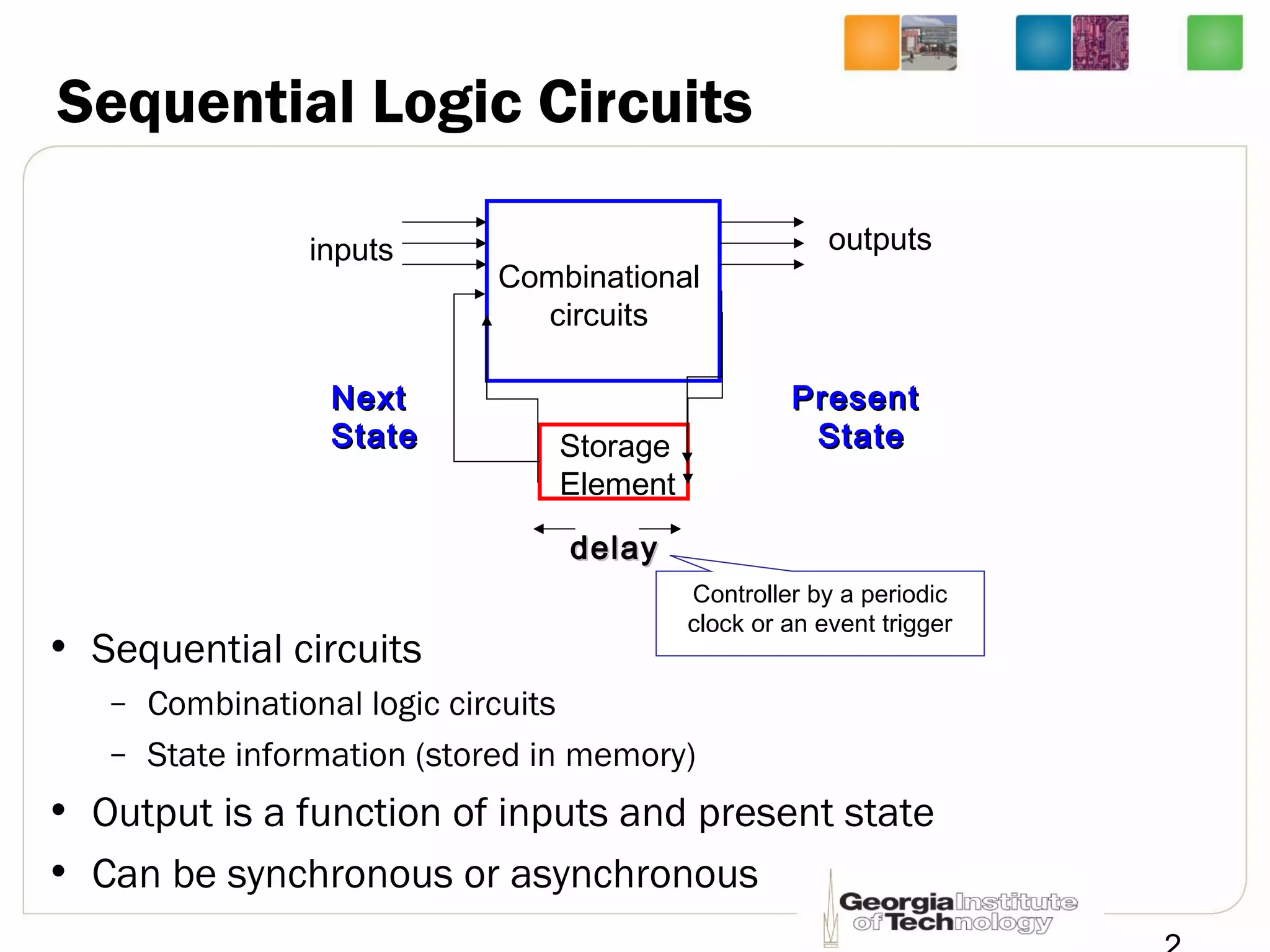
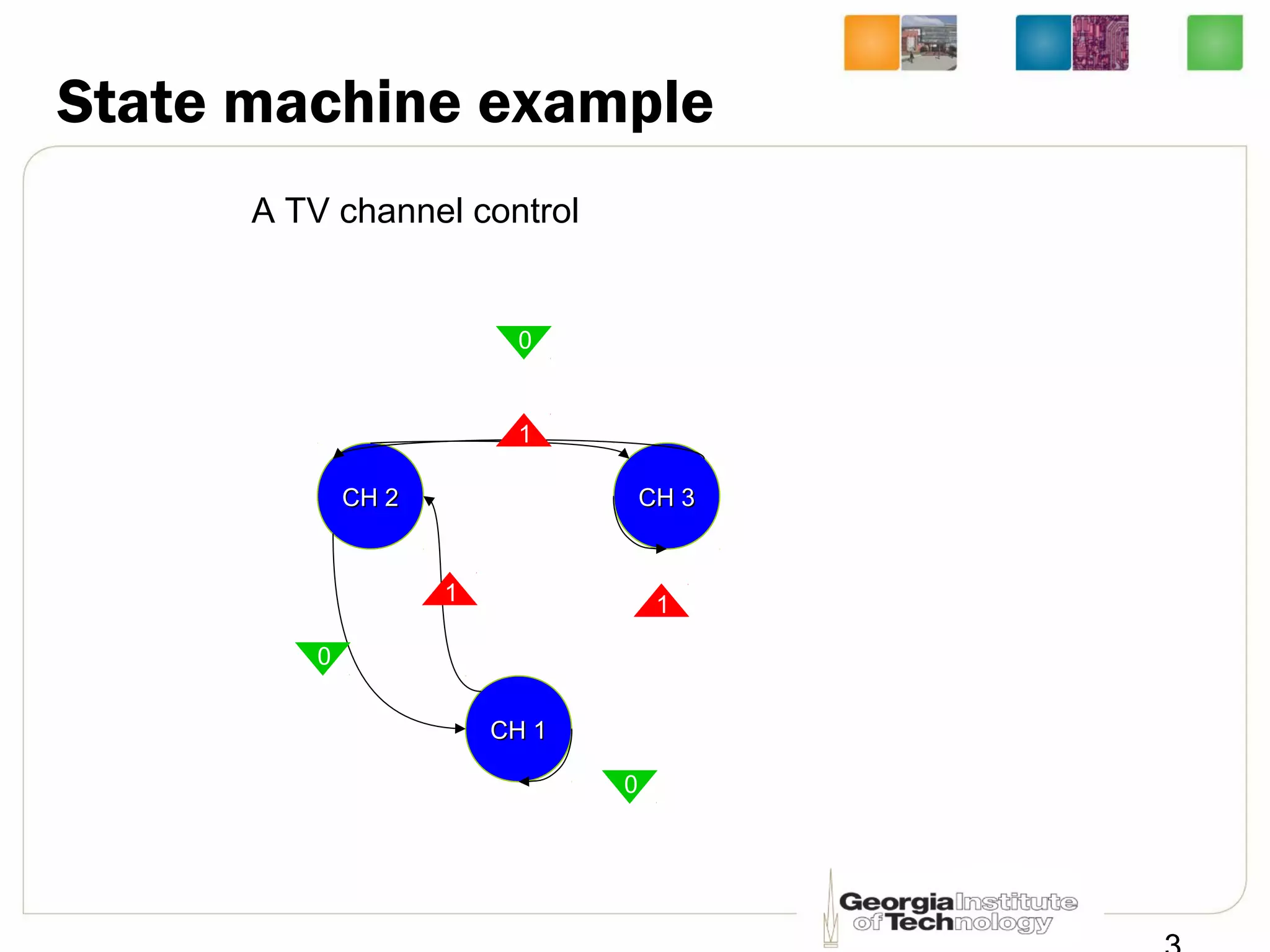
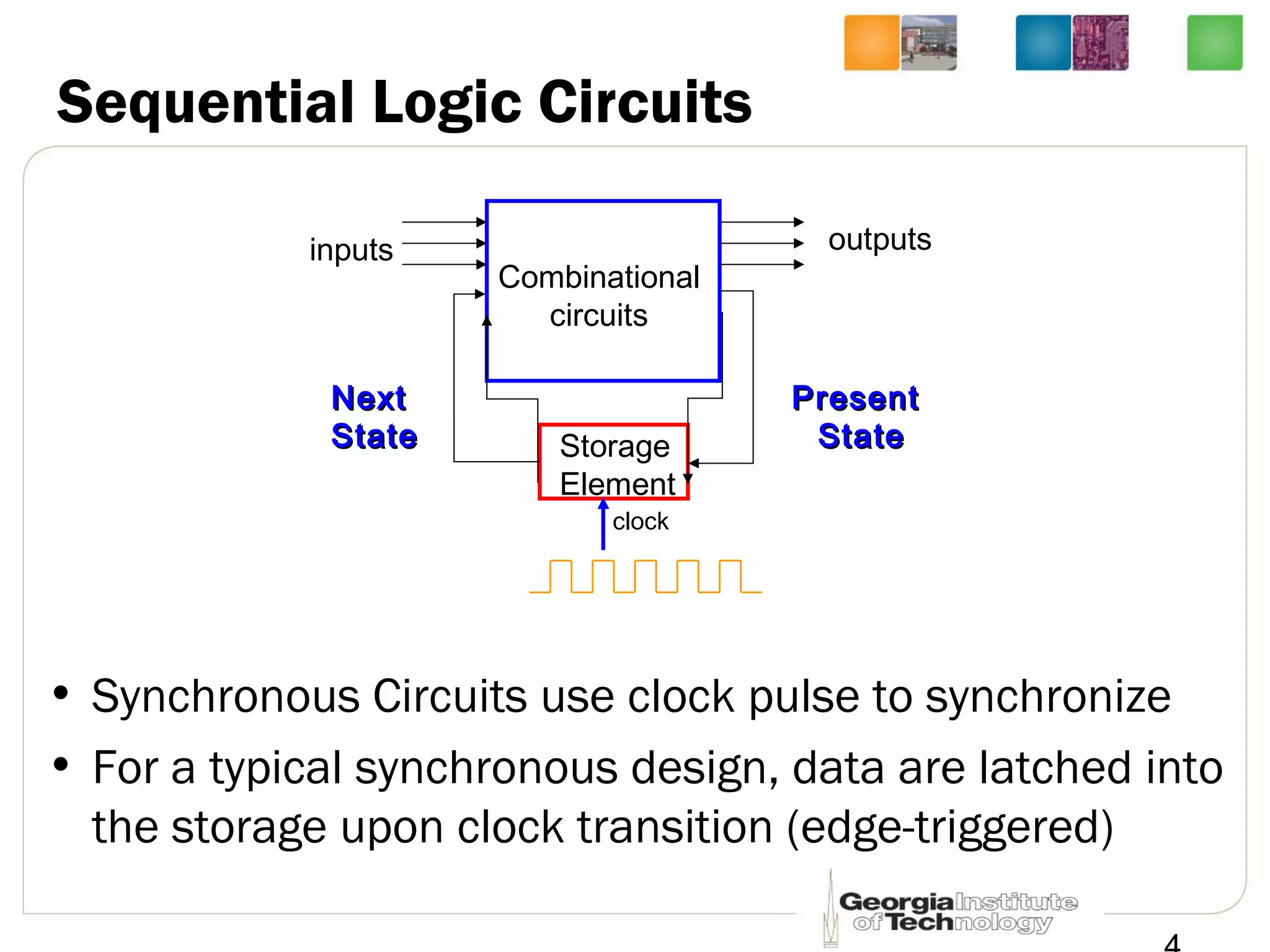
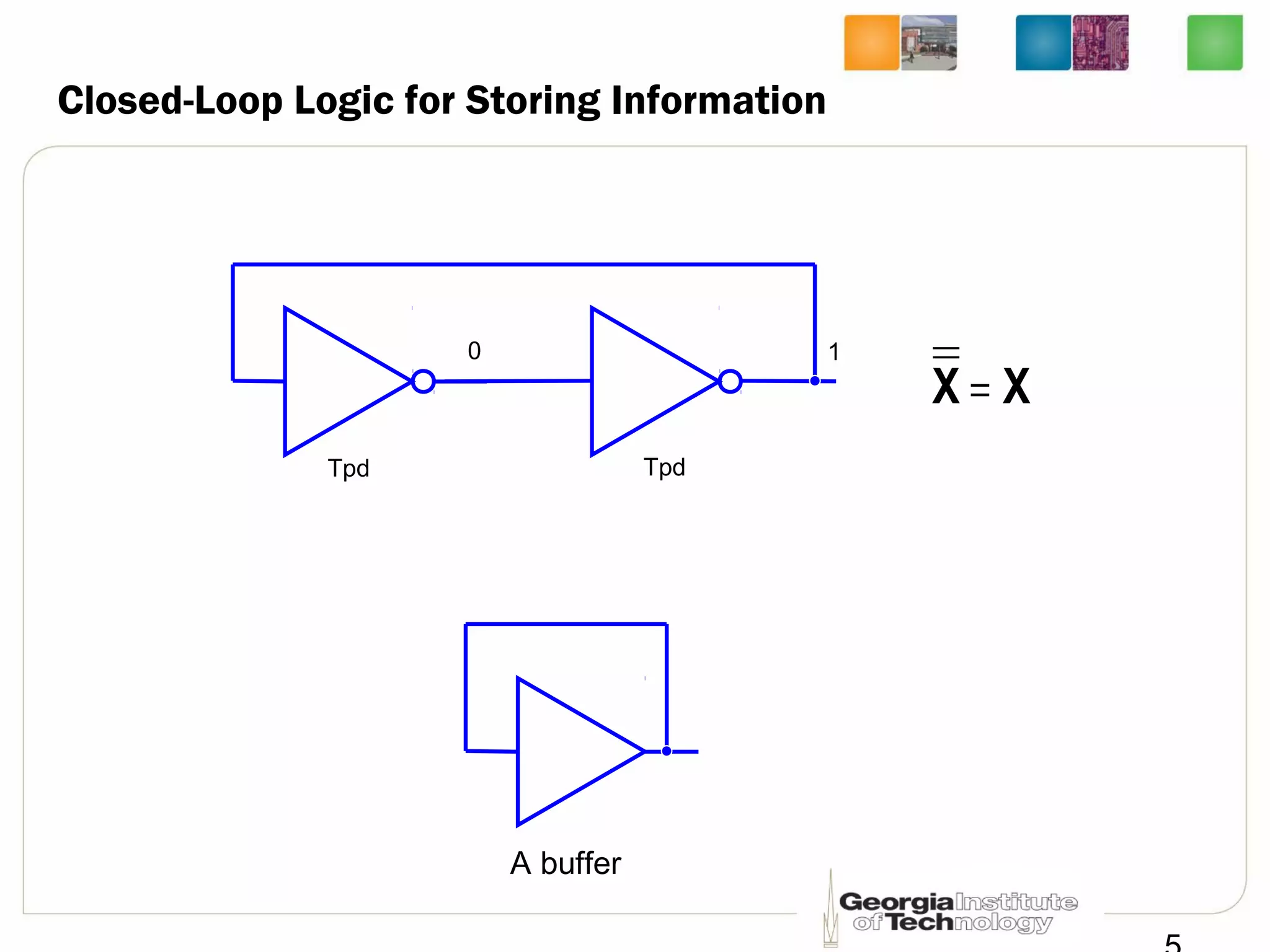
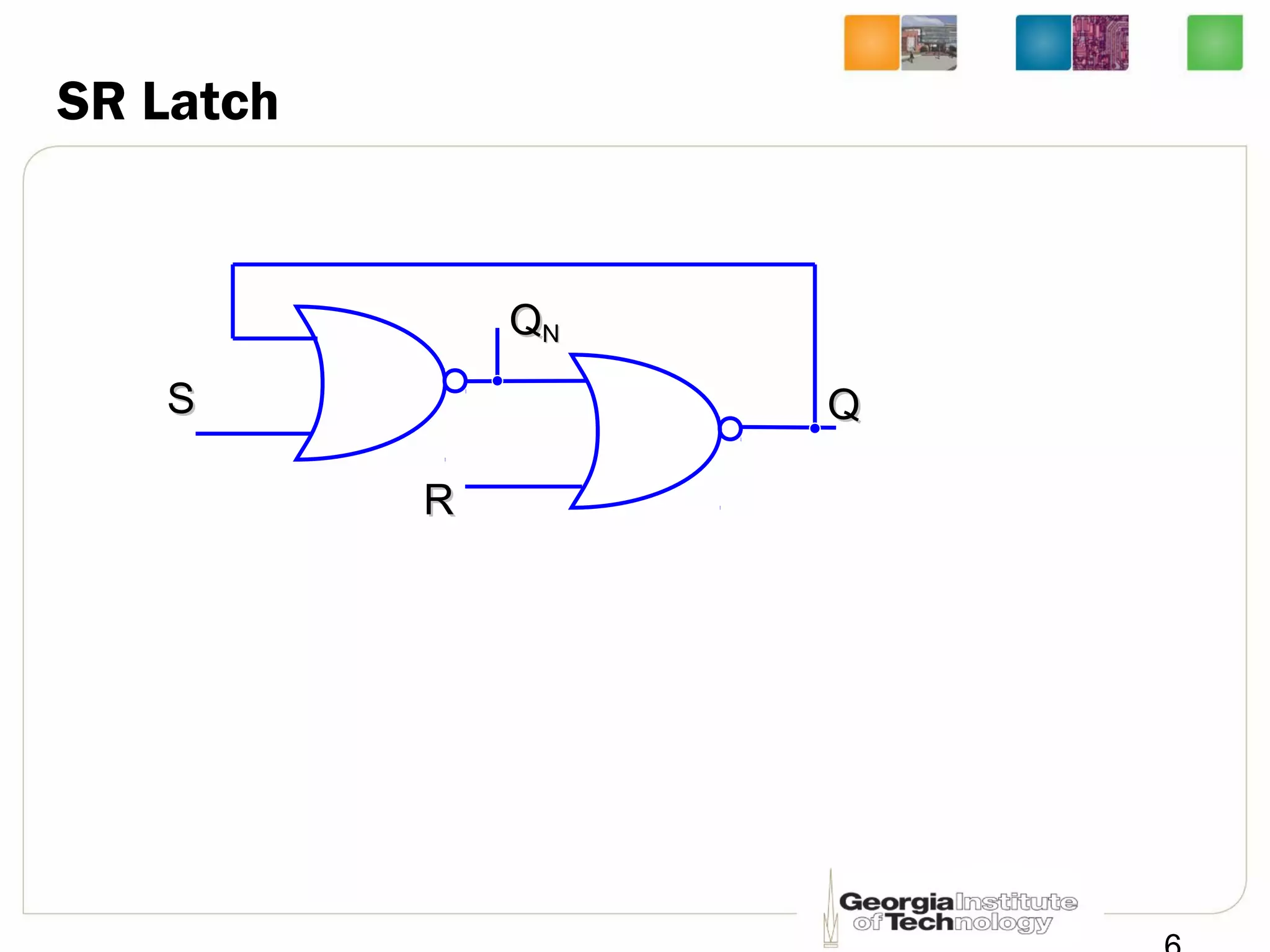
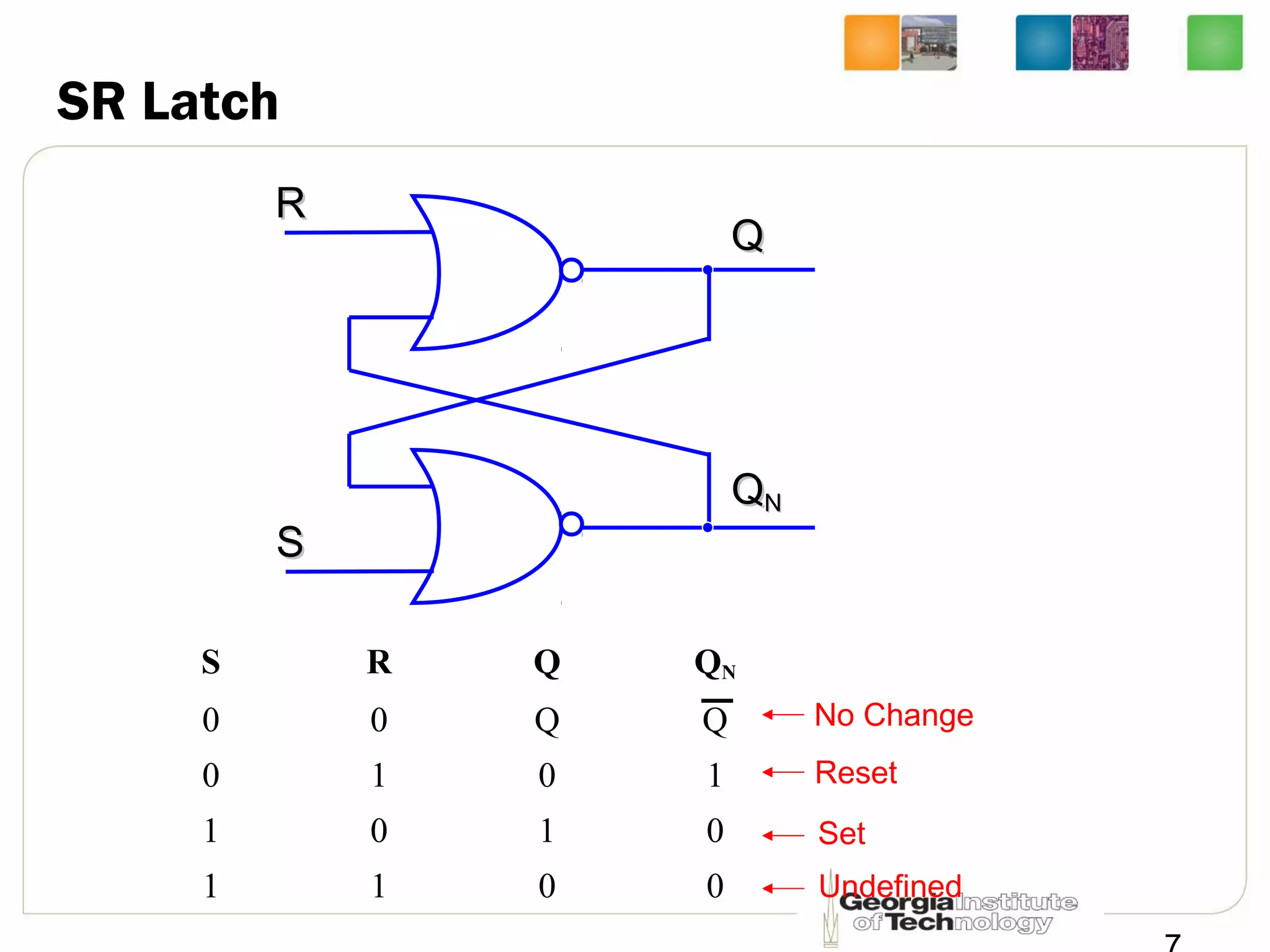
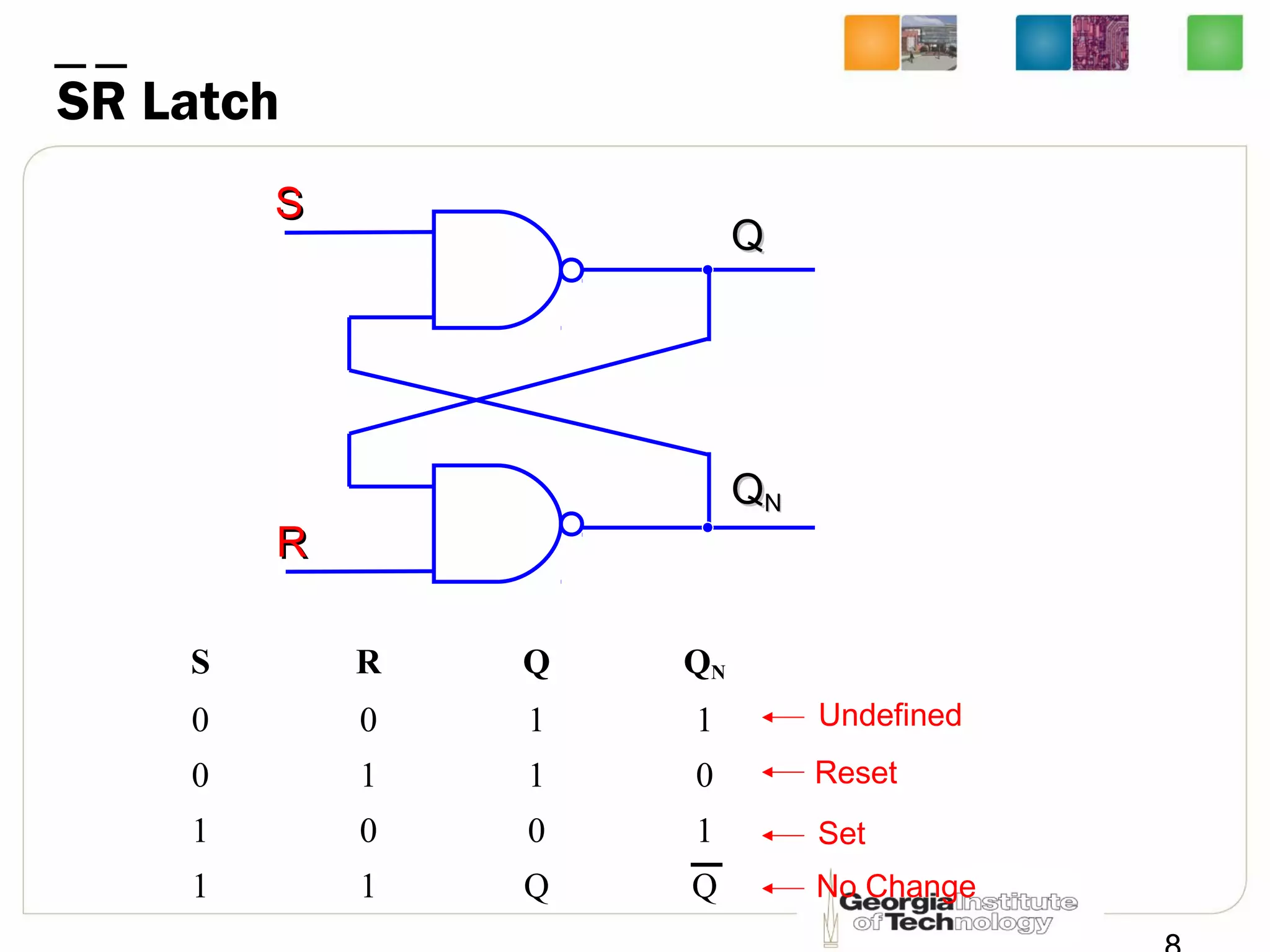
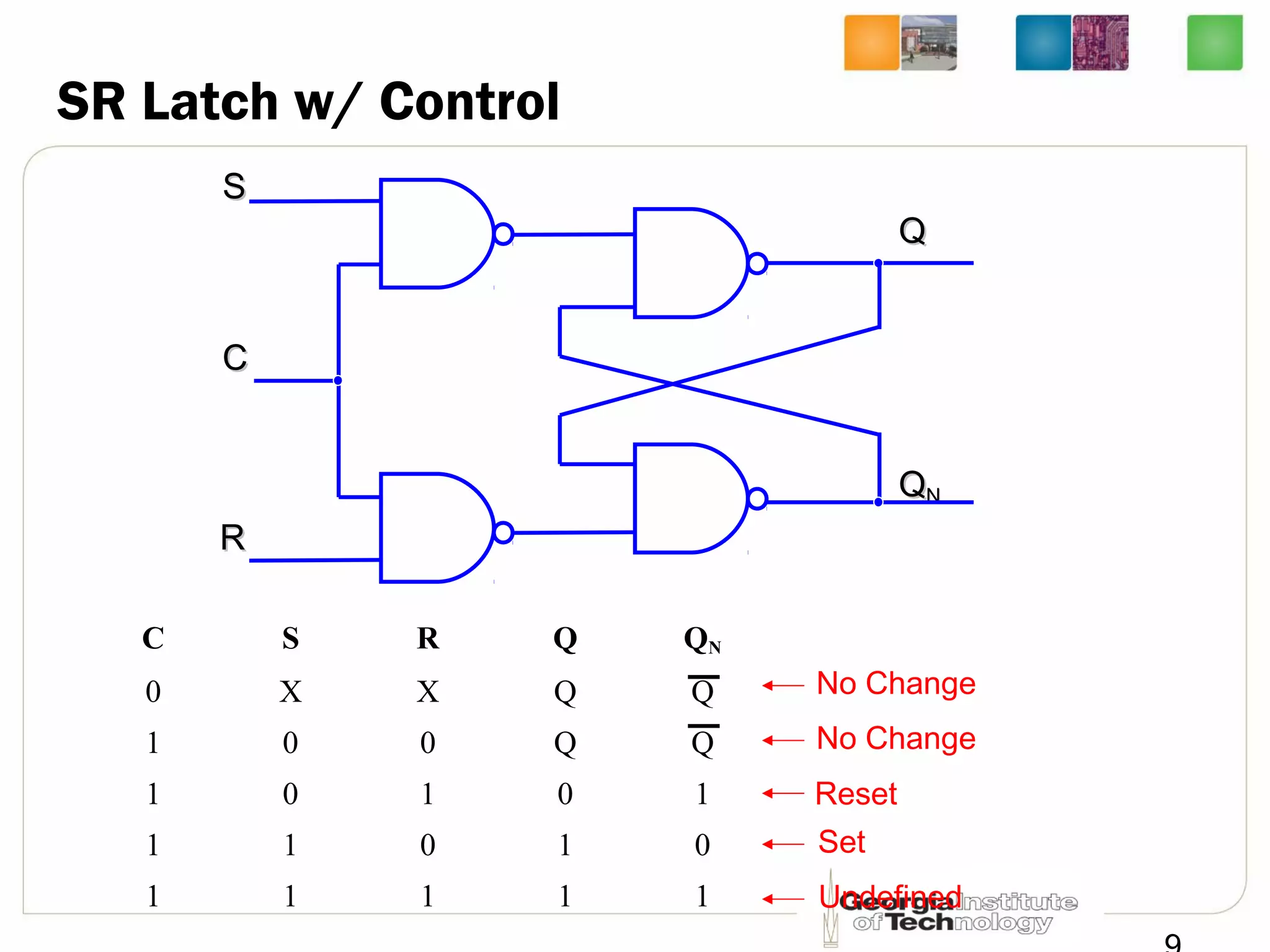
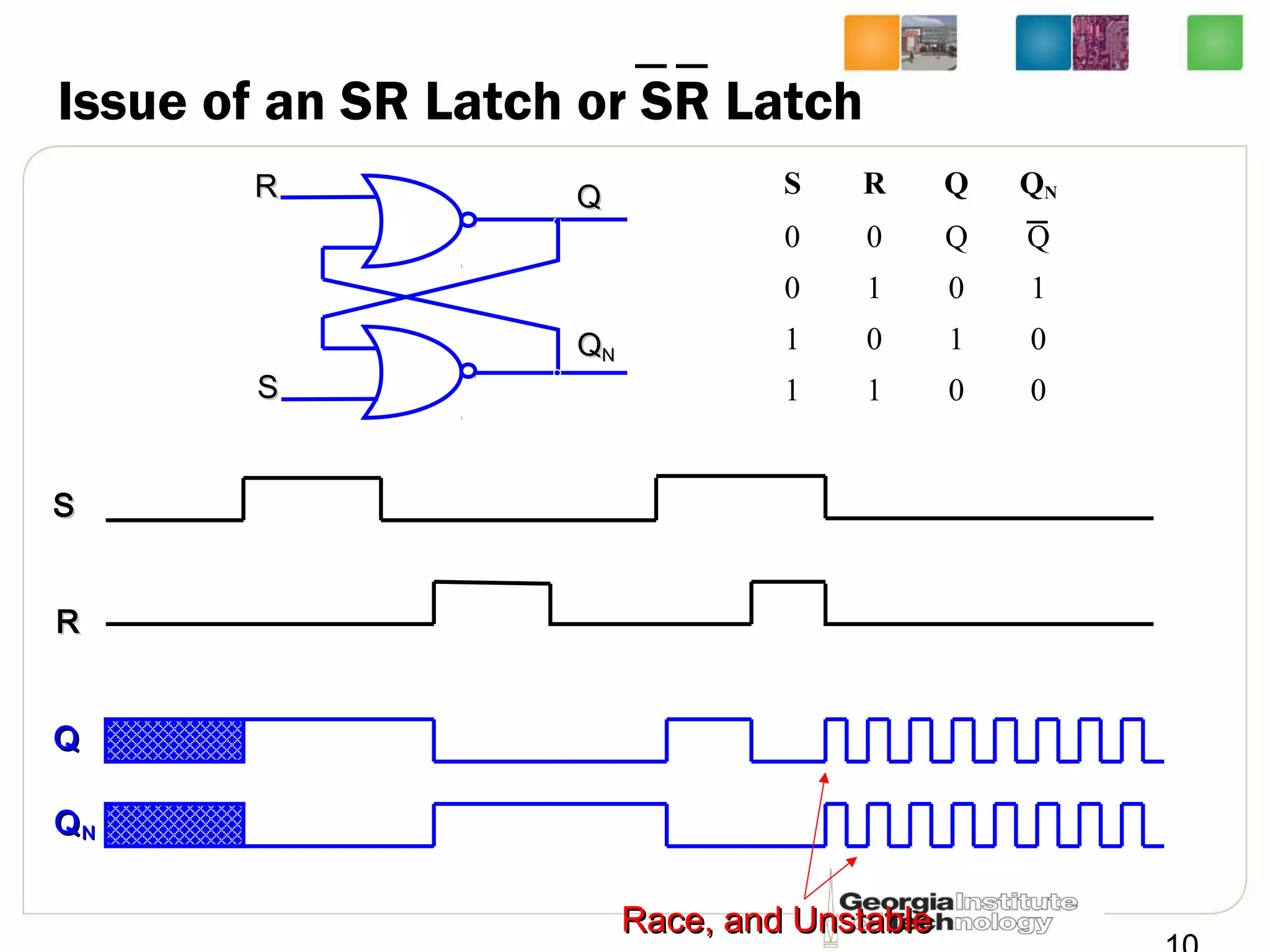
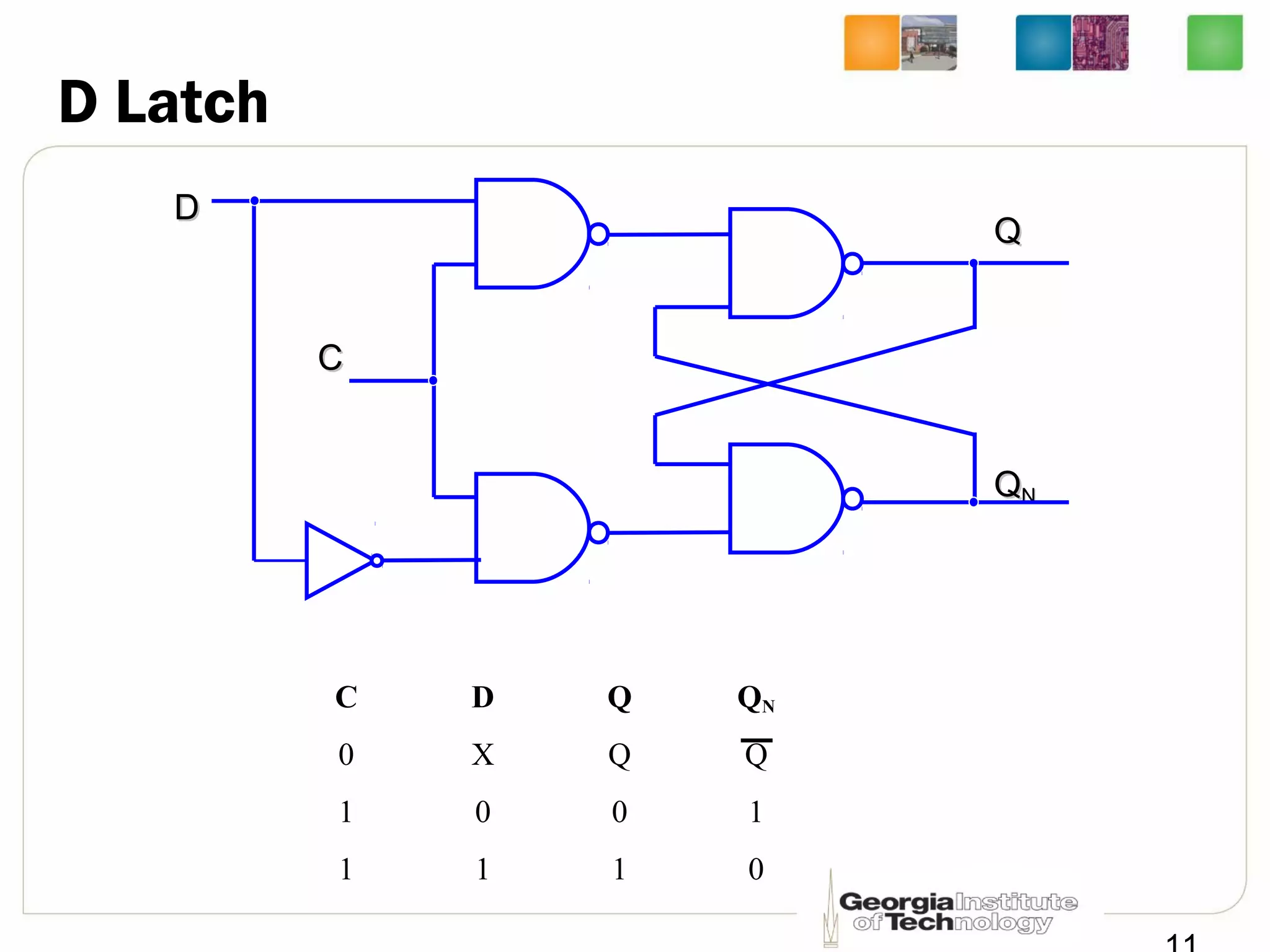
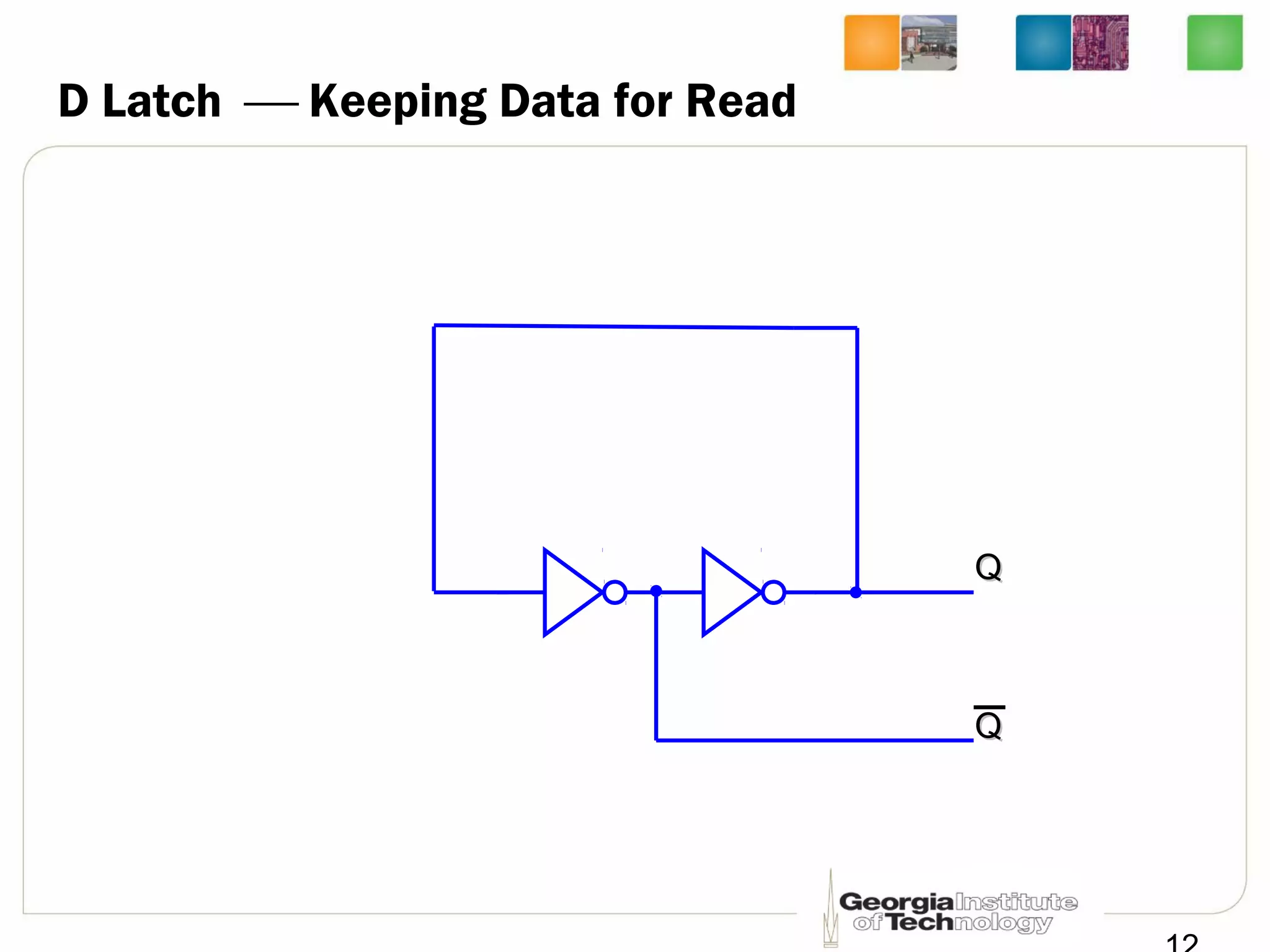
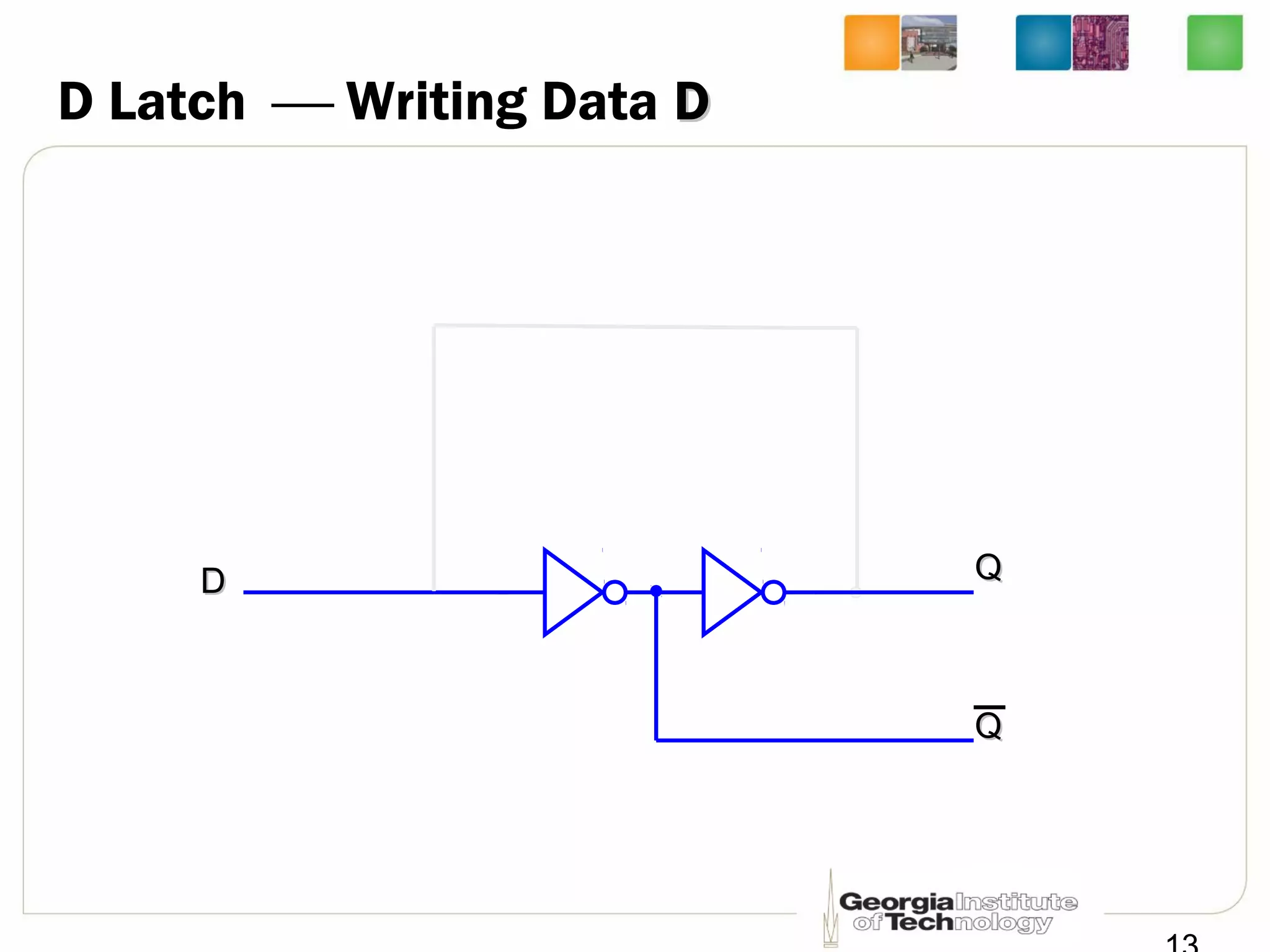
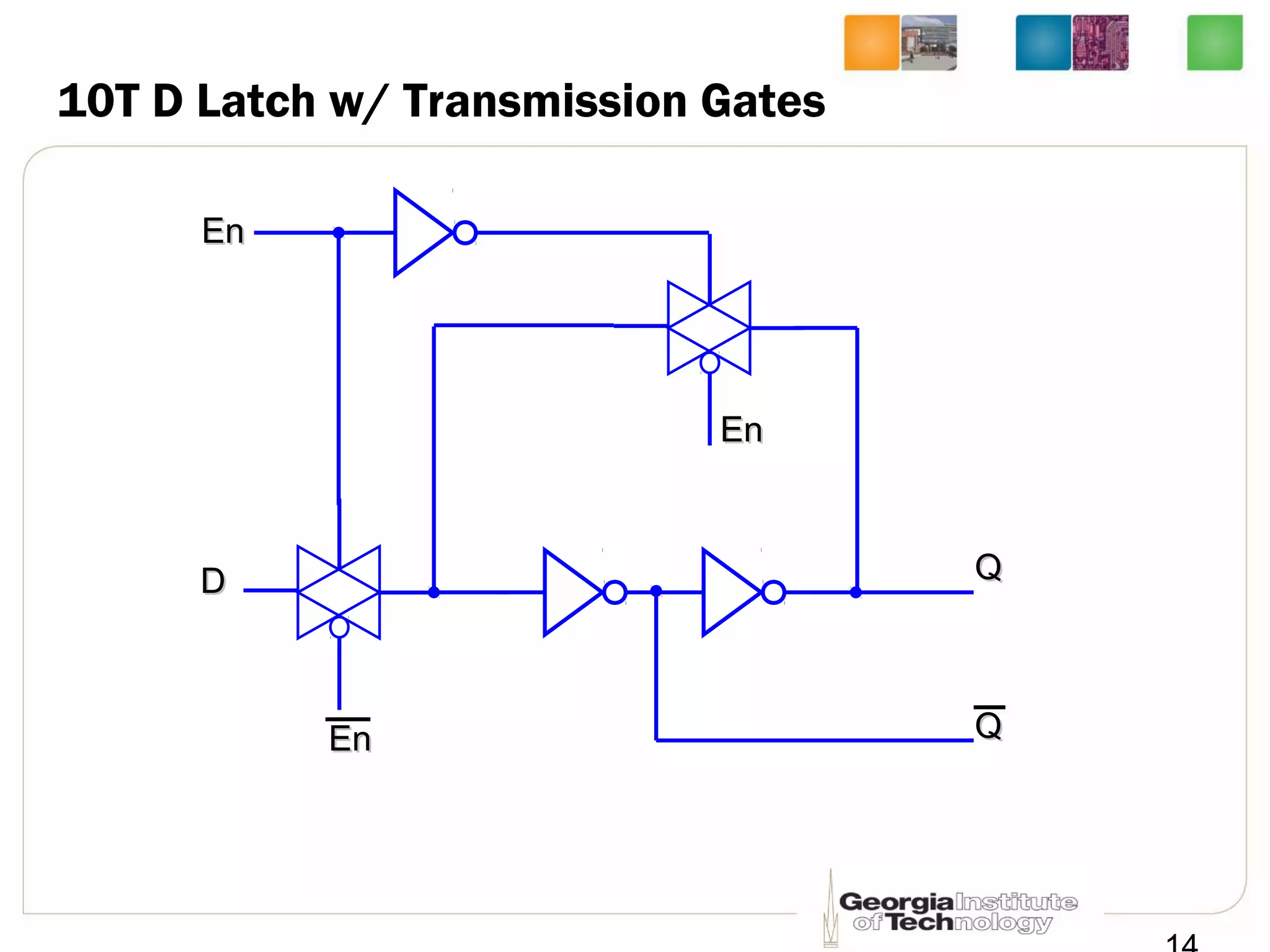
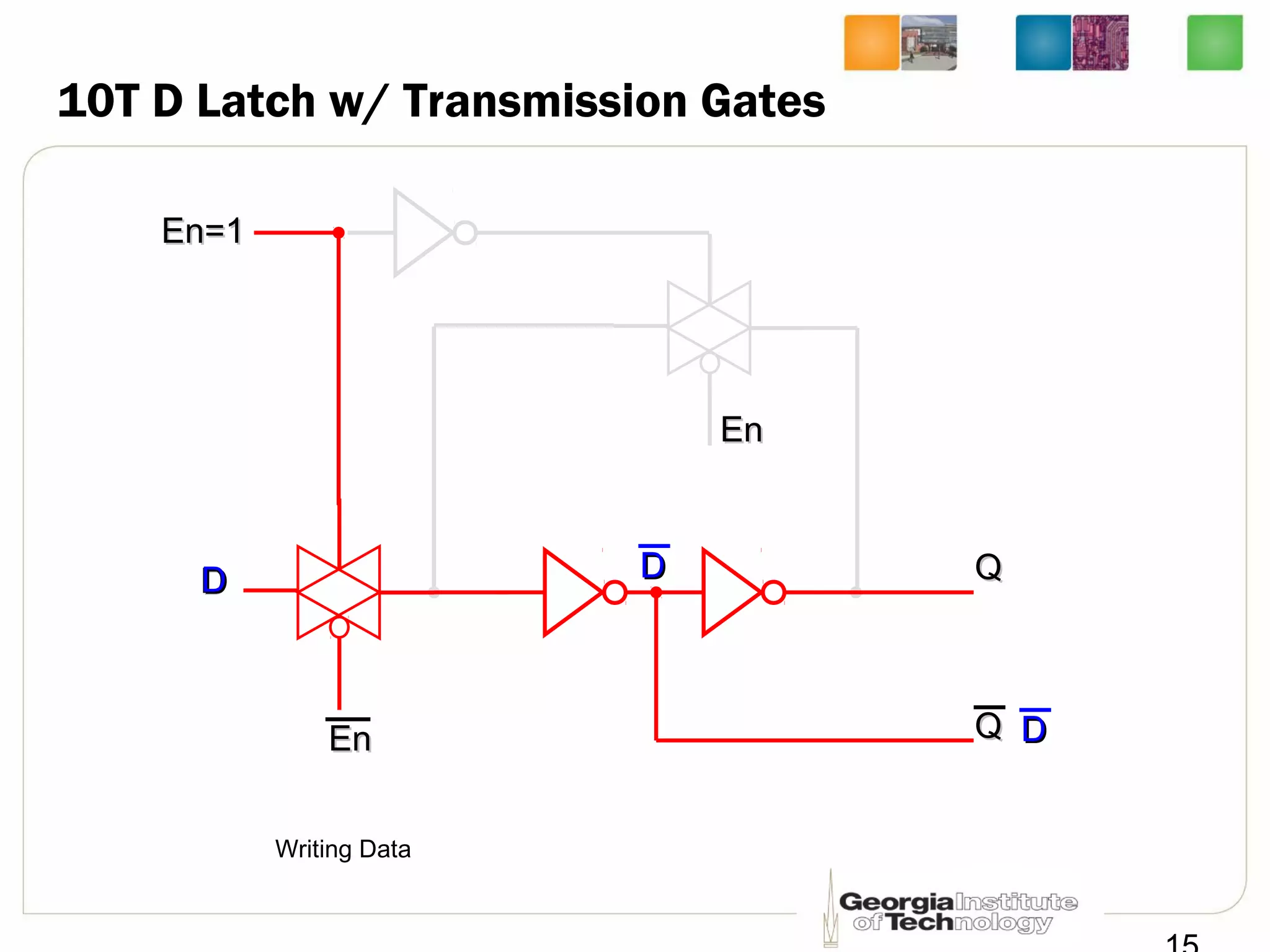
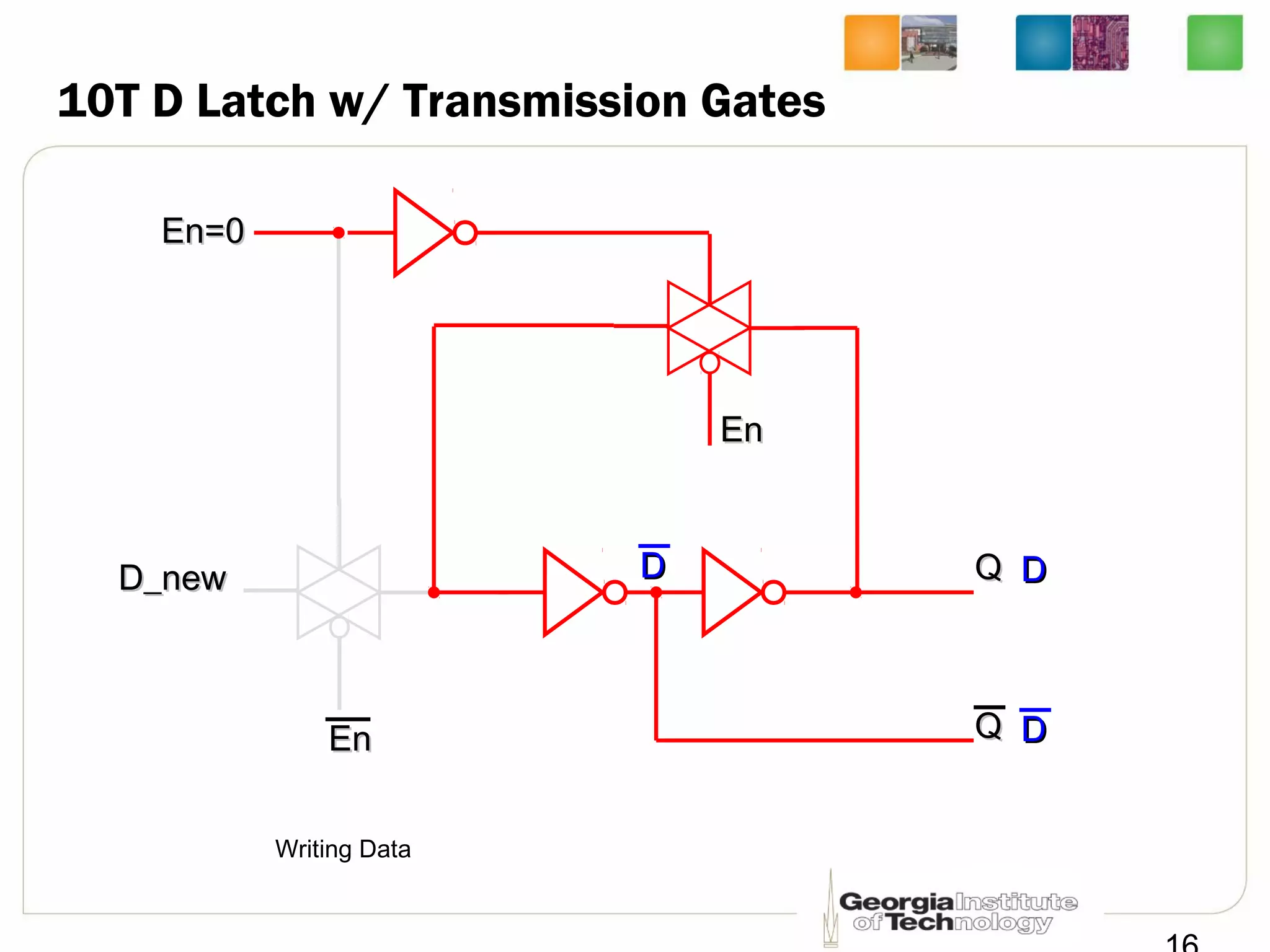
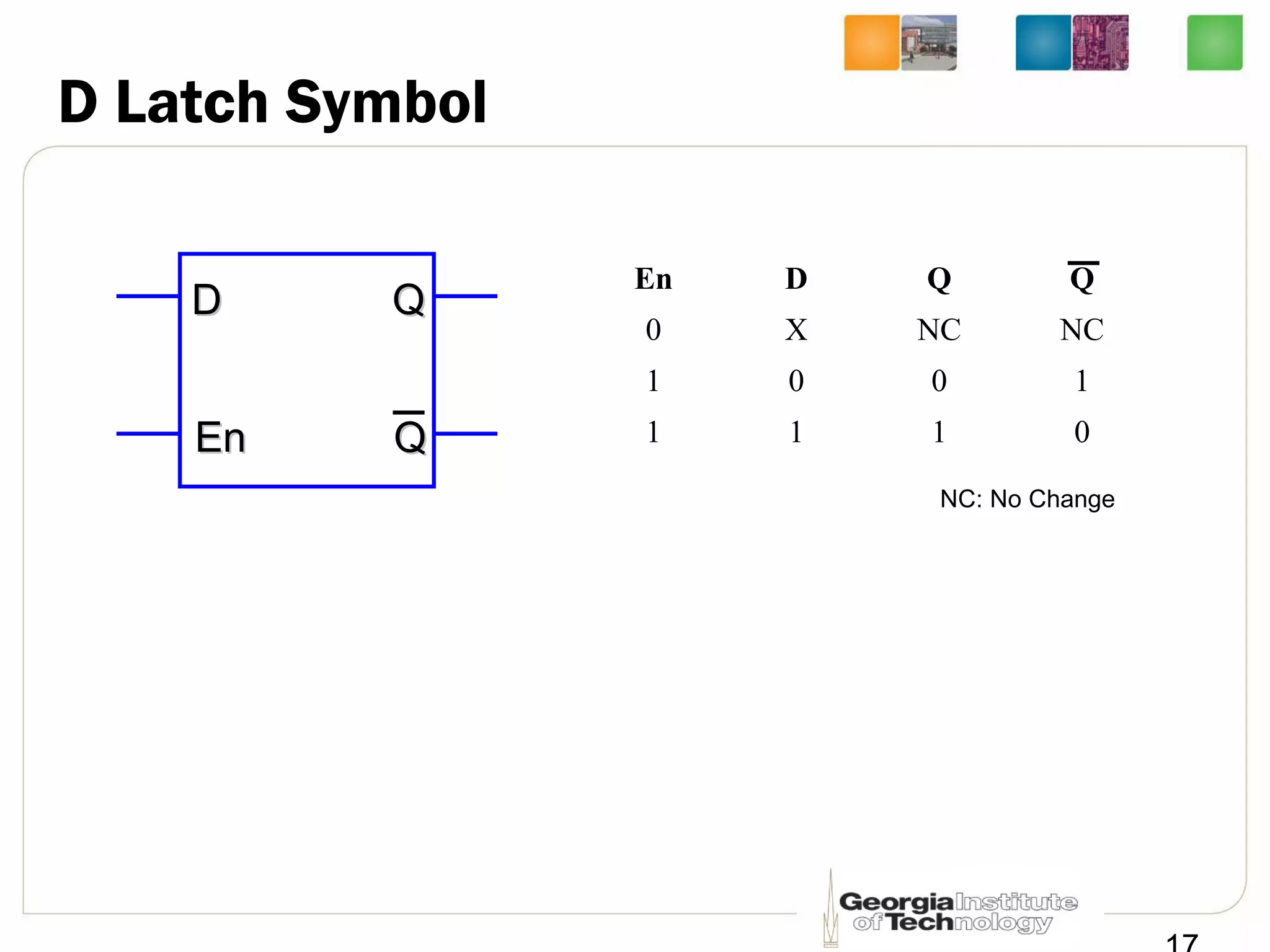
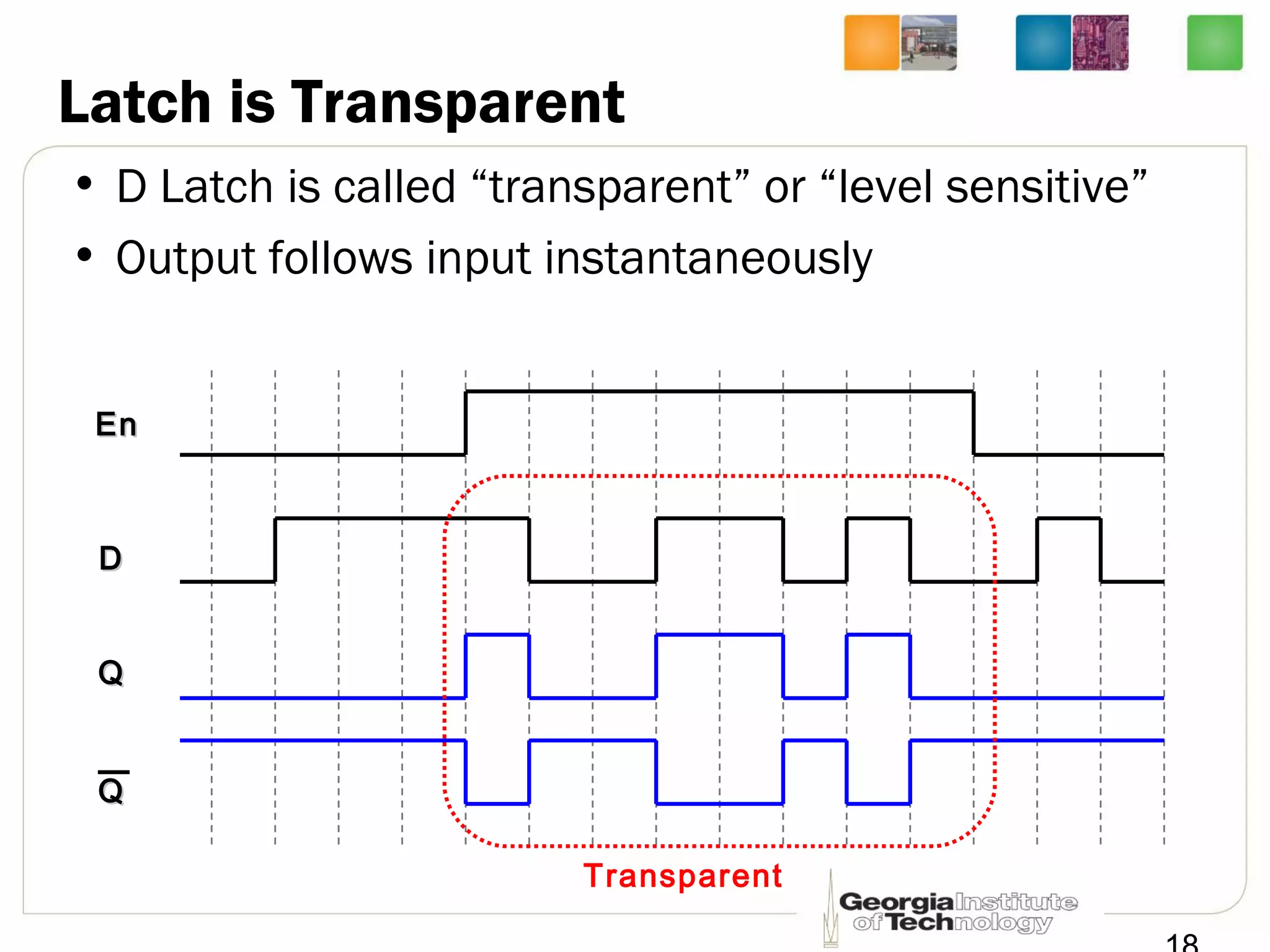
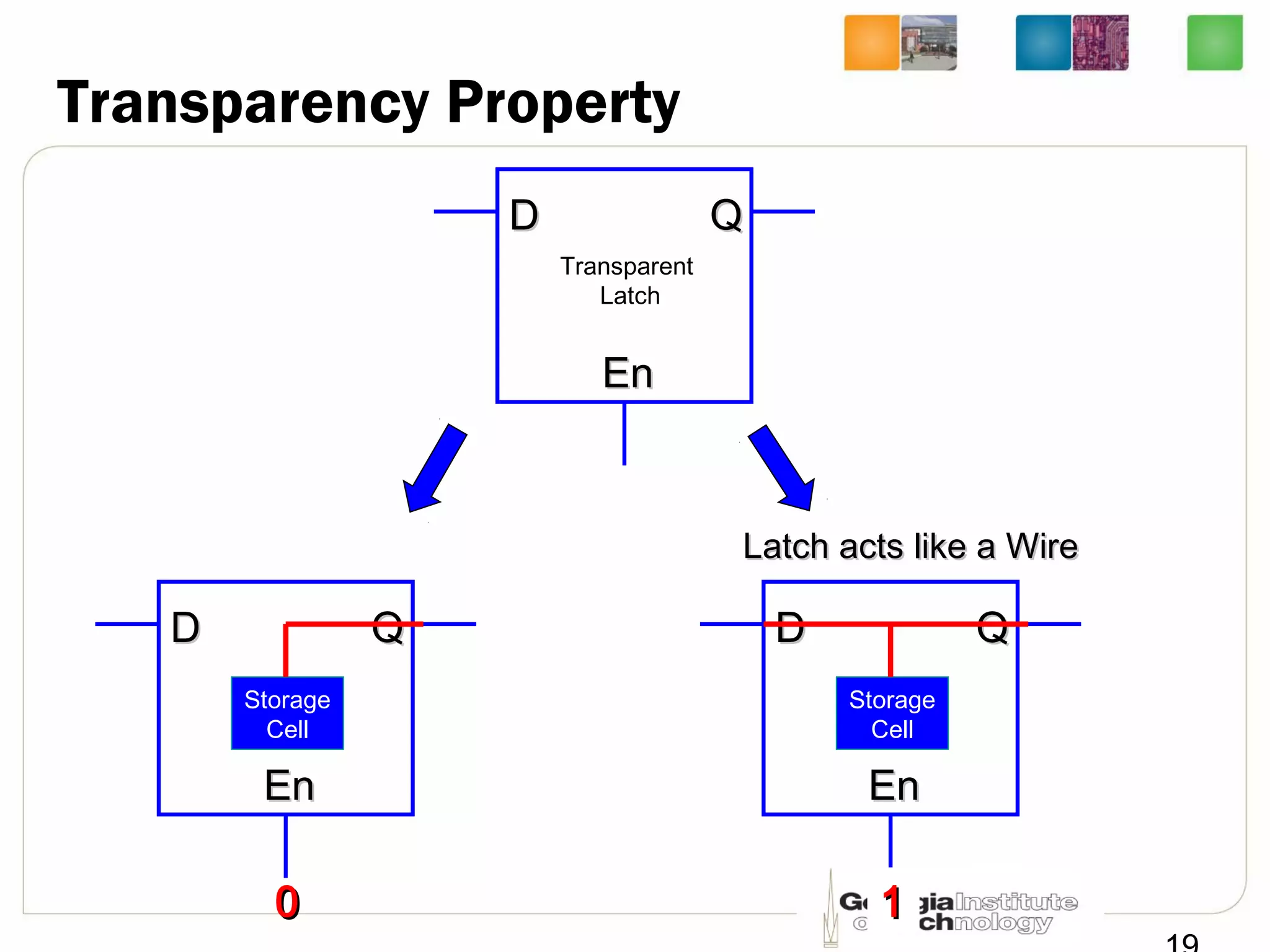
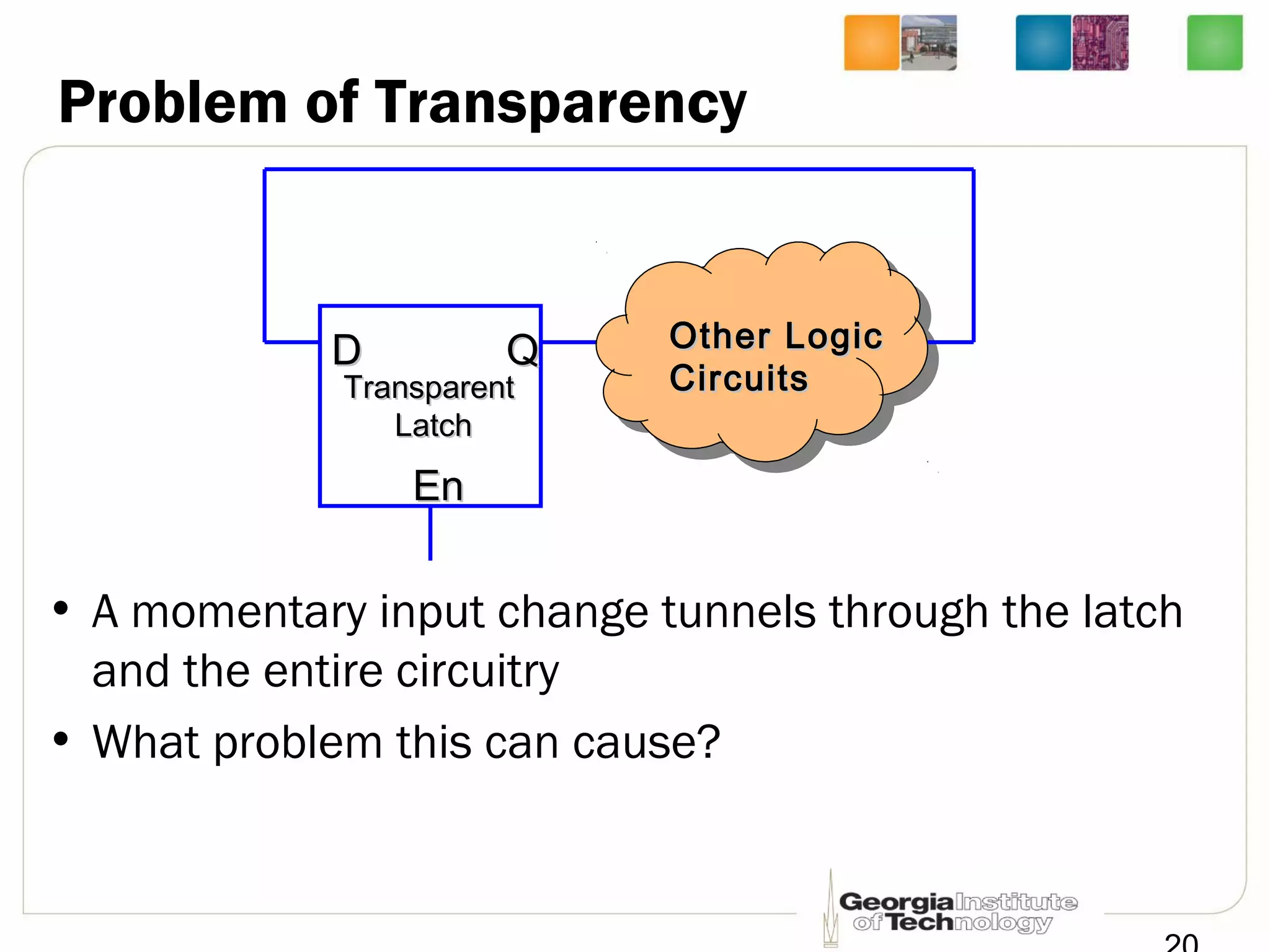
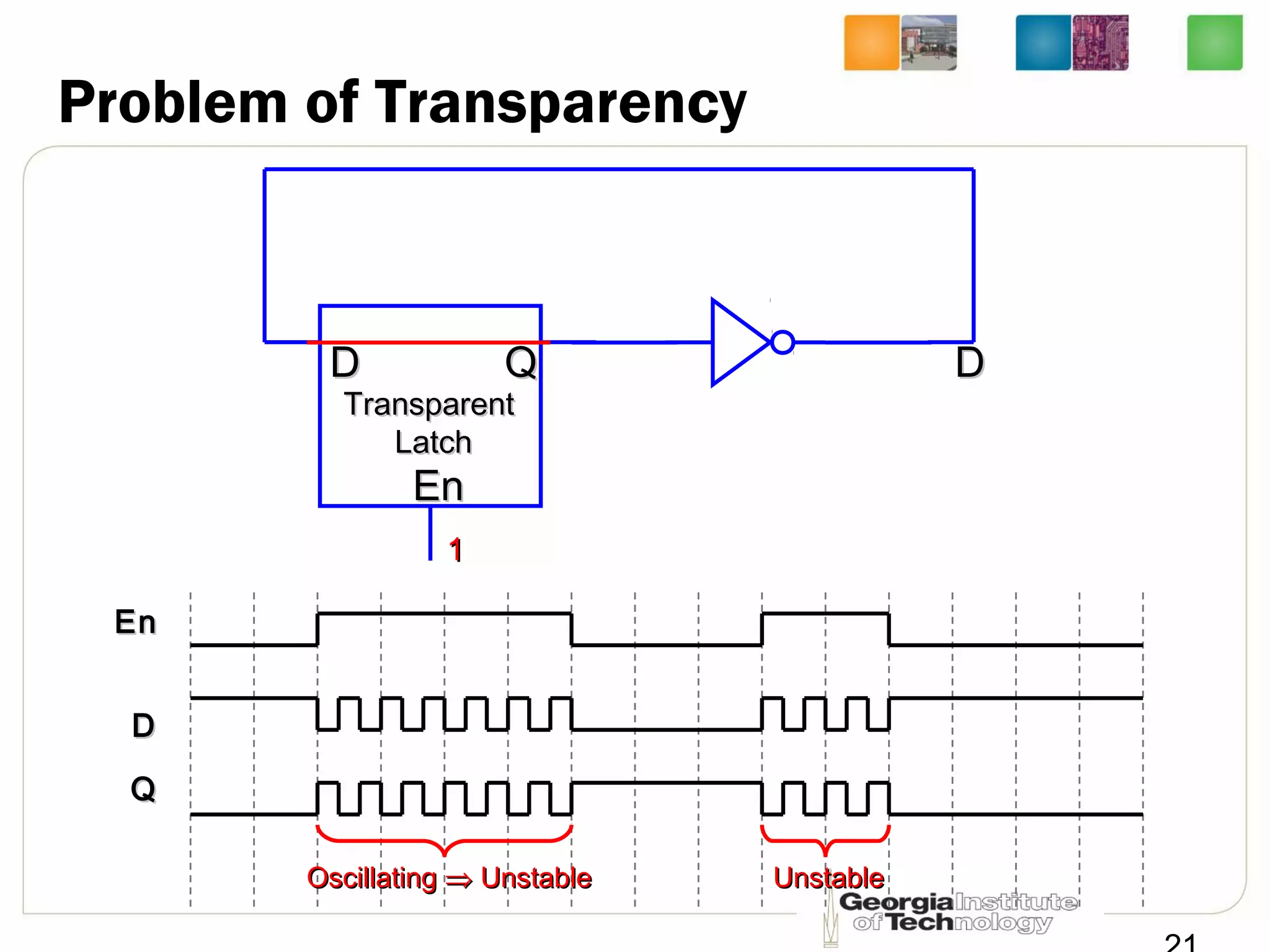
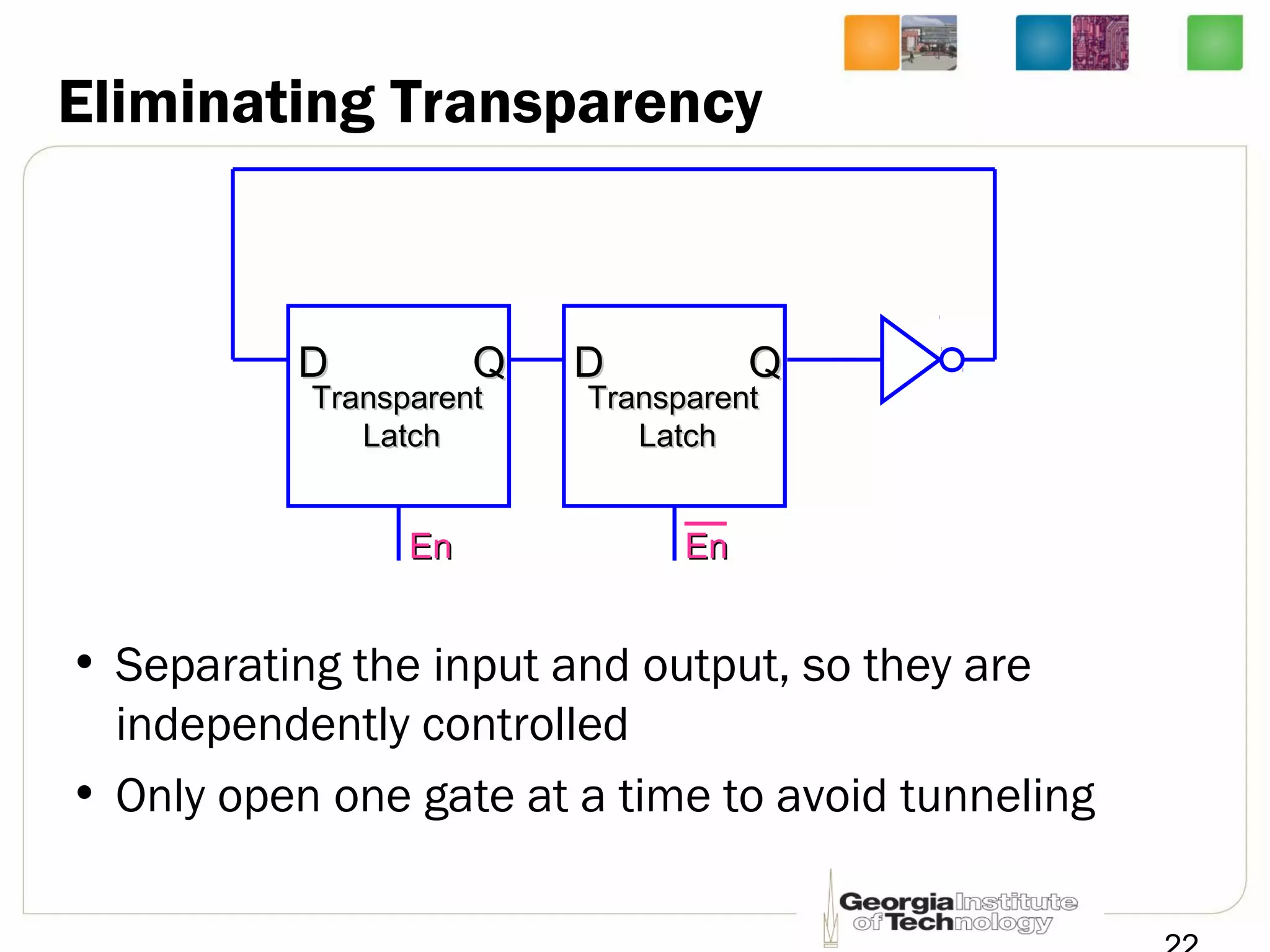
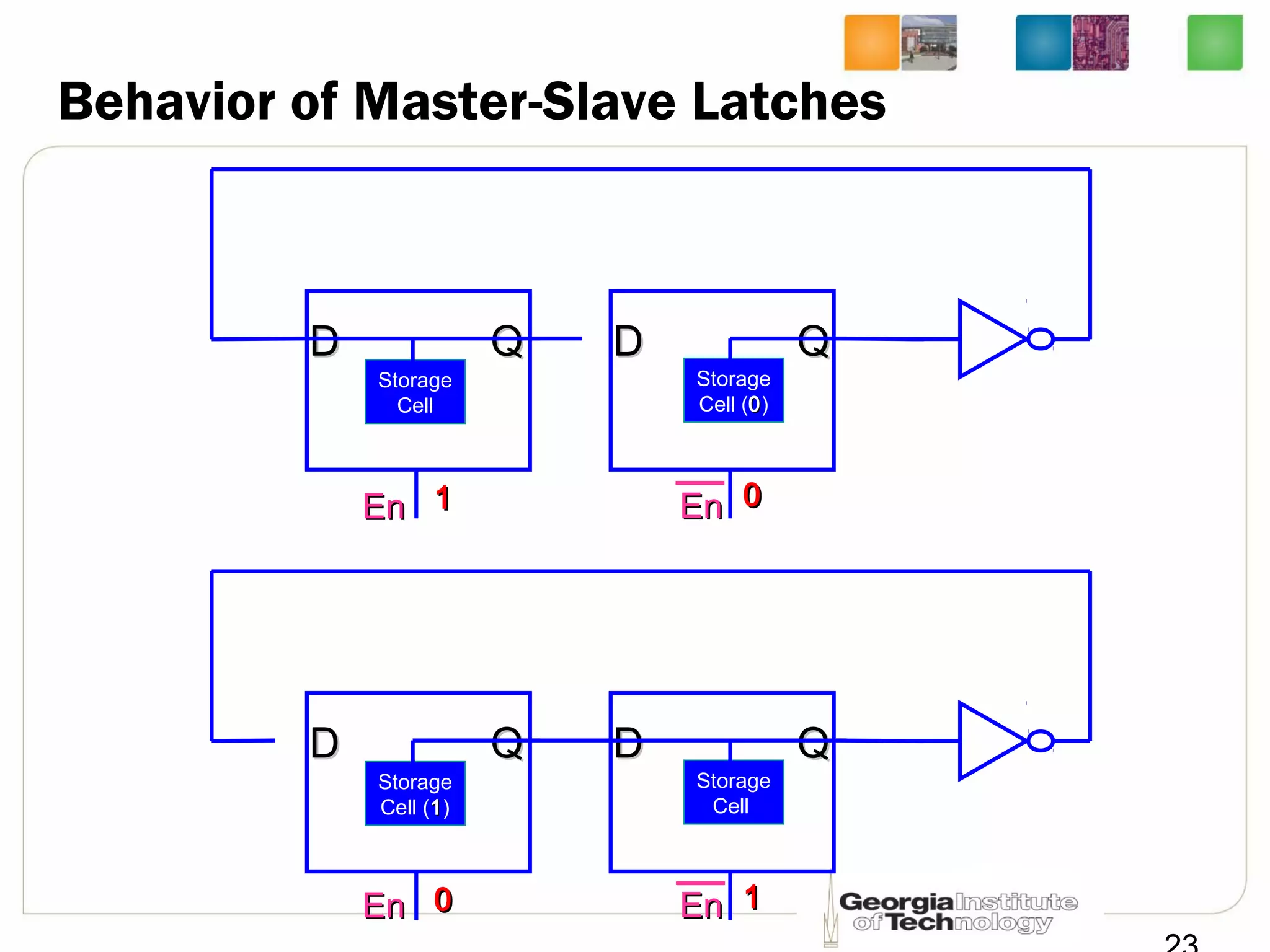
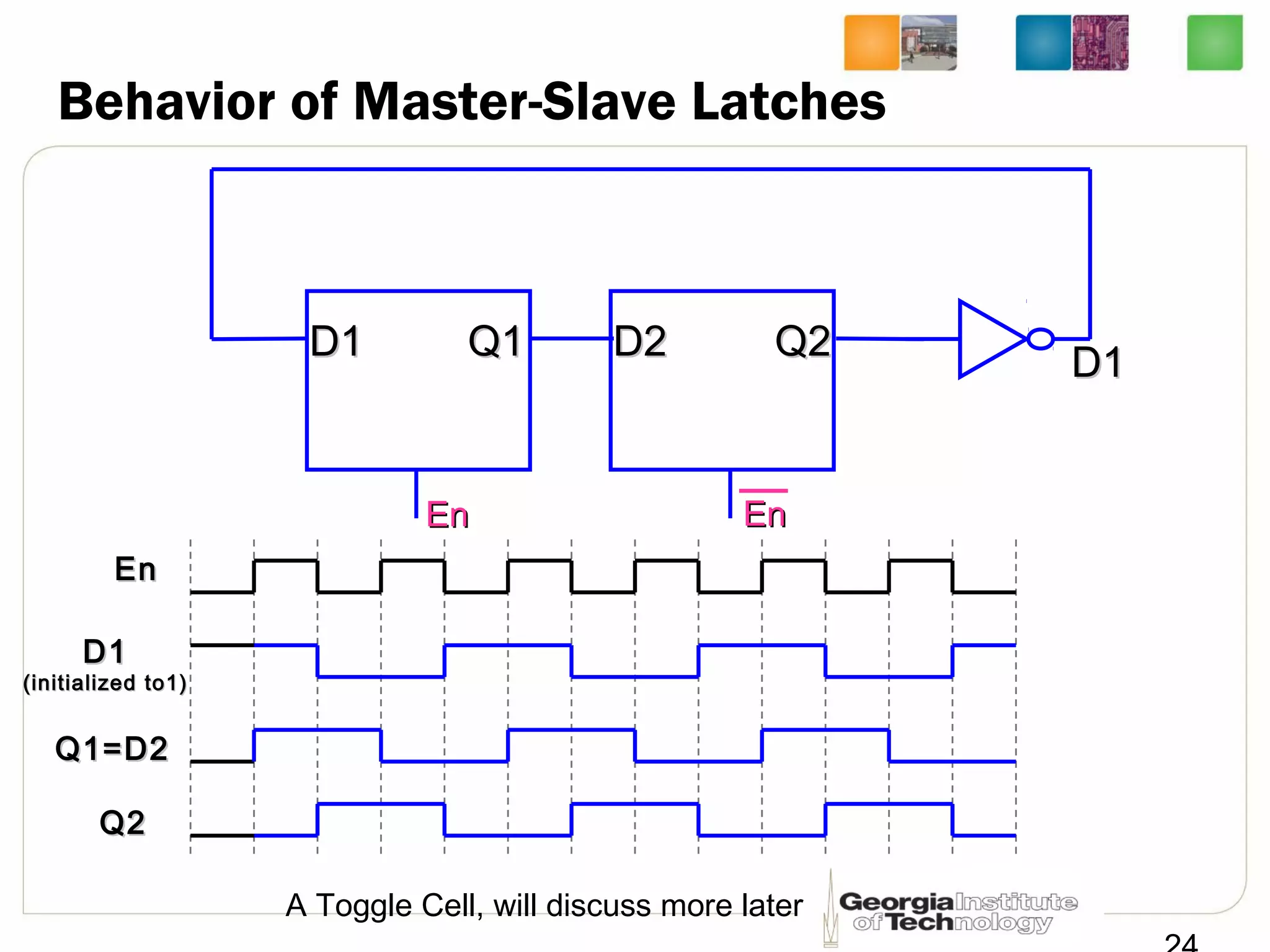
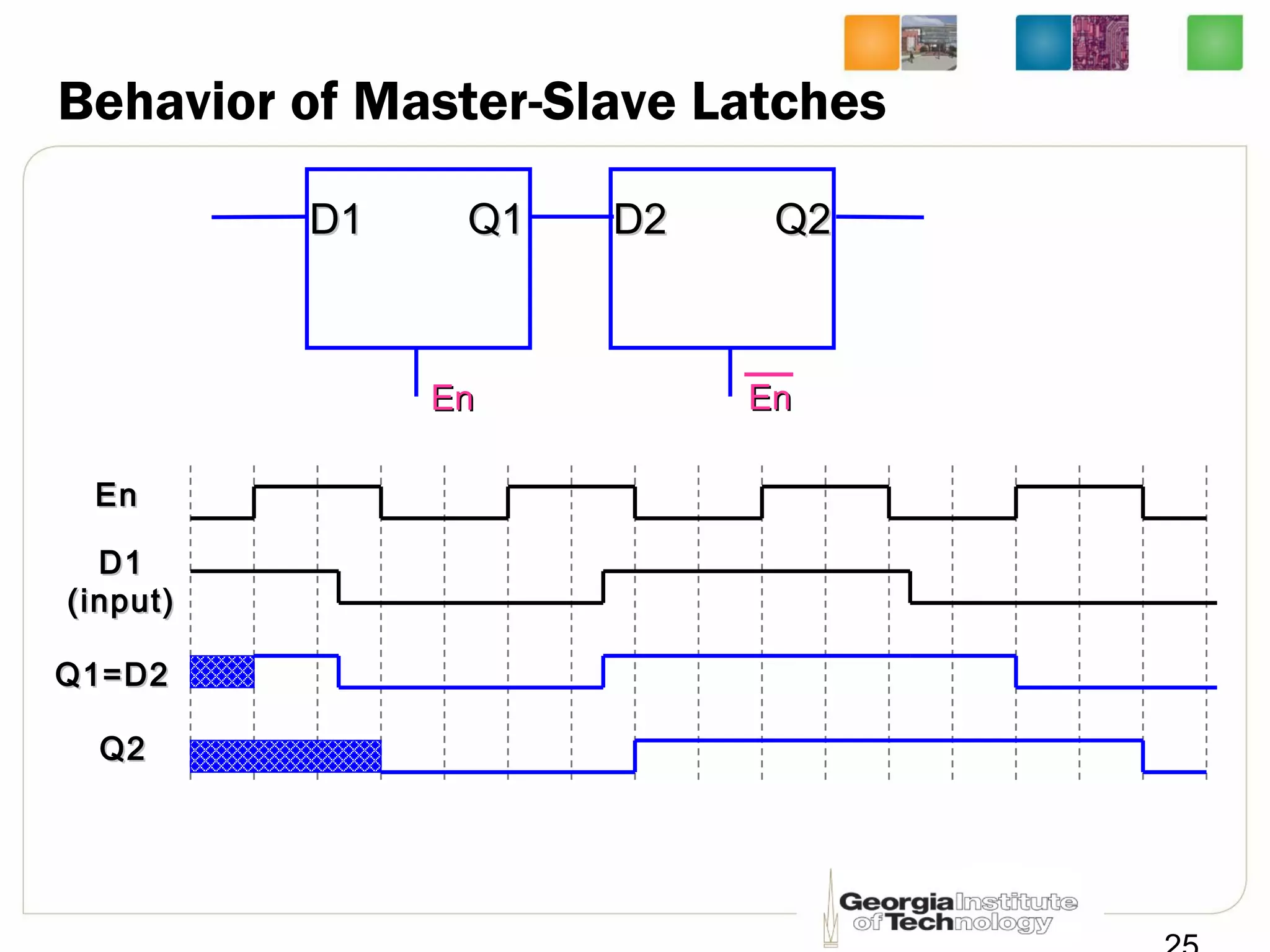
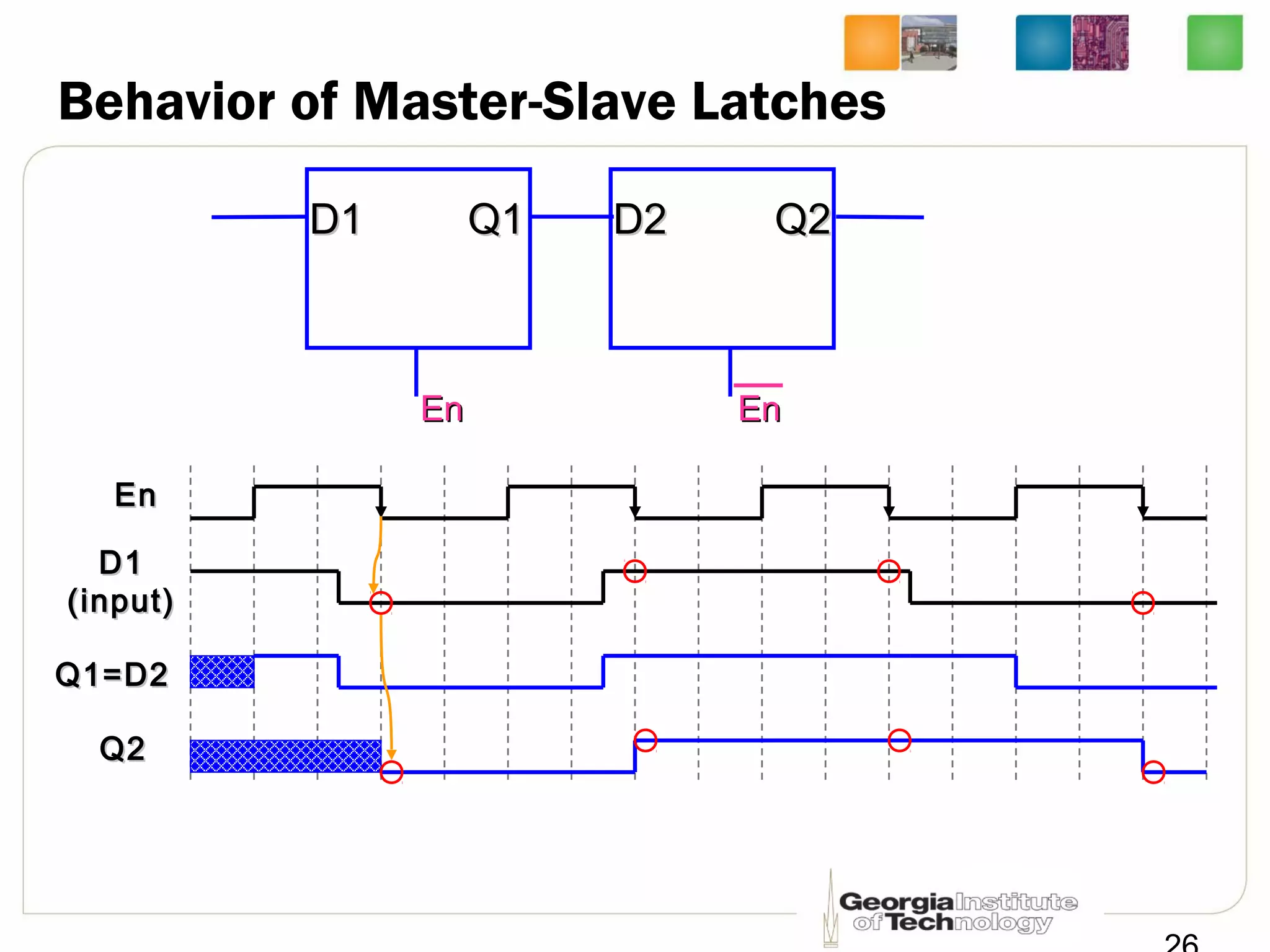
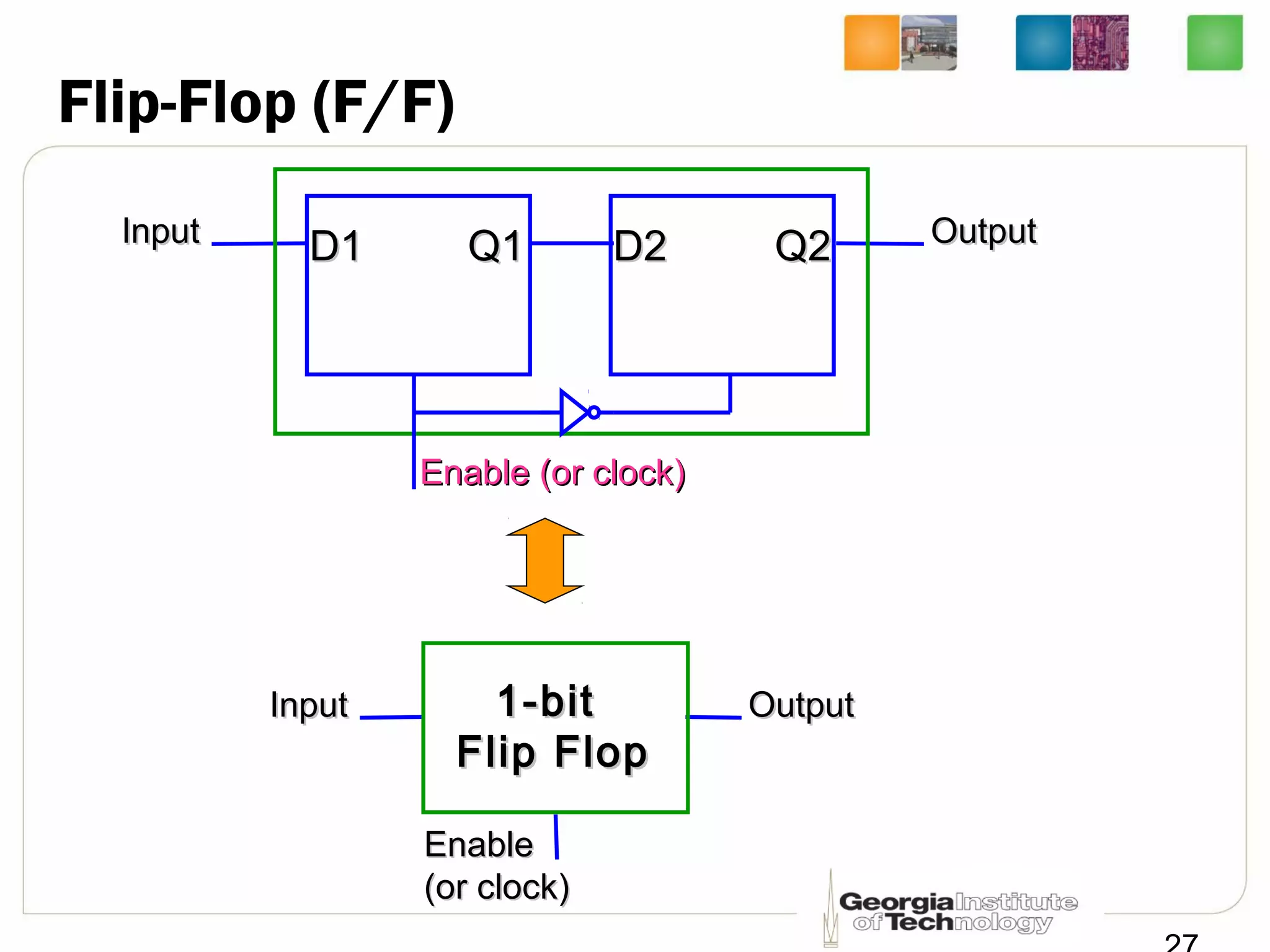
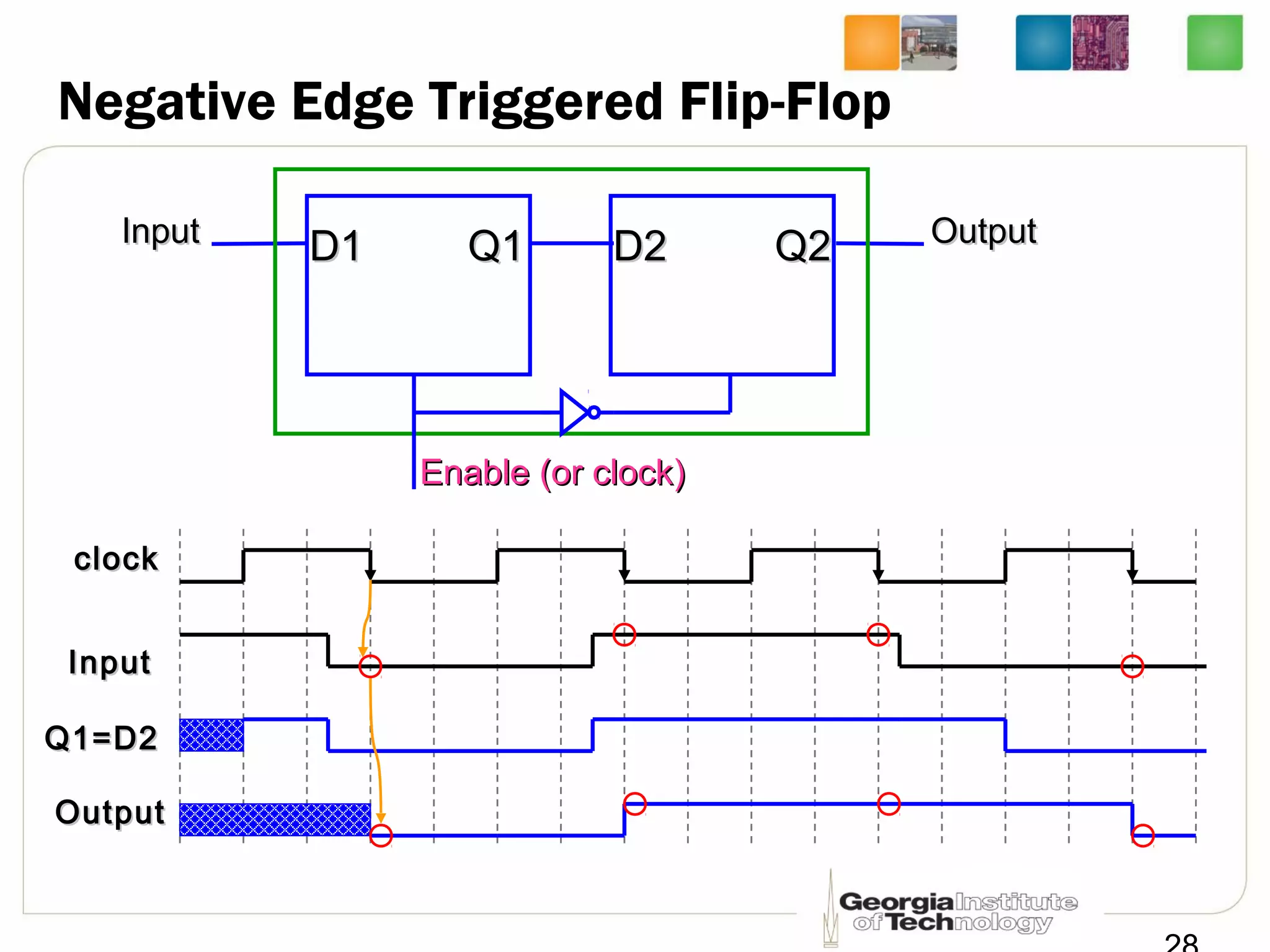
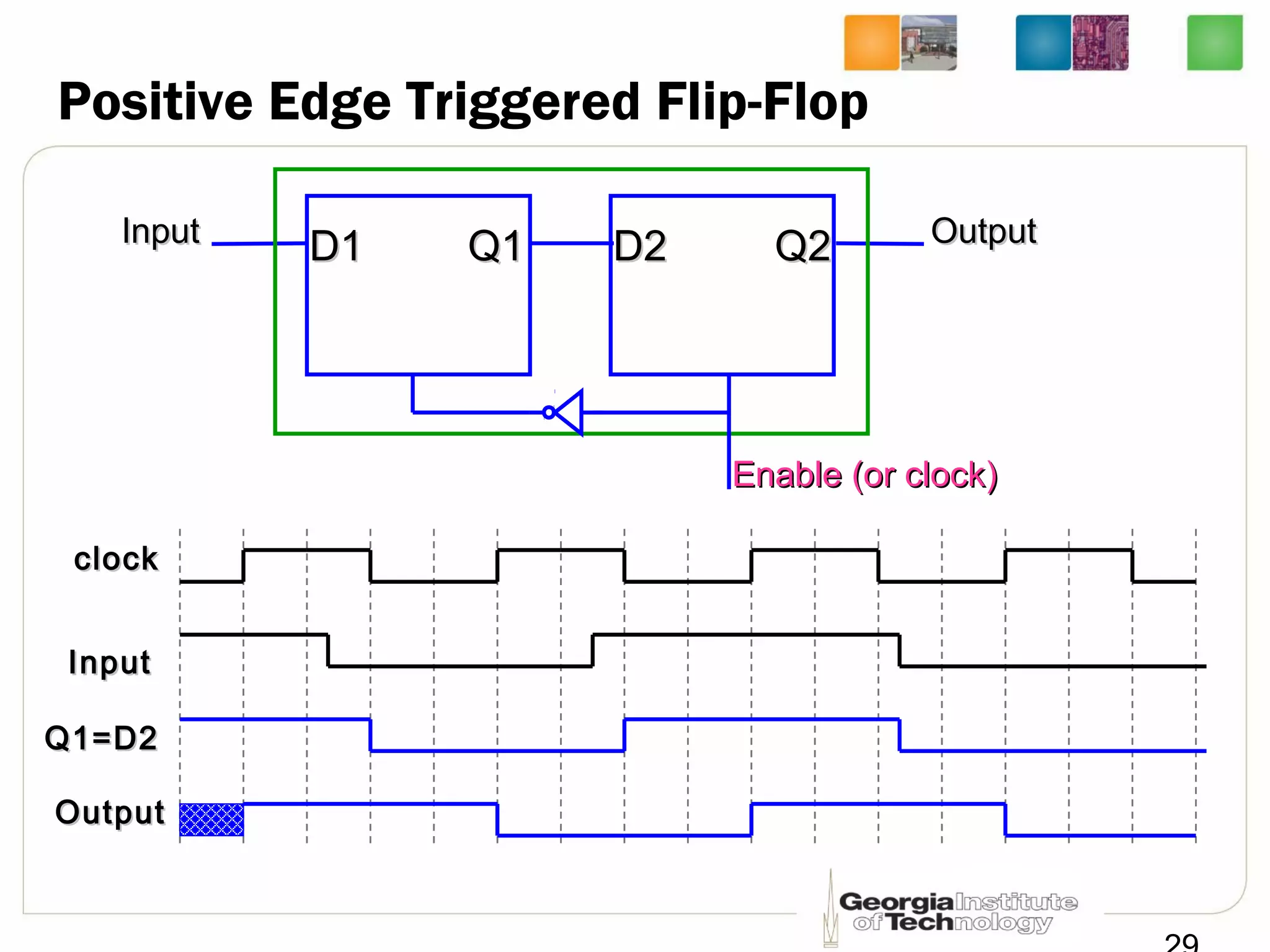
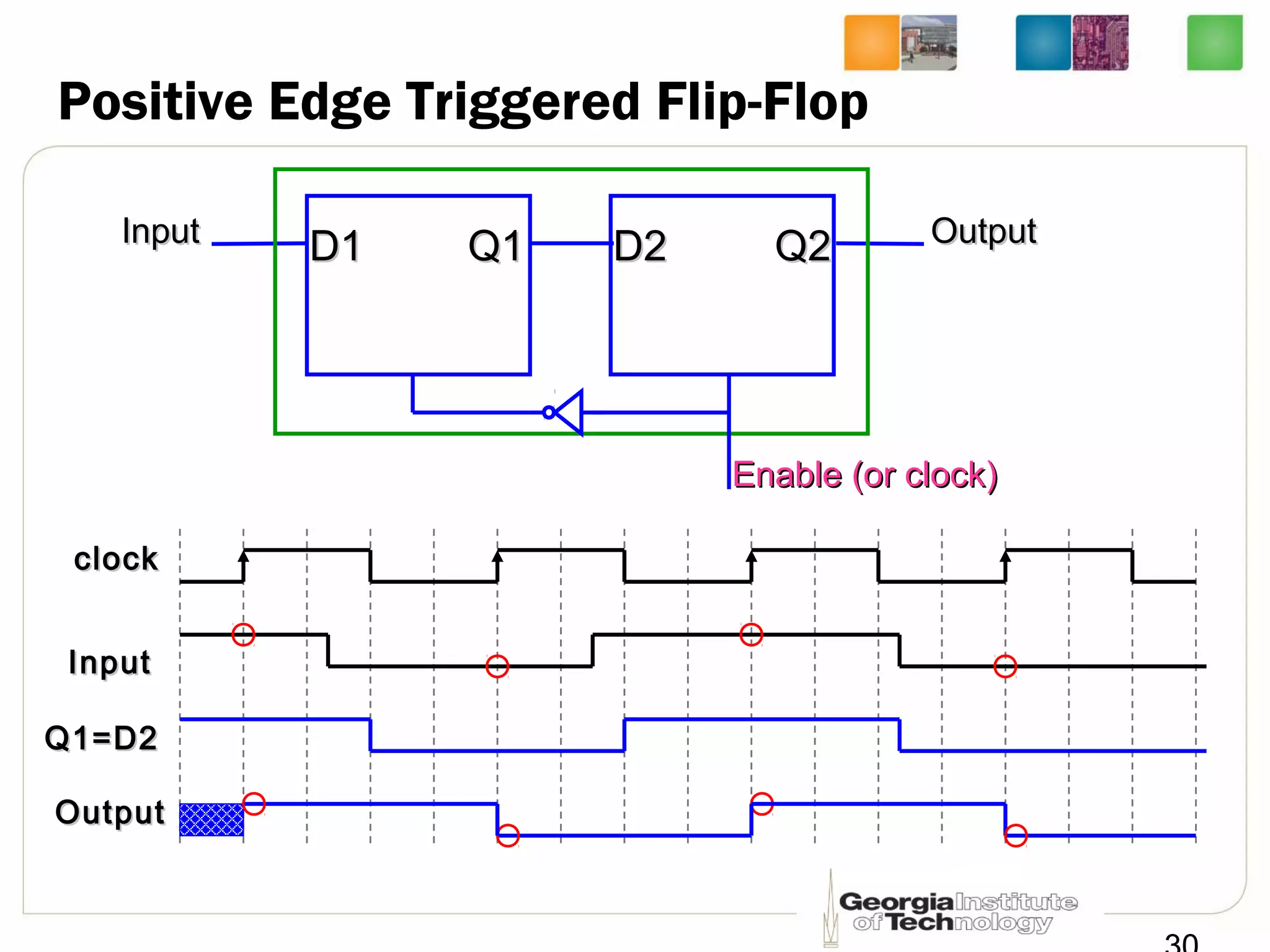
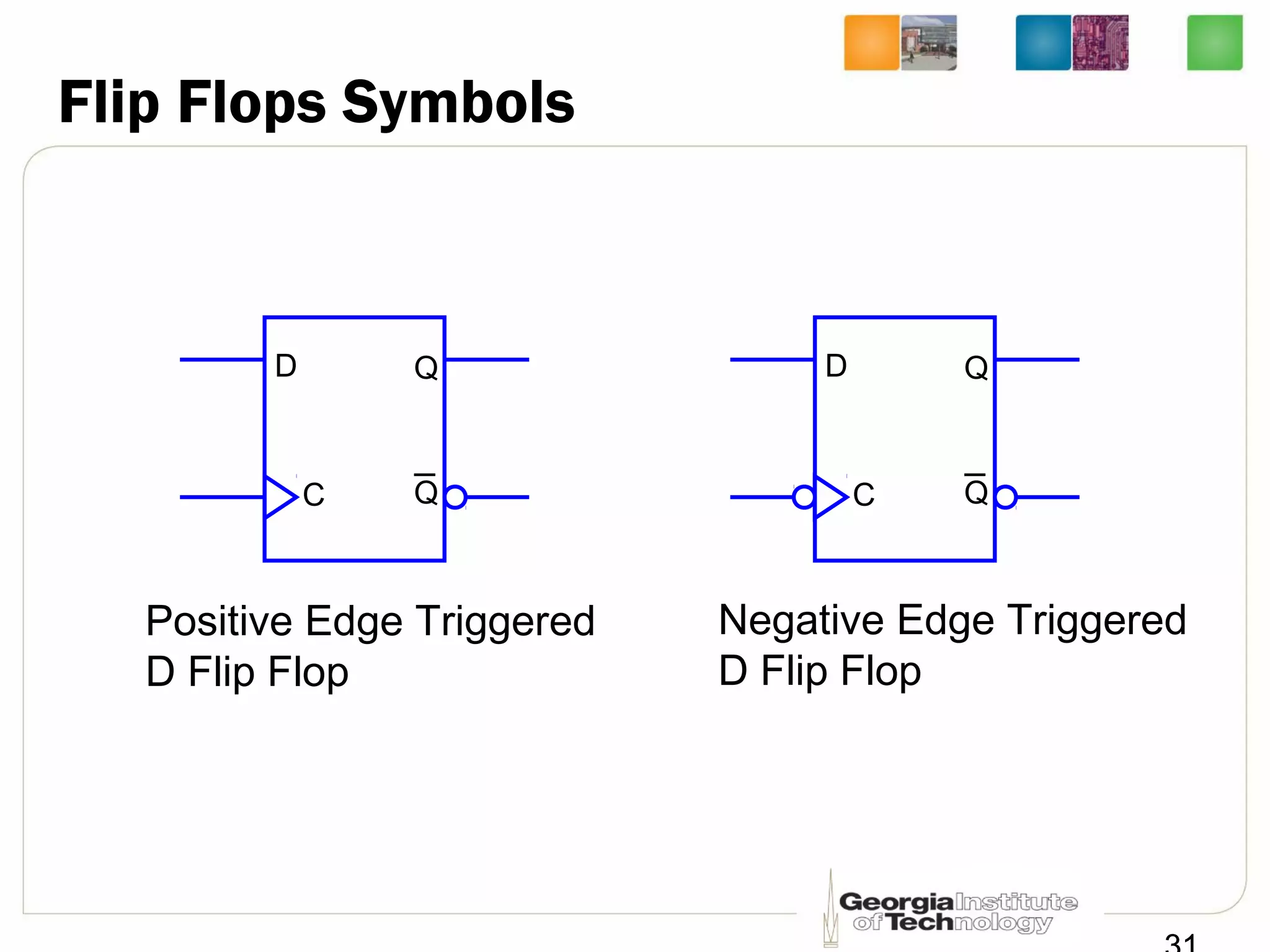
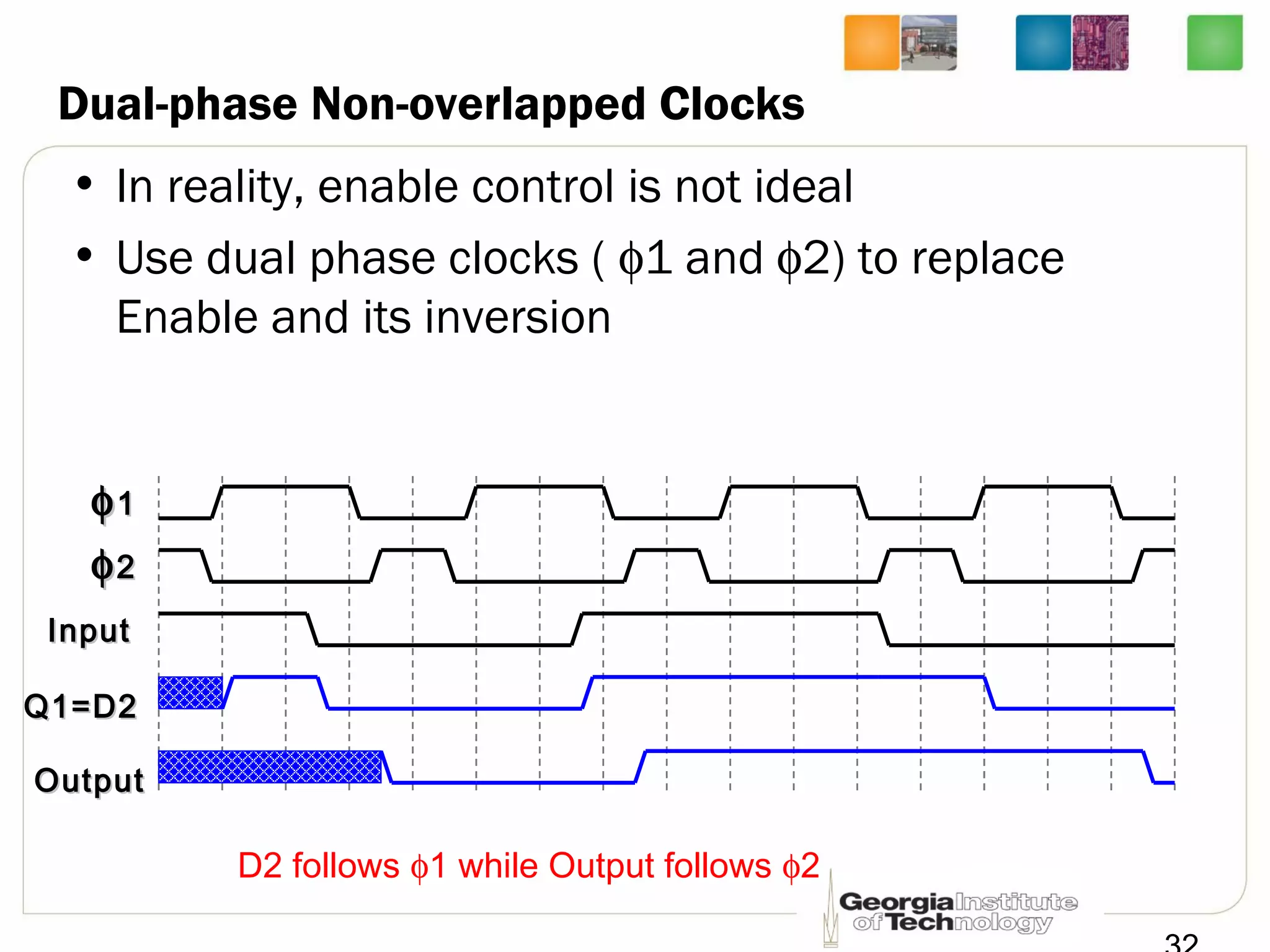
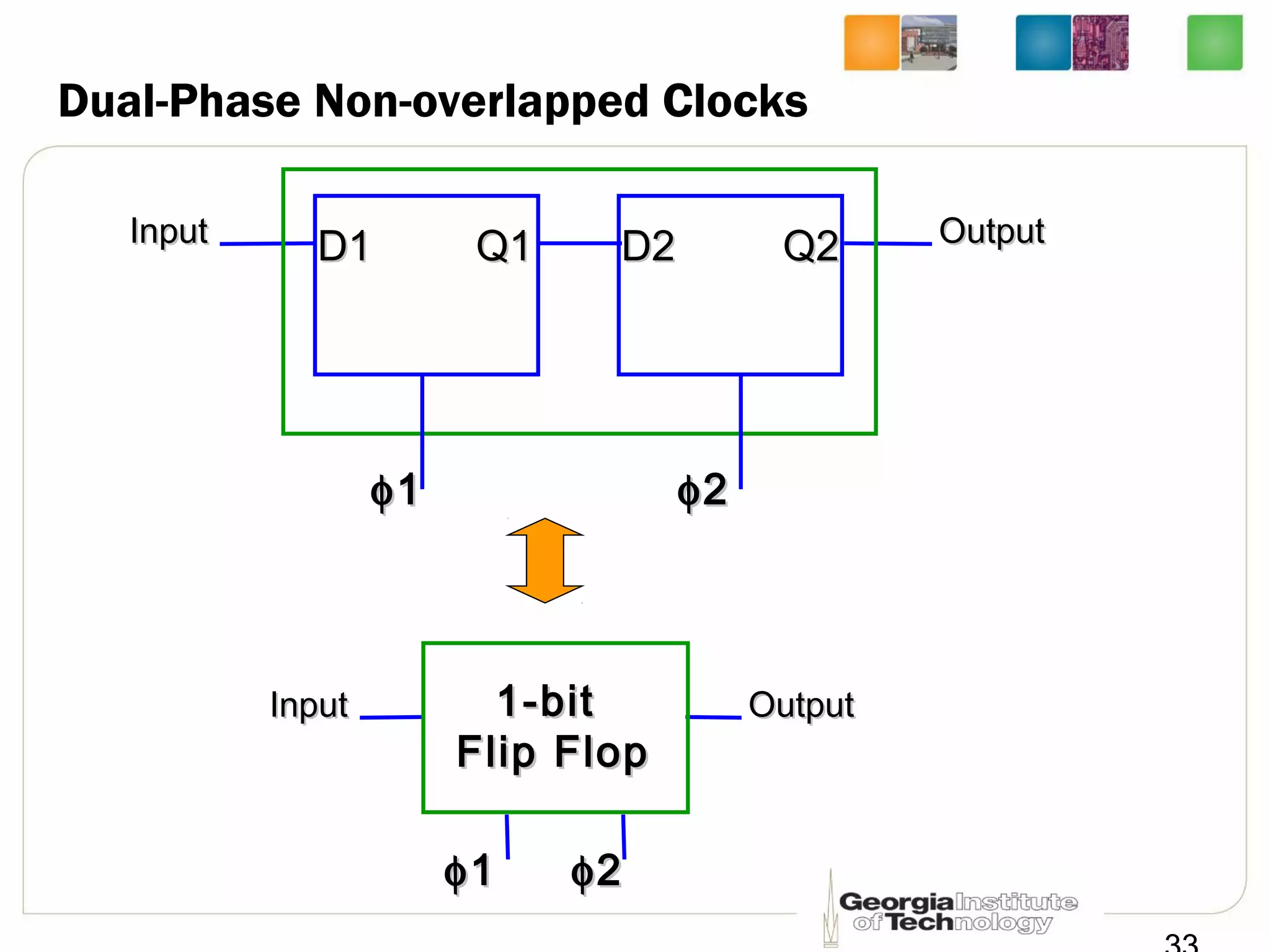
This document discusses sequential logic circuits, which differ from combinational logic circuits in that they have state information stored in memory elements like flip-flops. The output of a sequential circuit depends on both the inputs and the present state. Common types of sequential elements discussed include SR latches, D latches, and edge-triggered flip-flops. Master-slave configurations are used to avoid problems with transparency in latches. Dual-phase non-overlapping clocks are introduced to control the transfer of data between latches in a flip-flop.