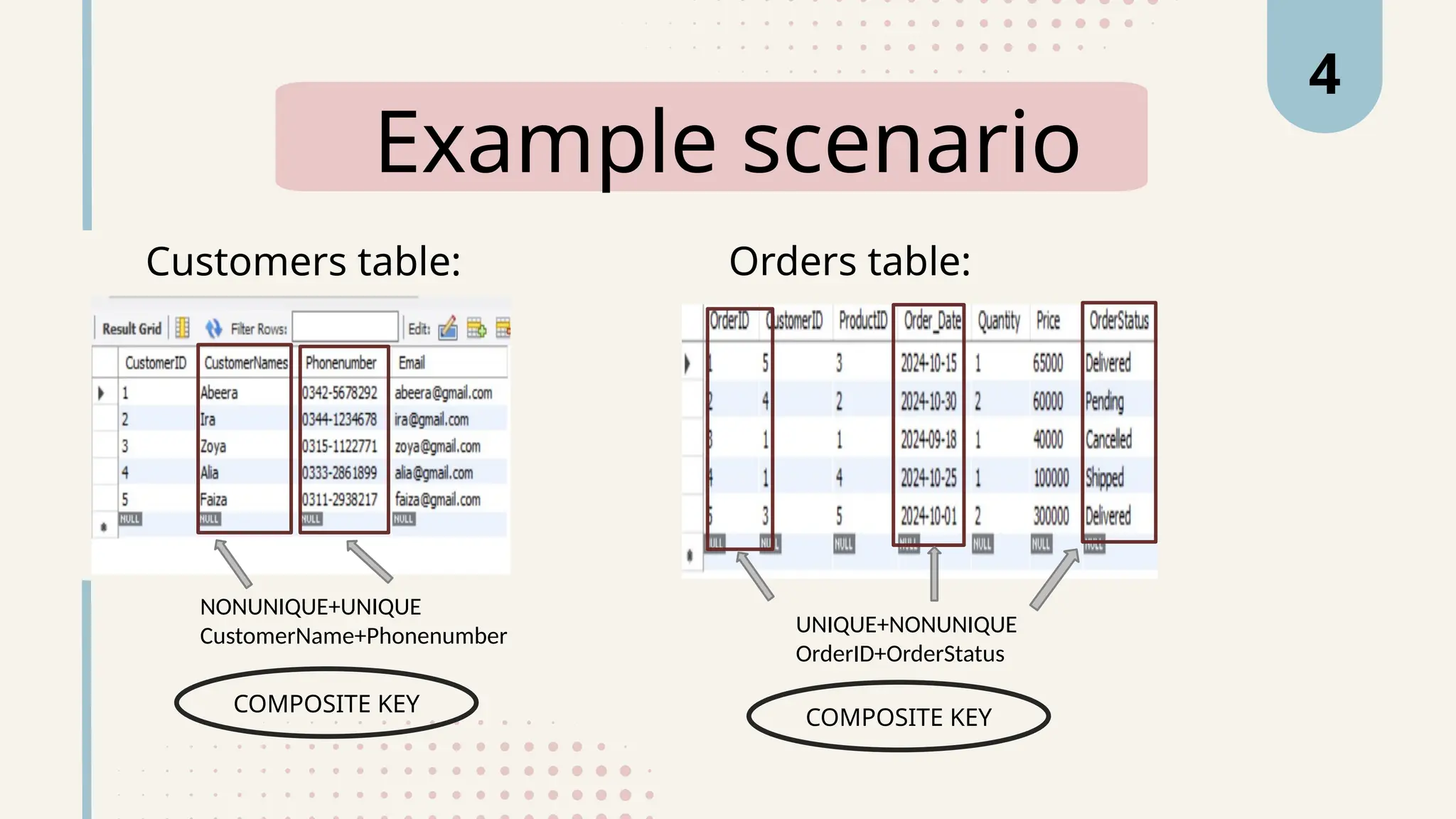
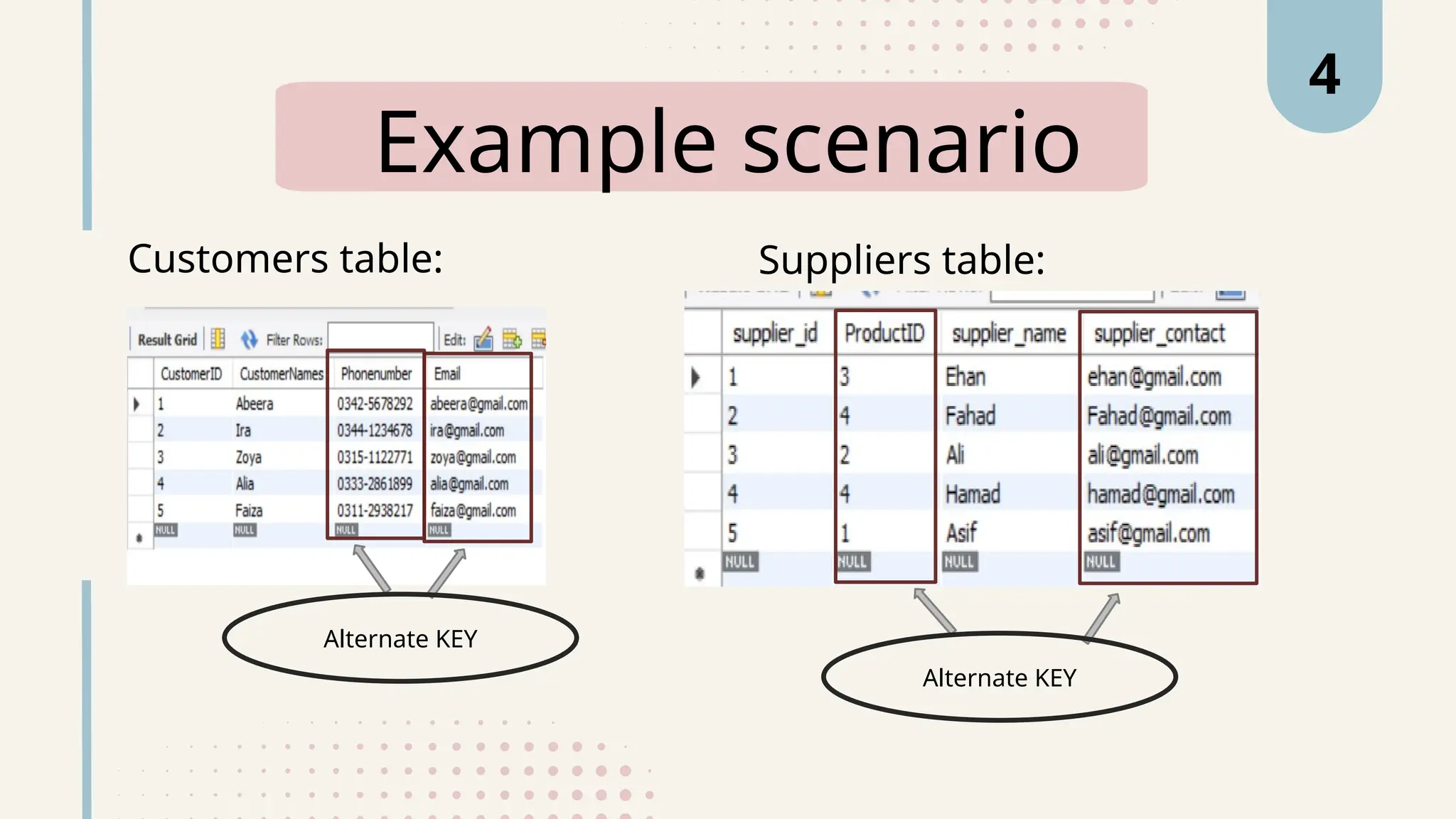
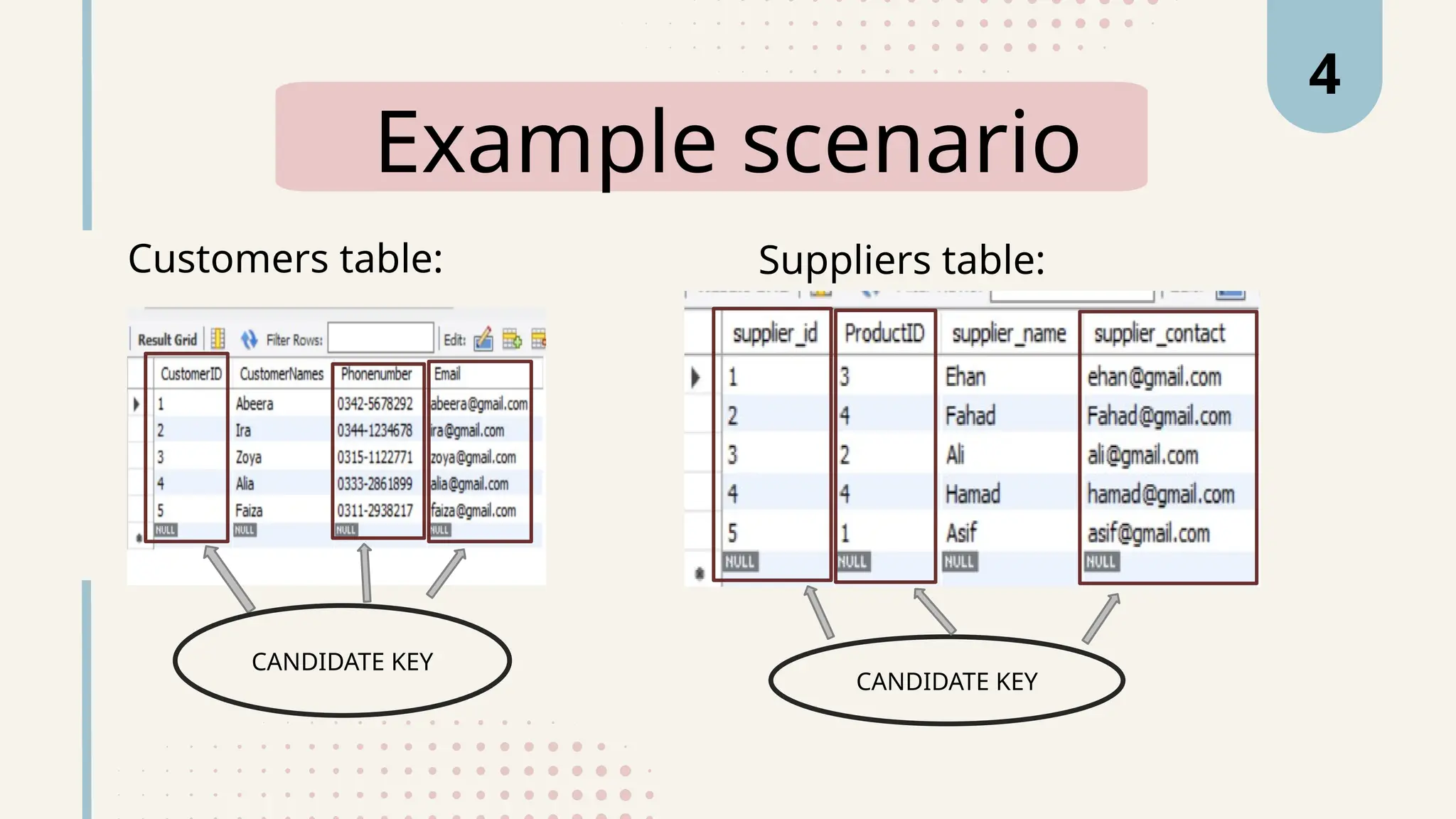
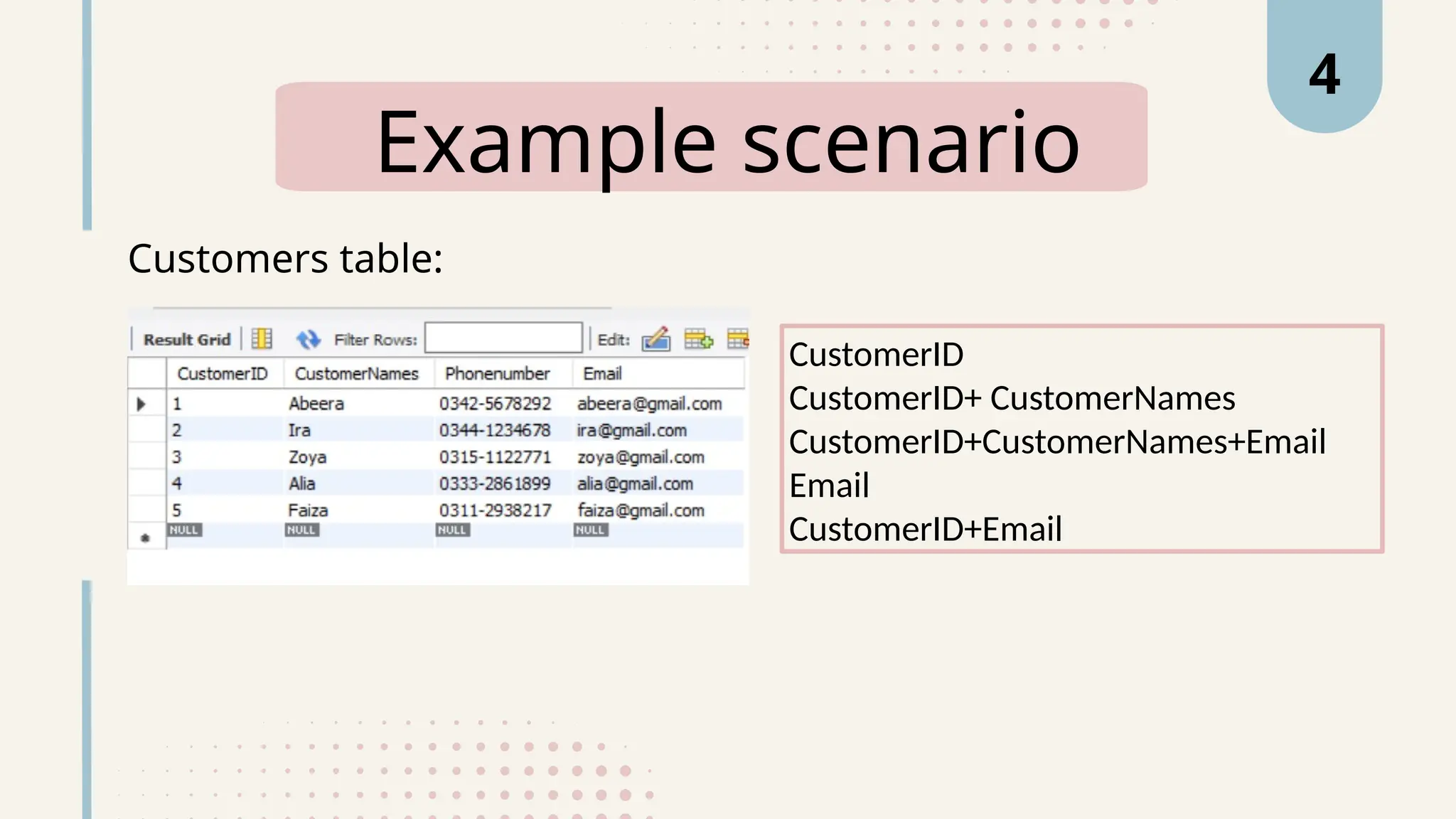
The document explains various types of keys in SQL, including primary, foreign, composite, candidate, alternate, and super keys, detailing their definitions, use cases, and syntactical representations. Primary keys uniquely identify records and can only exist once per table, while foreign keys establish relationships between tables. Composite keys combine multiple columns to ensure record uniqueness, and alternate and candidate keys can also uniquely identify records, with specific rules for their usage and null values.